VLQC circuit
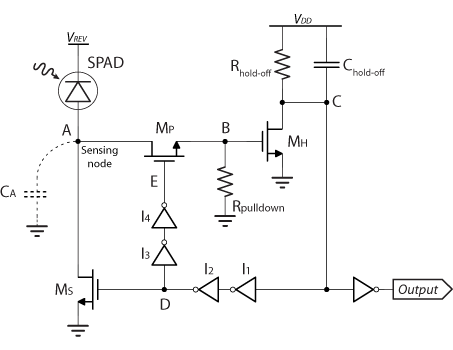
VLQC is a quenching circuit developed in the laboratory to meet the specific requirements of an array, including high compactness, cross-talk avoidance, and low afterpulsing. In the VLQC design, a single transistor is utilized to perform the sensing, quenching, and reset functions, significantly reducing the overall parasitic capacitance of the detector and consequently lowering system power consumption, as well as minimizing pixel-to-pixel optical coupling and afterpulsing. The accompanying image illustrates a test integrated circuit that incorporates the VLQC. Aside from the output buffer, which is essential for driving pads, the area occupied by the VLQC is comparable to that of a 20µm SPAD.
The VLQC circuit is engineered to optimize performance in applications where space and efficiency are critical. The integration of a single transistor for multiple functions simplifies the design and minimizes the number of components, which contributes to the compactness of the overall system. This arrangement not only enhances the reliability of the circuit by reducing potential points of failure but also allows for easier integration into larger systems.
The quenching process is vital in ensuring that the detector can reset rapidly after a photon detection event, thus enabling it to be ready for the next event without significant downtime. The low afterpulsing characteristic is particularly important in high-speed applications, as it reduces the likelihood of false signals that can arise from residual charge in the detector.
Moreover, the output buffer plays a crucial role by ensuring that the VLQC can effectively interface with external circuits or pads, providing the necessary drive strength to accommodate various load conditions. The compact design of the VLQC, comparable to a 20µm SPAD, allows for high-density arrangements in sensor arrays, making it suitable for applications such as imaging systems, LIDAR, and other optical detection technologies where space and performance are paramount.
In conclusion, the VLQC represents a significant advancement in quenching circuit design, balancing the need for compactness with the operational requirements of modern detection systems. Its innovative use of a single transistor for multiple roles, combined with a design that minimizes parasitic capacitance, positions it as a leading solution in the field of photodetection.VLQC is a quenching circuit designed in our laboratories to perfectly suit the constraints of an array, i. e. high compactness, cross-talk avoidance and low afterpulsing. In VLQC a single transistor performs the sensing, quenching and reset tasks drastically reducing the overall detector parasitic capacitance and thus system power consumption, pixel-to-pixel optical
coupling and afterpulsing. The picture below shows a test integrated circuit comprising the VLQC. A part from the output buffer that is necessary to drive pads, VLQC area is comparable with a 20um SPAD area. 🔗 External reference
The VLQC circuit is engineered to optimize performance in applications where space and efficiency are critical. The integration of a single transistor for multiple functions simplifies the design and minimizes the number of components, which contributes to the compactness of the overall system. This arrangement not only enhances the reliability of the circuit by reducing potential points of failure but also allows for easier integration into larger systems.
The quenching process is vital in ensuring that the detector can reset rapidly after a photon detection event, thus enabling it to be ready for the next event without significant downtime. The low afterpulsing characteristic is particularly important in high-speed applications, as it reduces the likelihood of false signals that can arise from residual charge in the detector.
Moreover, the output buffer plays a crucial role by ensuring that the VLQC can effectively interface with external circuits or pads, providing the necessary drive strength to accommodate various load conditions. The compact design of the VLQC, comparable to a 20µm SPAD, allows for high-density arrangements in sensor arrays, making it suitable for applications such as imaging systems, LIDAR, and other optical detection technologies where space and performance are paramount.
In conclusion, the VLQC represents a significant advancement in quenching circuit design, balancing the need for compactness with the operational requirements of modern detection systems. Its innovative use of a single transistor for multiple roles, combined with a design that minimizes parasitic capacitance, positions it as a leading solution in the field of photodetection.VLQC is a quenching circuit designed in our laboratories to perfectly suit the constraints of an array, i. e. high compactness, cross-talk avoidance and low afterpulsing. In VLQC a single transistor performs the sensing, quenching and reset tasks drastically reducing the overall detector parasitic capacitance and thus system power consumption, pixel-to-pixel optical
coupling and afterpulsing. The picture below shows a test integrated circuit comprising the VLQC. A part from the output buffer that is necessary to drive pads, VLQC area is comparable with a 20um SPAD area. 🔗 External reference