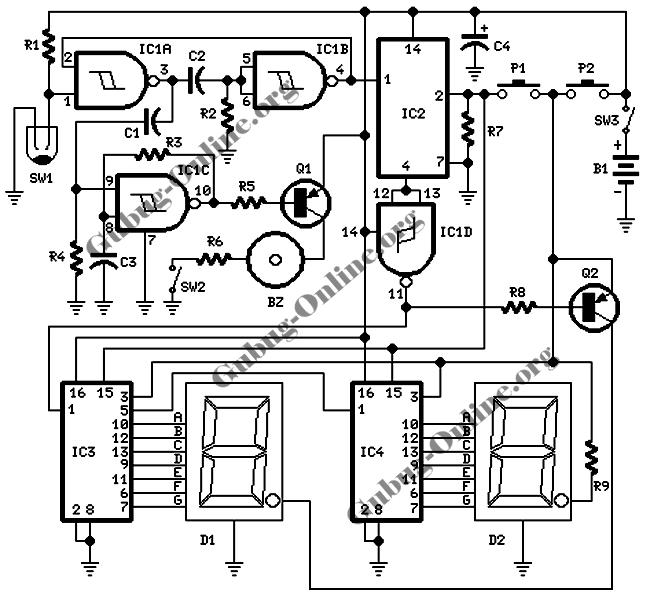
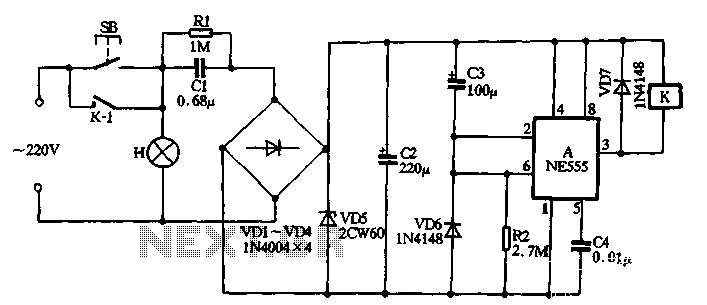
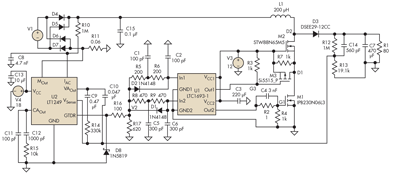
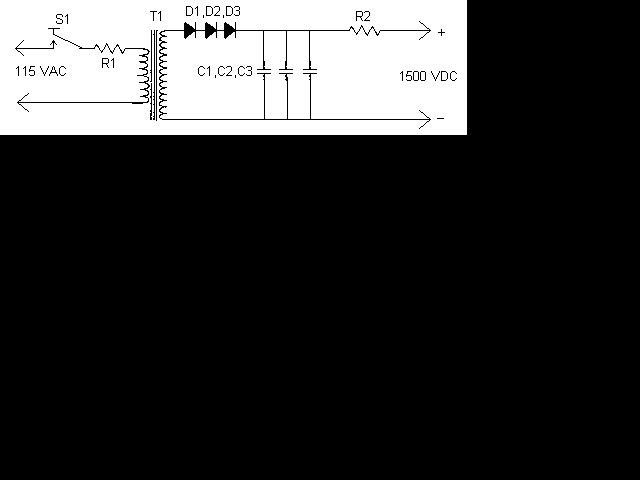
Video/Audio Switcher Circuit
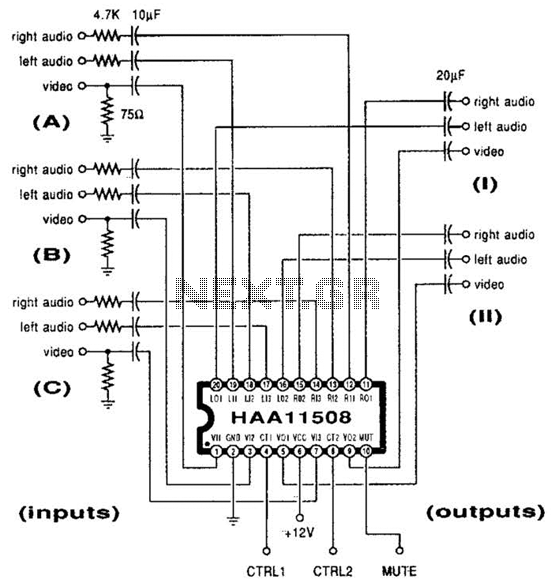
This channel selector selects video and stereo audio from any one of three different sources. The circuit should be constructed on a PC board with plenty of ground plane to minimize noise.
The channel selector circuit is designed to facilitate the selection of video and stereo audio signals from three distinct input sources. This functionality is essential in applications where multiple signal sources need to be managed efficiently, such as in home theater systems or professional audio-visual setups.
The core of the circuit involves the use of analog switches or multiplexers that route the selected input to the output based on user control. Each of the three input sources is connected to the switch, allowing for seamless transitions between them without the need for physical reconnections. The control mechanism can be implemented using a manual switch or a microcontroller for automated selection.
To ensure high-quality signal integrity, the circuit should be implemented on a printed circuit board (PCB) featuring a substantial ground plane. This ground plane serves to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and minimizes noise pickup, which is critical for maintaining the clarity of both audio and video signals. Proper layout techniques should be employed, including short trace lengths for signal paths and the strategic placement of decoupling capacitors near power supply pins to further mitigate noise.
Additionally, the use of high-quality components, such as low-on-resistance switches and capacitors with low equivalent series resistance (ESR), will contribute to the overall performance of the channel selector. The circuit should also incorporate appropriate filtering techniques to eliminate any unwanted frequencies that may affect audio and video quality.
In summary, the design of the channel selector circuit must prioritize signal integrity and noise reduction while providing a user-friendly interface for selecting between multiple sources. This approach will ensure optimal performance in a variety of audio-visual applications. This channel selector selects video and stereo audio from any one of three different sources. The circuit should be constructed on a PC board with plenty of ground plane to minimize noise.
The channel selector circuit is designed to facilitate the selection of video and stereo audio signals from three distinct input sources. This functionality is essential in applications where multiple signal sources need to be managed efficiently, such as in home theater systems or professional audio-visual setups.
The core of the circuit involves the use of analog switches or multiplexers that route the selected input to the output based on user control. Each of the three input sources is connected to the switch, allowing for seamless transitions between them without the need for physical reconnections. The control mechanism can be implemented using a manual switch or a microcontroller for automated selection.
To ensure high-quality signal integrity, the circuit should be implemented on a printed circuit board (PCB) featuring a substantial ground plane. This ground plane serves to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and minimizes noise pickup, which is critical for maintaining the clarity of both audio and video signals. Proper layout techniques should be employed, including short trace lengths for signal paths and the strategic placement of decoupling capacitors near power supply pins to further mitigate noise.
Additionally, the use of high-quality components, such as low-on-resistance switches and capacitors with low equivalent series resistance (ESR), will contribute to the overall performance of the channel selector. The circuit should also incorporate appropriate filtering techniques to eliminate any unwanted frequencies that may affect audio and video quality.
In summary, the design of the channel selector circuit must prioritize signal integrity and noise reduction while providing a user-friendly interface for selecting between multiple sources. This approach will ensure optimal performance in a variety of audio-visual applications. This channel selector selects video and stereo audio from any one of three different sources. The circuit should be constructed on a PC board with plenty of ground plane to minimize noise.