Video enhancement circuit diagram
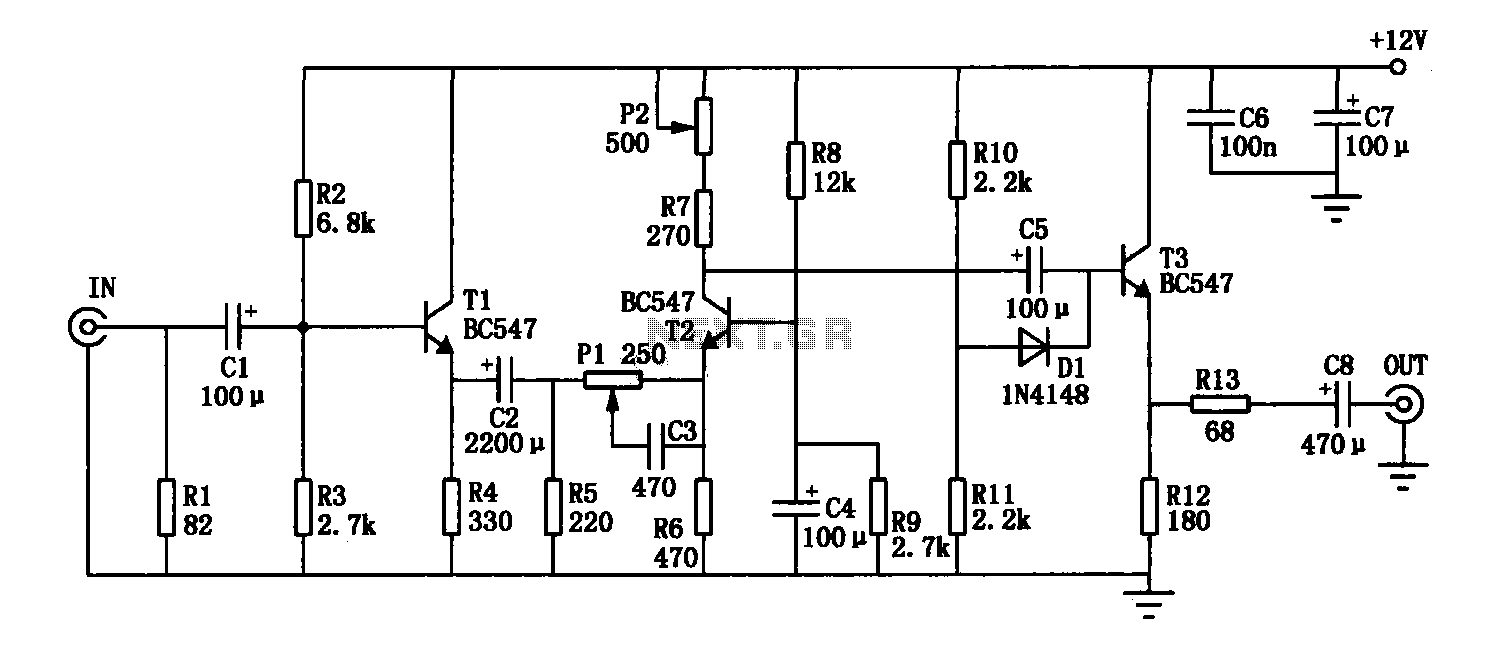
The enhancement circuit, as depicted, increases the high-frequency components of the video signal, thereby improving the contrast of the television image. It can be connected between the VCR and the TV SCART input. The circuit utilizes transistor T1 for its dampening effect. Resistor R1 ensures that the input impedance of the circuit is approximately 75 ohms. The signal is applied to the amplifier stage T2, where the gain is adjustable based on the position of potentiometer P2. The frequency characteristics of the signal at the base of T2 are influenced by components P1, R6, and C6, allowing for user control via P1. The buffer stage T3 provides sufficient current to drive a typical 75-ohm load. By adjusting potentiometer P2, the output can reach 1 Vp-p, while the open-circuit output level should be 2 Vp-p.
