Winding electronic counter 2
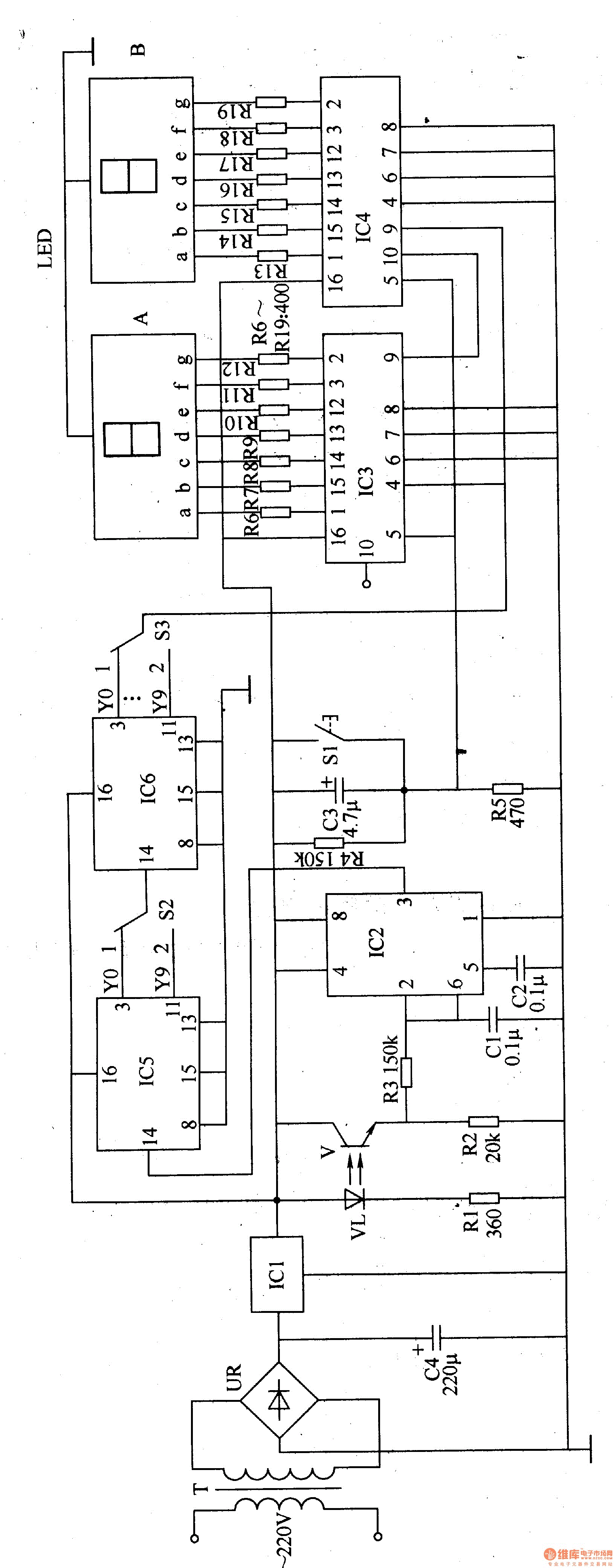
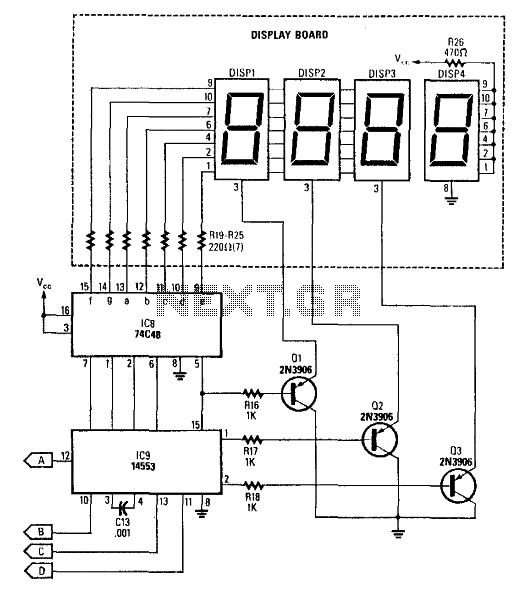
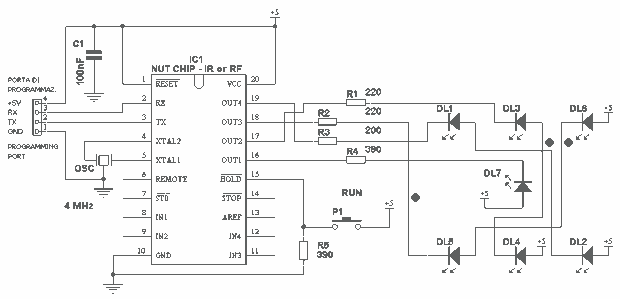
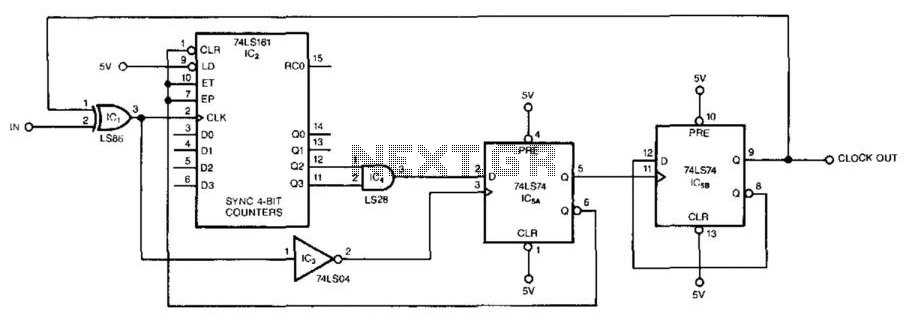
The electronic counter of the winding machine utilizes an LED digital display to indicate the number of turns of the wound coil, with a maximum counting capacity of 9900 turns. The operational principle of the winding machine circuit consists of several components: a power circuit, an infrared switch circuit, a shaping/transformation circuit, a reset circuit, a divider circuit, and the LED counter.
The winding machine's electronic counter is designed to accurately measure and display the number of turns made during the winding process. The power circuit supplies the necessary voltage and current to the entire system, ensuring stable operation. The infrared switch circuit serves as a sensor to detect the position of the coil, triggering the counting mechanism each time a complete turn is made.
The shaping/transformation circuit processes the signals received from the infrared switch, converting them into a suitable format for counting. This circuit may include components such as operational amplifiers or Schmitt triggers to ensure clean and reliable signal transitions. The reset circuit allows the user to set the counter back to zero, providing flexibility for multiple winding operations without manual intervention.
The divider circuit is crucial as it can scale down the input signals to the appropriate level for the LED counter. This ensures that the counter can accurately reflect the number of turns, especially in applications where the coil may be wound rapidly. Finally, the LED counter visually presents the data, allowing operators to monitor the winding process in real-time.
Overall, the design of the winding machine electronic counter integrates multiple circuits to achieve precise measurement and user-friendly operation, making it an essential component in automated winding applications.The winding machine electronic counter described in the example uses LED digital display to show the wound coil turns, the use of maximum count rate is 9900 turns. The working principle The winding machine circuit is composed of the power circuit, infrared switch circuit, shaping / transformation circuit, reset circuit, divider circuit and the LED counter..
