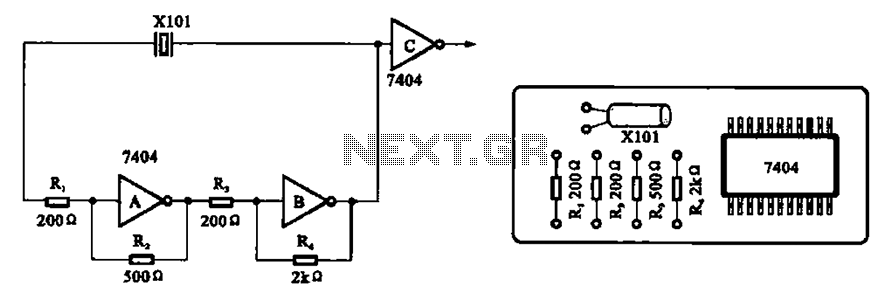
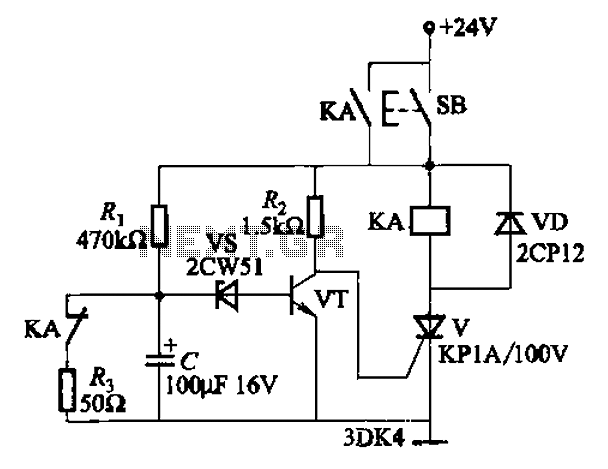
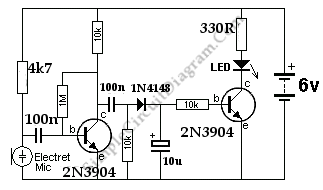
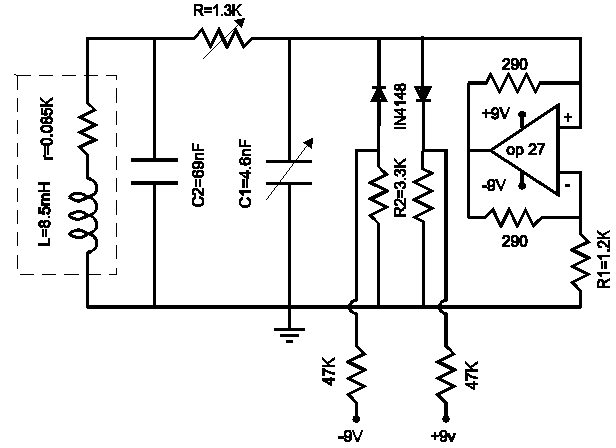
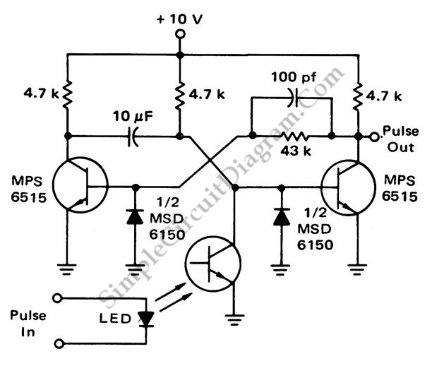
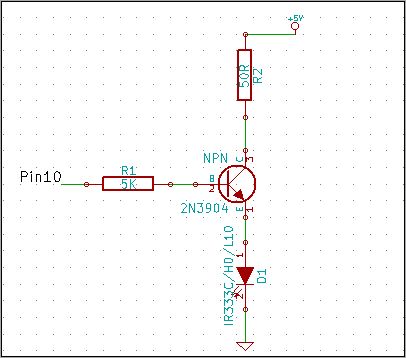
Cooling fan control socket synchronous circuit diagram
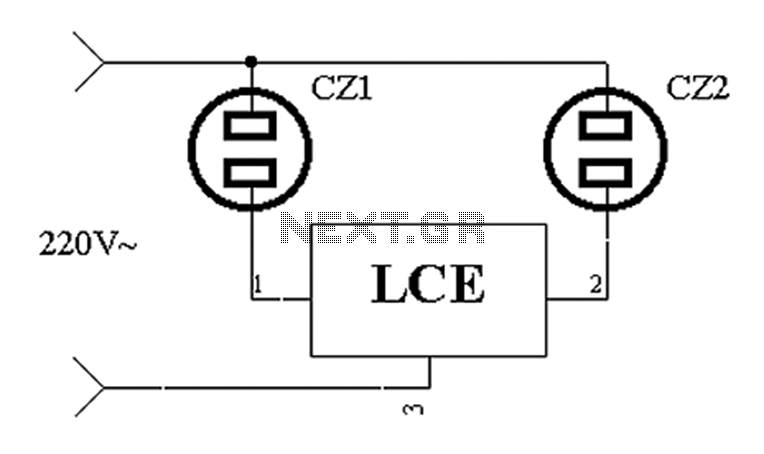
The application circuit operates the device as illustrated below. It is designed for cooling electrical equipment, typically utilizing a cooling fan to dissipate heat. The LCE employs a synchronous control socket on the device and its connections remain unchanged. As long as the power plug of the electrical equipment is connected to the power outlet CZ1, the fan can be plugged into the power outlet CZ2. When the electrical equipment is powered on, the fan will automatically start running, and when the power to the electrical equipment is turned off, the fan will also cease operation immediately.
The described circuit functions as an automatic cooling system for electrical devices, ensuring that heat generated during operation is effectively managed. The synchronous control mechanism enables seamless operation of the cooling fan in conjunction with the primary device.
The circuit typically includes a relay or a solid-state switch that is activated when the primary device is powered on. This relay connects the fan to the power supply, allowing it to operate concurrently with the electrical equipment. The power outlets CZ1 and CZ2 are strategically placed to facilitate easy connections for both the primary device and the cooling fan.
In terms of electrical specifications, the circuit may be designed to handle various voltage levels, depending on the requirements of the cooling fan and the primary electrical equipment. The use of appropriate fuses or circuit breakers is recommended to protect against overcurrent conditions that may arise during operation.
Additionally, the design can incorporate a thermal sensor that monitors the temperature of the electrical equipment. If the temperature exceeds a predetermined threshold, the sensor can trigger the relay to activate the fan even if the primary device is not powered on. This feature enhances the cooling efficiency and prolongs the lifespan of the electrical equipment by preventing overheating.
