Wideband Active Antenna Circuit
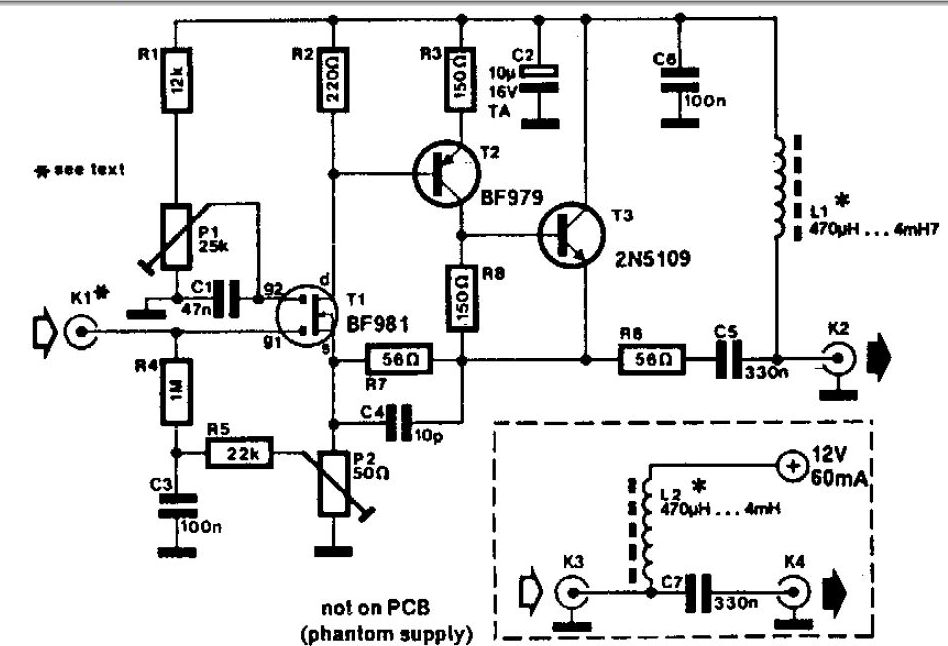
A whip antenna measuring between 30 to 50 cm is capable of receiving signals from 10 MHz to over 220 MHz. The circuit incorporates a BF981 dual-gate MOSFET (T1), which offers low noise characteristics, high input impedance, and enhanced performance.
The circuit utilizes a whip antenna, which is a type of monopole antenna known for its simplicity and effectiveness in receiving a wide range of frequencies. The length of the whip antenna is critical; at 30 to 50 cm, it is optimized for the frequency range of interest, allowing for efficient signal reception across the specified bandwidth from 10 MHz to 220 MHz.
The BF981 MOSFET serves as an important component in this design. Its dual-gate configuration allows for better control of gain and frequency response, making it suitable for applications requiring low noise amplification. The high input impedance characteristic of the BF981 ensures minimal loading on the antenna, preserving signal integrity and maximizing the antenna's performance.
In terms of circuit design, the whip antenna is connected to the gate of the BF981, where it acts as the input stage. The output of the MOSFET can be connected to further amplification stages or directly to a receiver, depending on the application. Proper biasing of the MOSFET is essential to maintain its operation in the desired region, ensuring optimal performance.
Additionally, the circuit may include passive components such as resistors and capacitors to filter unwanted signals and stabilize the gain of the MOSFET. Attention should be given to the layout of the circuit to minimize noise and interference, which can significantly affect the performance of the antenna system.
Overall, this antenna circuit is well-suited for applications in radio communications, amateur radio, and other areas where reliable reception of signals in the specified frequency range is required.A 30 to 50 cm whip antenna provides reception from 10 MHz to over 220 MHz. T1 BF981, a dual-gate MOSFET, provides low noise, high-input impedance and high.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a whip antenna, which is a type of monopole antenna known for its simplicity and effectiveness in receiving a wide range of frequencies. The length of the whip antenna is critical; at 30 to 50 cm, it is optimized for the frequency range of interest, allowing for efficient signal reception across the specified bandwidth from 10 MHz to 220 MHz.
The BF981 MOSFET serves as an important component in this design. Its dual-gate configuration allows for better control of gain and frequency response, making it suitable for applications requiring low noise amplification. The high input impedance characteristic of the BF981 ensures minimal loading on the antenna, preserving signal integrity and maximizing the antenna's performance.
In terms of circuit design, the whip antenna is connected to the gate of the BF981, where it acts as the input stage. The output of the MOSFET can be connected to further amplification stages or directly to a receiver, depending on the application. Proper biasing of the MOSFET is essential to maintain its operation in the desired region, ensuring optimal performance.
Additionally, the circuit may include passive components such as resistors and capacitors to filter unwanted signals and stabilize the gain of the MOSFET. Attention should be given to the layout of the circuit to minimize noise and interference, which can significantly affect the performance of the antenna system.
Overall, this antenna circuit is well-suited for applications in radio communications, amateur radio, and other areas where reliable reception of signals in the specified frequency range is required.A 30 to 50 cm whip antenna provides reception from 10 MHz to over 220 MHz. T1 BF981, a dual-gate MOSFET, provides low noise, high-input impedance and high.. 🔗 External reference