🔗 External reference
The winding machine's electronic counter is designed to accurately measure and display the number of turns made during the winding process. The power circuit supplies the necessary voltage and current to the entire system, ensuring stable operation. The infrared switch circuit serves as a sensor to detect the position of the coil, triggering the counting mechanism each time a complete turn is made.
The shaping/transformation circuit processes the signals received from the infrared switch, converting them into a suitable format for counting. This circuit may include components such as operational amplifiers or Schmitt triggers to ensure clean and reliable signal transitions. The reset circuit allows the user to set the counter back to zero, providing flexibility for multiple winding operations without manual intervention.
The divider circuit is crucial as it can scale down the input signals to the appropriate level for the LED counter. This ensures that the counter can accurately reflect the number of turns, especially in applications where the coil may be wound rapidly. Finally, the LED counter visually presents the data, allowing operators to monitor the winding process in real-time.
Overall, the design of the winding machine electronic counter integrates multiple circuits to achieve precise measurement and user-friendly operation, making it an essential component in automated winding applications.The winding machine electronic counter described in the example uses LED digital display to show the wound coil turns, the use of maximum count rate is 9900 turns. The working principle The winding machine circuit is composed of the power circuit, infrared switch circuit, shaping / transformation circuit, reset circuit, divider circuit and the LED counter..
🔗 External reference