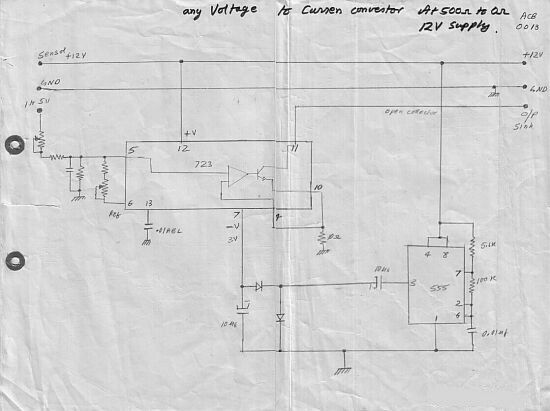
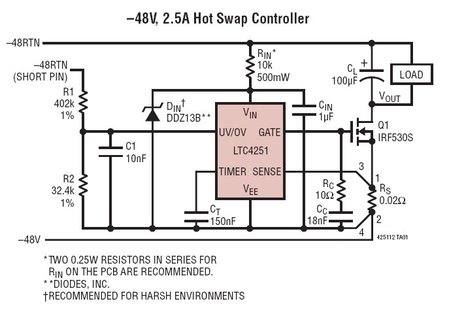
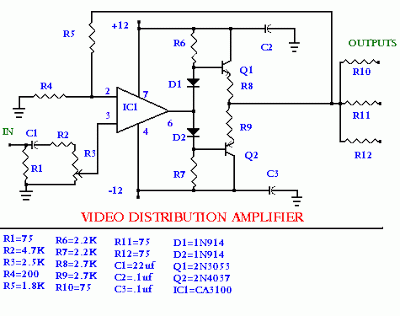
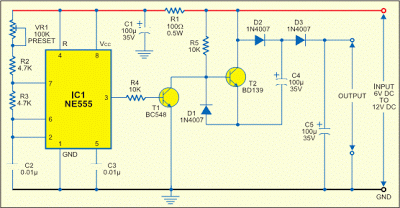
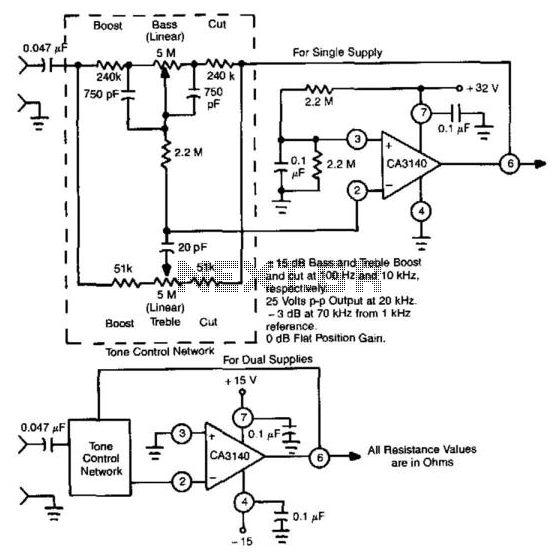
Voltage controlled variable gain amplifier
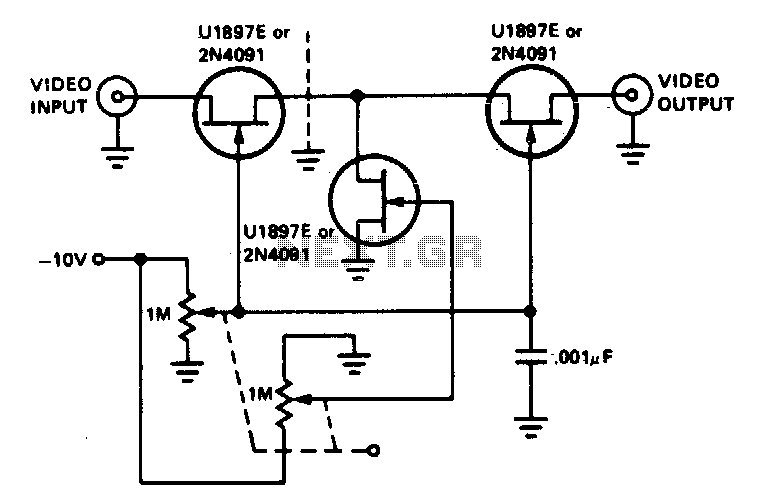
The tee attenuator offers optimal dynamic linear range attenuation of up to 100 dB, even at a frequency of 10.7 MHz with appropriate layout.
The tee attenuator is a crucial component in RF and audio applications where signal integrity and control are paramount. This passive device is designed to reduce the amplitude of a signal without distorting its waveform, thus maintaining the quality of the transmitted signal. The design typically consists of three ports: an input, an output, and a termination port, arranged in a "T" configuration.
The optimal dynamic linear range of up to 100 dB indicates that the attenuator can effectively manage signals over a wide range of amplitudes, making it suitable for various applications, including telecommunications, broadcasting, and instrumentation. The operational frequency of 10.7 MHz is significant, as it falls within the VHF range, commonly used in FM radio and other communication systems.
Proper layout is critical for the performance of the tee attenuator. Factors such as the placement of components, trace lengths, and grounding techniques can significantly affect the overall attenuation and frequency response. High-quality resistors with low temperature coefficients are typically employed to ensure stability and minimize variations due to environmental changes. Additionally, the use of appropriate PCB materials can reduce dielectric losses, further enhancing the performance of the attenuator.
In summary, the tee attenuator is an essential device for achieving precise signal management in various electronic applications, with specific attention required for layout and component selection to maximize its effectiveness at the specified operational frequency.The tee attenuator provides for optimum dynamic linear range attenuation up to 100 dB, even at f = 10 7 MHz with proper layout.
The tee attenuator is a crucial component in RF and audio applications where signal integrity and control are paramount. This passive device is designed to reduce the amplitude of a signal without distorting its waveform, thus maintaining the quality of the transmitted signal. The design typically consists of three ports: an input, an output, and a termination port, arranged in a "T" configuration.
The optimal dynamic linear range of up to 100 dB indicates that the attenuator can effectively manage signals over a wide range of amplitudes, making it suitable for various applications, including telecommunications, broadcasting, and instrumentation. The operational frequency of 10.7 MHz is significant, as it falls within the VHF range, commonly used in FM radio and other communication systems.
Proper layout is critical for the performance of the tee attenuator. Factors such as the placement of components, trace lengths, and grounding techniques can significantly affect the overall attenuation and frequency response. High-quality resistors with low temperature coefficients are typically employed to ensure stability and minimize variations due to environmental changes. Additionally, the use of appropriate PCB materials can reduce dielectric losses, further enhancing the performance of the attenuator.
In summary, the tee attenuator is an essential device for achieving precise signal management in various electronic applications, with specific attention required for layout and component selection to maximize its effectiveness at the specified operational frequency.The tee attenuator provides for optimum dynamic linear range attenuation up to 100 dB, even at f = 10 7 MHz with proper layout.