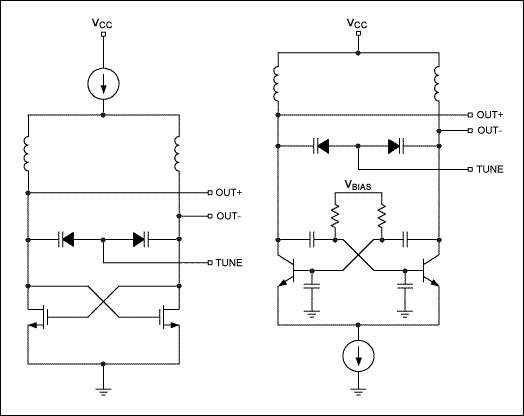
Vco
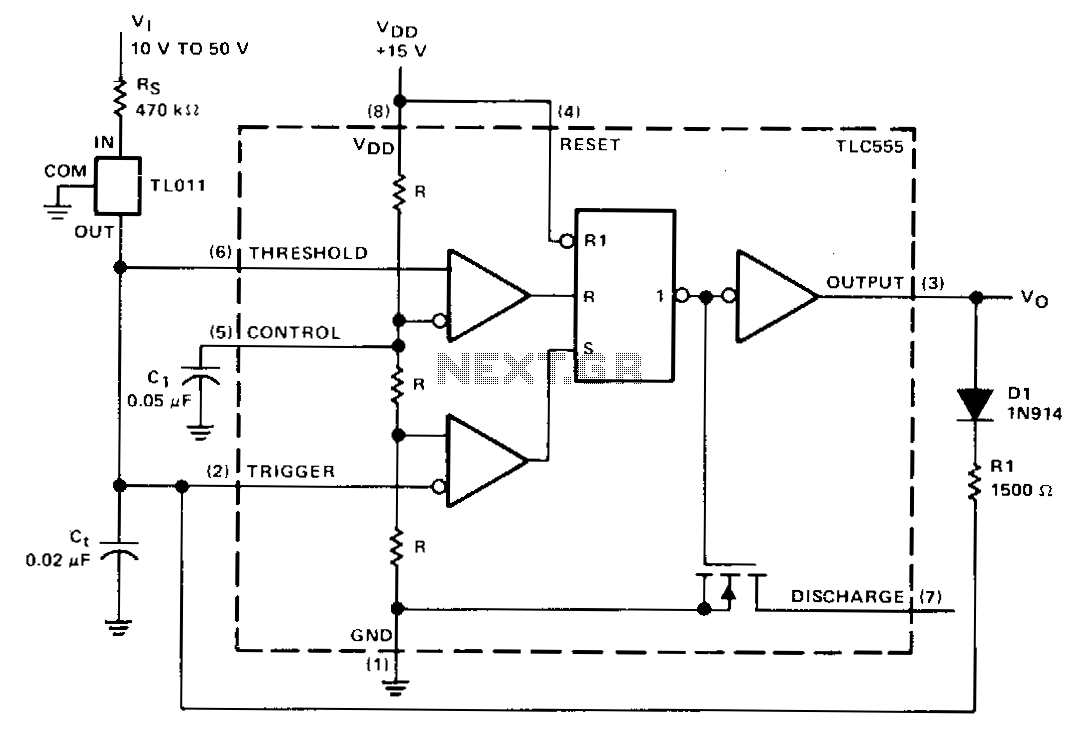
At startup, the voltage at the trigger input on pin 2 is below the trigger level voltage of 13 VDD, causing the timer to activate through pin 2. The output of the timer at pin 3 goes high, enabling capacitor C to charge rapidly via diode D1 and resistor R1. Once capacitor C reaches the upper threshold voltage of 2/3 VDD, the flip-flop resets, the output at pin 3 drops, and capacitor C discharges through the current mirror TLO11. Additionally, when the voltage at pin 2 reaches 1/3 VDD, the lower threshold or trigger level, the timer is triggered once more, and the cycle continues.
The described circuit utilizes a timer IC configured in astable mode, which produces a continuous square wave output. At the start, the voltage at pin 2, which serves as the trigger input, is lower than the defined threshold, initiating the timer operation. The rapid charging of capacitor C through diode D1 and resistor R1 is crucial for the timing characteristics of the circuit. The choice of resistor R1 and the capacitance of C will determine the charge time, influencing the frequency of the output waveform.
When the voltage across capacitor C reaches 2/3 of the supply voltage (VDD), it triggers the reset of the flip-flop inside the timer IC. This action causes the output on pin 3 to drop, leading to the discharge of capacitor C. The discharge path is facilitated by the current mirror TLO11, which ensures a controlled discharge rate, thereby stabilizing the output.
The cycle repeats when the voltage at pin 2 reaches 1/3 VDD, which serves as the lower threshold for triggering the timer again. This mechanism creates a self-sustaining oscillation, where the timer continuously alternates between charging and discharging the capacitor, resulting in a square wave output. The frequency and duty cycle of the output can be adjusted by varying the values of R1 and C, allowing for flexibility in applications such as pulse generation, timing circuits, or clock signals in digital systems.At startup, the voltage in the trigger input at pin 2 is less than the trigger level voltage, "13 VDD. caus ing the timer to be triggered via pin 2. The output of the timer at pin 3 becomes high, allowing capacitor c, to charge very rapidly through diode Dl and resistor Rl.
When capacitor C, charges to the upper threshold voltage 2 /3 V00, the flip-flop is reset, the output at pin 3 decreases, and capacitor C, discharges through the current mirror, TLOll. When the voltage at pin 2 re-dches 1/3 VDD. the lower threshold or trigger level, the timer triggers again and the cycle is repeated.
The described circuit utilizes a timer IC configured in astable mode, which produces a continuous square wave output. At the start, the voltage at pin 2, which serves as the trigger input, is lower than the defined threshold, initiating the timer operation. The rapid charging of capacitor C through diode D1 and resistor R1 is crucial for the timing characteristics of the circuit. The choice of resistor R1 and the capacitance of C will determine the charge time, influencing the frequency of the output waveform.
When the voltage across capacitor C reaches 2/3 of the supply voltage (VDD), it triggers the reset of the flip-flop inside the timer IC. This action causes the output on pin 3 to drop, leading to the discharge of capacitor C. The discharge path is facilitated by the current mirror TLO11, which ensures a controlled discharge rate, thereby stabilizing the output.
The cycle repeats when the voltage at pin 2 reaches 1/3 VDD, which serves as the lower threshold for triggering the timer again. This mechanism creates a self-sustaining oscillation, where the timer continuously alternates between charging and discharging the capacitor, resulting in a square wave output. The frequency and duty cycle of the output can be adjusted by varying the values of R1 and C, allowing for flexibility in applications such as pulse generation, timing circuits, or clock signals in digital systems.At startup, the voltage in the trigger input at pin 2 is less than the trigger level voltage, "13 VDD. caus ing the timer to be triggered via pin 2. The output of the timer at pin 3 becomes high, allowing capacitor c, to charge very rapidly through diode Dl and resistor Rl.
When capacitor C, charges to the upper threshold voltage 2 /3 V00, the flip-flop is reset, the output at pin 3 decreases, and capacitor C, discharges through the current mirror, TLOll. When the voltage at pin 2 re-dches 1/3 VDD. the lower threshold or trigger level, the timer triggers again and the cycle is repeated.