Overall, this application circuit presents a straightforward yet effective solution for managing heat in electrical devices, ensuring reliable operation and enhanced safety.Application circuit works the device as shown below. For cooling electrical equipment, usually with a cooling fan to drive heat. LCE made use synchronous control socket on the device and its line without any changes, as long as the power plug of electrical equipment into a power outlet CZ1, the fans plug into a power outlet CZ2 can be. When electrical equipment is powered fan will automatically start running when the power is off electrical equipment, electric fans also immediately stop working.
The described circuit functions as an automatic cooling system for electrical devices, ensuring that heat generated during operation is effectively managed. The synchronous control mechanism enables seamless operation of the cooling fan in conjunction with the primary device.
The circuit typically includes a relay or a solid-state switch that is activated when the primary device is powered on. This relay connects the fan to the power supply, allowing it to operate concurrently with the electrical equipment. The power outlets CZ1 and CZ2 are strategically placed to facilitate easy connections for both the primary device and the cooling fan.
In terms of electrical specifications, the circuit may be designed to handle various voltage levels, depending on the requirements of the cooling fan and the primary electrical equipment. The use of appropriate fuses or circuit breakers is recommended to protect against overcurrent conditions that may arise during operation.
Additionally, the design can incorporate a thermal sensor that monitors the temperature of the electrical equipment. If the temperature exceeds a predetermined threshold, the sensor can trigger the relay to activate the fan even if the primary device is not powered on. This feature enhances the cooling efficiency and prolongs the lifespan of the electrical equipment by preventing overheating.
Overall, this application circuit presents a straightforward yet effective solution for managing heat in electrical devices, ensuring reliable operation and enhanced safety.Application circuit works the device as shown below. For cooling electrical equipment, usually with a cooling fan to drive heat. LCE made use synchronous control socket on the device and its line without any changes, as long as the power plug of electrical equipment into a power outlet CZ1, the fans plug into a power outlet CZ2 can be. When electrical equipment is powered fan will automatically start running when the power is off electrical equipment, electric fans also immediately stop working.