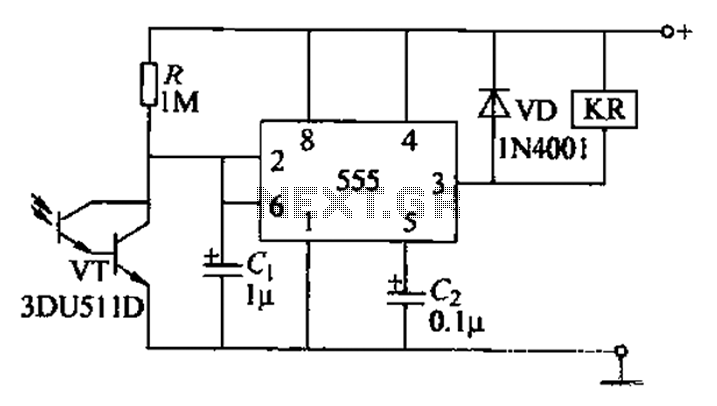
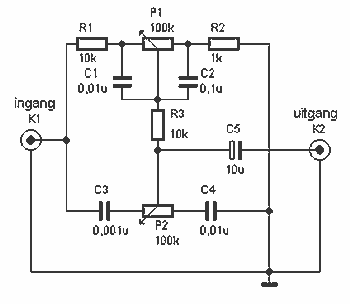
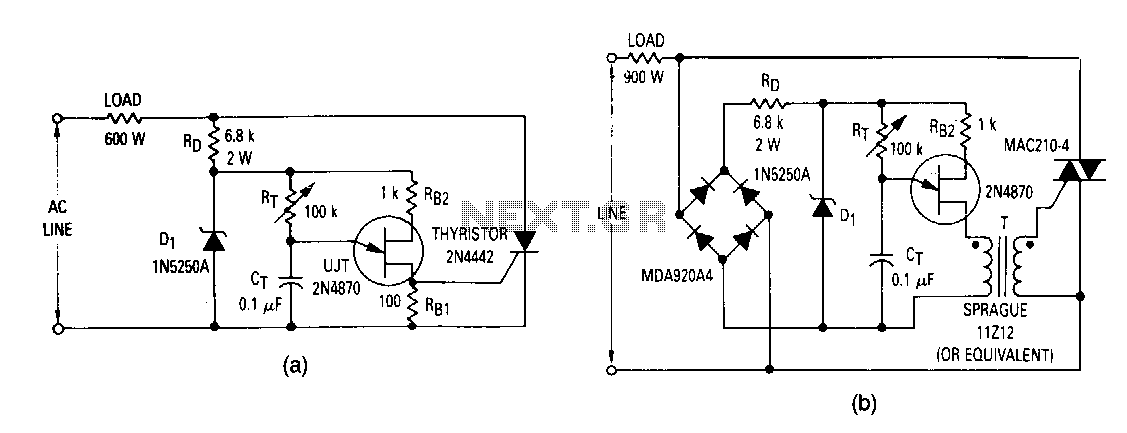
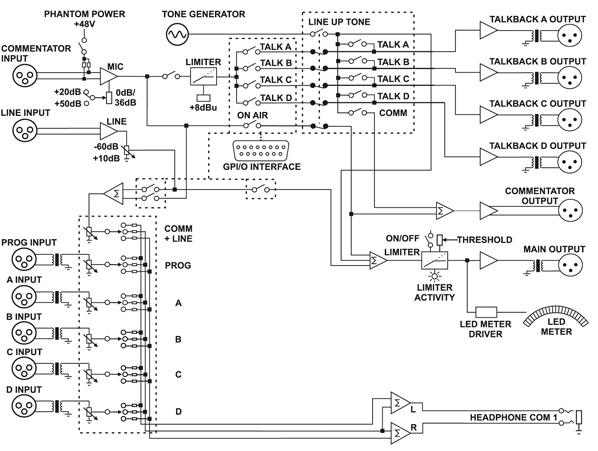
Windshield wiper hesitation control unit
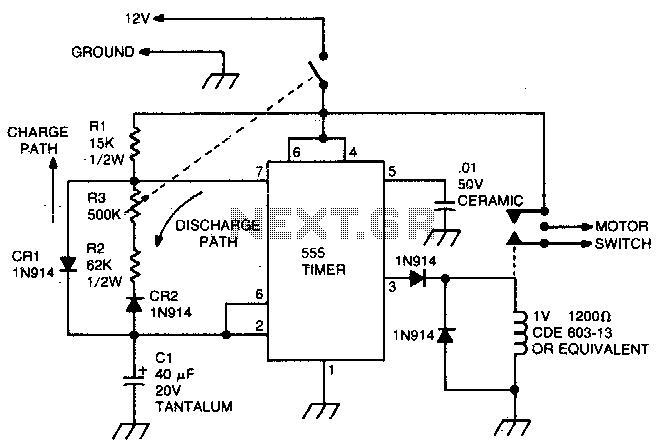
This circuit utilizes the 555 timer in astable or oscillatory mode. The duration for which the timer remains off is determined by the values of capacitor C1, resistor R2, and resistor R3. A potentiometer is incorporated to adjust the amount of "hesitation," allowing for a timing range of approximately 2 to 15 seconds. Resistor R2 establishes a minimum time delay when resistor R3 is set to zero ohms.