The enhancement circuit is designed to improve the quality of video signals by amplifying high-frequency components, which are crucial for image clarity and contrast. The circuit operates by connecting the output between a VCR and a television's SCART input, facilitating seamless integration into existing setups. The use of transistor T1 serves to dampen unwanted signals, ensuring that only the desired frequencies are amplified.
Resistor R1 is critical in maintaining an input impedance of approximately 75 ohms, which is standard for video signals, allowing for optimal signal transfer and minimizing reflections. The amplifier stage, represented by transistor T2, is where the main signal amplification occurs. The gain of this stage is adjustable through potentiometer P2, which provides flexibility for varying input signal strengths. The frequency response of T2 is shaped by the interaction of components P1, R6, and C6, allowing users to tailor the circuit's performance to their specific needs.
Transistor T3 functions as a buffer, ensuring that the circuit can drive a standard 75-ohm load effectively. This is important for maintaining signal integrity when interfacing with other equipment. The output level can be fine-tuned using potentiometer P2, allowing for an output of 1 Vp-p, with the expectation that the open-circuit output will reach 2 Vp-p. This design not only enhances the visual quality of the television image but also provides users with the ability to customize their viewing experience.Enhancement circuit as shown in the high-frequency component of the video signal can be increased, thereby enhancing the contrast of the TV image, it can also be connected to t he output terminal between the VCR and the TV SCART input. Circuit transistor Tl dampening effect. The resistance Rl ensure enhanced input impedance of the circuit is approximately 75. Signal applied to the amplifier stage T2, the gain depends on the position of the potentiometer P2. T2 signal frequency characteristics of the base by Pl, R6, C6 constraints, and therefore to some extent, controllable by the user (via Pl). T3 buffer stage provides sufficient current for properly driving the vast majority 75 load. Adjust the potentiometer P2, the output is 1Vp-p (open-circuit output level should be 2Vp-p).
The enhancement circuit is designed to improve the quality of video signals by amplifying high-frequency components, which are crucial for image clarity and contrast. The circuit operates by connecting the output between a VCR and a television's SCART input, facilitating seamless integration into existing setups. The use of transistor T1 serves to dampen unwanted signals, ensuring that only the desired frequencies are amplified.
Resistor R1 is critical in maintaining an input impedance of approximately 75 ohms, which is standard for video signals, allowing for optimal signal transfer and minimizing reflections. The amplifier stage, represented by transistor T2, is where the main signal amplification occurs. The gain of this stage is adjustable through potentiometer P2, which provides flexibility for varying input signal strengths. The frequency response of T2 is shaped by the interaction of components P1, R6, and C6, allowing users to tailor the circuit's performance to their specific needs.
Transistor T3 functions as a buffer, ensuring that the circuit can drive a standard 75-ohm load effectively. This is important for maintaining signal integrity when interfacing with other equipment. The output level can be fine-tuned using potentiometer P2, allowing for an output of 1 Vp-p, with the expectation that the open-circuit output will reach 2 Vp-p. This design not only enhances the visual quality of the television image but also provides users with the ability to customize their viewing experience.Enhancement circuit as shown in the high-frequency component of the video signal can be increased, thereby enhancing the contrast of the TV image, it can also be connected to t he output terminal between the VCR and the TV SCART input. Circuit transistor Tl dampening effect. The resistance Rl ensure enhanced input impedance of the circuit is approximately 75. Signal applied to the amplifier stage T2, the gain depends on the position of the potentiometer P2. T2 signal frequency characteristics of the base by Pl, R6, C6 constraints, and therefore to some extent, controllable by the user (via Pl). T3 buffer stage provides sufficient current for properly driving the vast majority 75 load. Adjust the potentiometer P2, the output is 1Vp-p (open-circuit output level should be 2Vp-p).