Voltage-mode control and compensation: Intricacies for buck regulators

Before designing with one of today's powerful buck regulator ICs, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of voltage mode control and compensation.
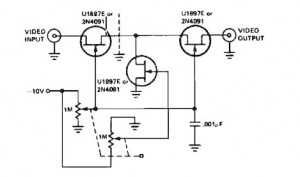
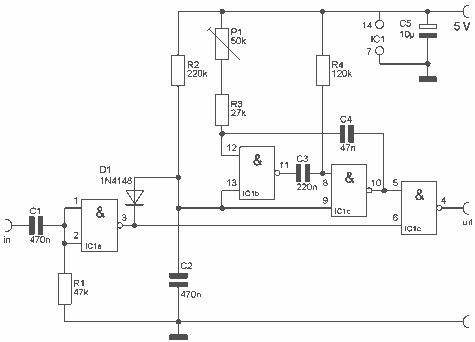
Voltage mode control is a widely used method in switching power supplies, particularly in buck converters. This technique regulates the output voltage by comparing it to a reference voltage and adjusting the duty cycle of the switching element accordingly. The control loop's stability and transient response are critical parameters that must be optimized to ensure reliable operation across varying load conditions.
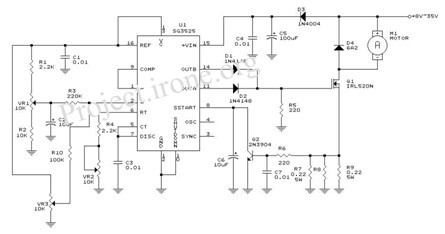
Compensation in voltage mode control is necessary to achieve stable operation. It involves the design of a compensation network that shapes the frequency response of the control loop. Common compensation techniques include Type I, Type II, and Type III compensators, each offering different trade-offs in terms of phase margin, bandwidth, and transient response. The selection of the appropriate compensation scheme depends on the specific application requirements, load characteristics, and desired performance metrics.
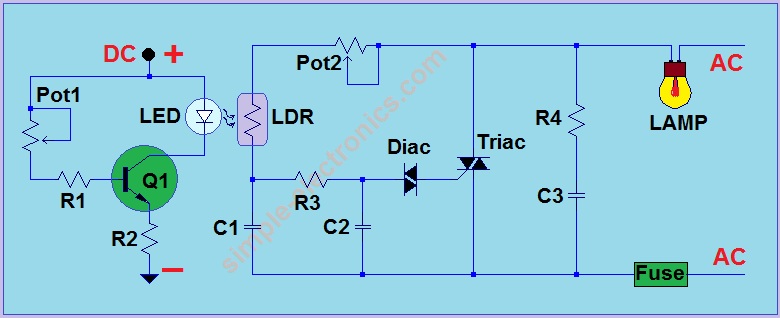
When designing a buck converter, it is important to consider the following elements: input and output capacitors, inductor selection, diode characteristics, and PCB layout. Input capacitors must be chosen to handle the input voltage ripple, while output capacitors affect the output voltage ripple and transient response. Inductor selection impacts the efficiency and current ripple, and the diode must be rated for the expected current and voltage conditions.
Additionally, PCB layout plays a significant role in the performance of the buck converter. Proper grounding, trace widths, and component placement are crucial to minimize parasitic inductance and resistance, which can adversely affect the regulator's performance.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of voltage mode control and compensation is vital for the effective design of buck regulator circuits. Proper selection of components and careful attention to layout will enhance the performance and reliability of the power supply design.Before designing with one of today`s powerful buck regulator ICs, you`ll want a thorough understanding of voltage mode control and compensation. .. 🔗 External reference
Voltage mode control is a widely used method in switching power supplies, particularly in buck converters. This technique regulates the output voltage by comparing it to a reference voltage and adjusting the duty cycle of the switching element accordingly. The control loop's stability and transient response are critical parameters that must be optimized to ensure reliable operation across varying load conditions.
Compensation in voltage mode control is necessary to achieve stable operation. It involves the design of a compensation network that shapes the frequency response of the control loop. Common compensation techniques include Type I, Type II, and Type III compensators, each offering different trade-offs in terms of phase margin, bandwidth, and transient response. The selection of the appropriate compensation scheme depends on the specific application requirements, load characteristics, and desired performance metrics.
When designing a buck converter, it is important to consider the following elements: input and output capacitors, inductor selection, diode characteristics, and PCB layout. Input capacitors must be chosen to handle the input voltage ripple, while output capacitors affect the output voltage ripple and transient response. Inductor selection impacts the efficiency and current ripple, and the diode must be rated for the expected current and voltage conditions.
Additionally, PCB layout plays a significant role in the performance of the buck converter. Proper grounding, trace widths, and component placement are crucial to minimize parasitic inductance and resistance, which can adversely affect the regulator's performance.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of voltage mode control and compensation is vital for the effective design of buck regulator circuits. Proper selection of components and careful attention to layout will enhance the performance and reliability of the power supply design.Before designing with one of today`s powerful buck regulator ICs, you`ll want a thorough understanding of voltage mode control and compensation. .. 🔗 External reference
.jpg)