The 555 timer in astable mode operates by continuously switching between its high and low states, generating a square wave output. In this configuration, the timing cycle is defined by the resistors and capacitor connected to the timer. The formula for calculating the frequency (f) of the oscillation is given by:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \cdot C1} \]
Where:
- R1 is the resistor connected between the discharge pin (pin 7) and Vcc.
- R2 is the resistor connected from the threshold pin (pin 6) to the discharge pin (pin 7).
- C1 is the timing capacitor connected between the threshold pin (pin 6) and ground.
The duty cycle, which determines the proportion of time the output is high versus low, is influenced by R2 and R3, particularly the potentiometer used for adjustment. When the potentiometer is varied, it changes the resistance in the circuit, thereby altering the timing intervals. The minimum time delay, when R3 is at zero ohms, is established by R2, ensuring that the circuit operates within the desired timing range.
In practical applications, this circuit can be employed in various timing and delay scenarios, such as in light flashers, timer circuits, and sound generators. The ability to adjust the timing with a potentiometer provides flexibility for different requirements, making this circuit versatile in electronic designs. Proper selection of the capacitor and resistor values is essential for achieving the desired oscillation frequency and duty cycle.This circuit uses the 555 timer in the asta-ble or oscillatory mode. The length of time the timer is off is a function of the values of CI, R2, and R3. The potentiometer which controls the amount of "hesitation" (Approximately 2 to 15 seconds) R2 provides a minimum time delay when R3 is at its zero ohms position.
The 555 timer in astable mode operates by continuously switching between its high and low states, generating a square wave output. In this configuration, the timing cycle is defined by the resistors and capacitor connected to the timer. The formula for calculating the frequency (f) of the oscillation is given by:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \cdot C1} \]
Where:
- R1 is the resistor connected between the discharge pin (pin 7) and Vcc.
- R2 is the resistor connected from the threshold pin (pin 6) to the discharge pin (pin 7).
- C1 is the timing capacitor connected between the threshold pin (pin 6) and ground.
The duty cycle, which determines the proportion of time the output is high versus low, is influenced by R2 and R3, particularly the potentiometer used for adjustment. When the potentiometer is varied, it changes the resistance in the circuit, thereby altering the timing intervals. The minimum time delay, when R3 is at zero ohms, is established by R2, ensuring that the circuit operates within the desired timing range.
In practical applications, this circuit can be employed in various timing and delay scenarios, such as in light flashers, timer circuits, and sound generators. The ability to adjust the timing with a potentiometer provides flexibility for different requirements, making this circuit versatile in electronic designs. Proper selection of the capacitor and resistor values is essential for achieving the desired oscillation frequency and duty cycle.This circuit uses the 555 timer in the asta-ble or oscillatory mode. The length of time the timer is off is a function of the values of CI, R2, and R3. The potentiometer which controls the amount of "hesitation" (Approximately 2 to 15 seconds) R2 provides a minimum time delay when R3 is at its zero ohms position.