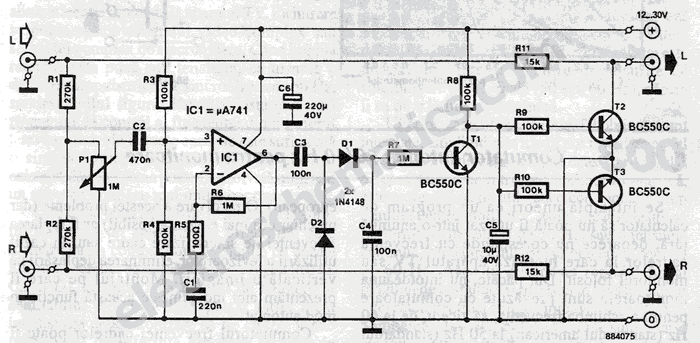
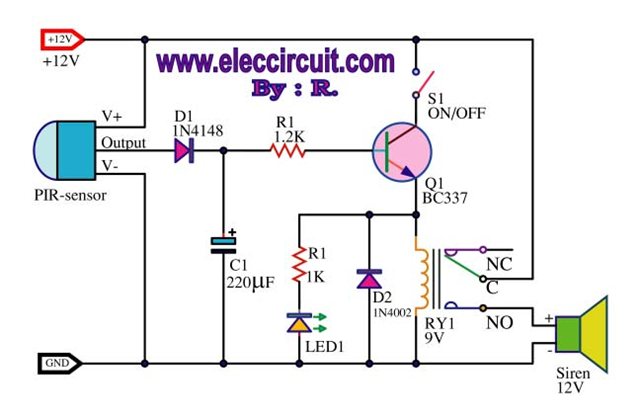
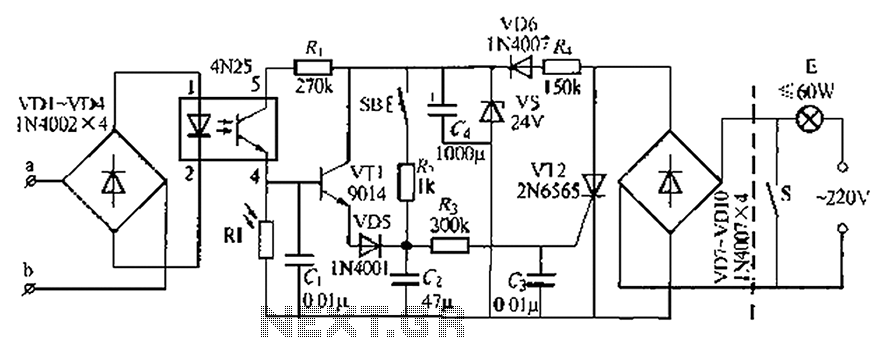
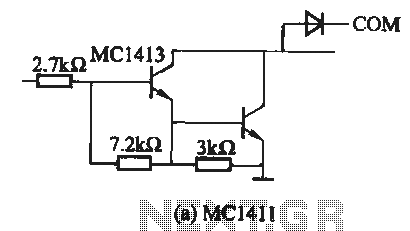
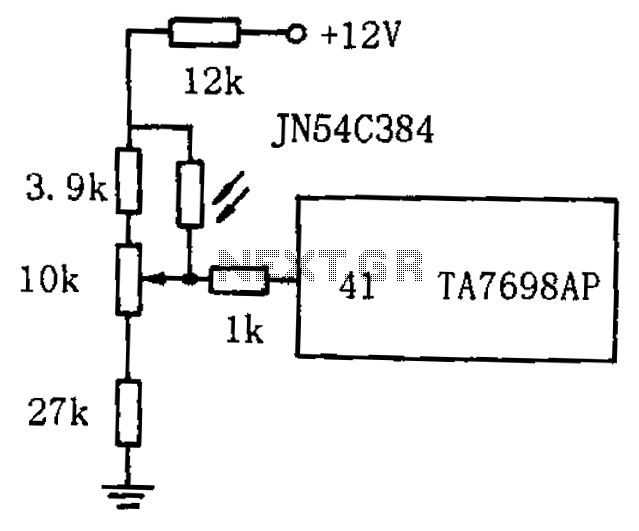
XTR112 114 bridge input current excitation circuit diagram
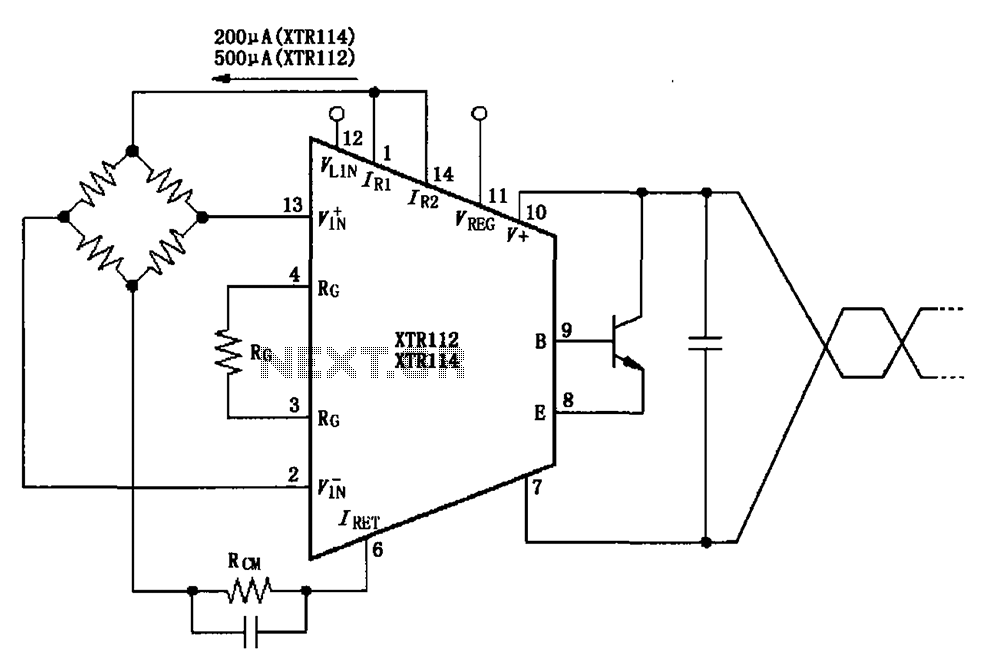
The two current sources within the chip (1 foot and 14 feet out) provide excitation. The output of each current source is 0.2 mA (XTR114) or 0.5 A (XTR112). The common mode input voltage is adjustable, ranging from 1.25 to 3.5 V.
The circuit features two distinct current sources designed to deliver precise excitation levels for various applications. The XTR114 current source outputs a nominal current of 0.2 mA, while the XTR112 is capable of providing a higher output of 0.5 A. This versatility allows for adaptability in different circuit configurations, depending on the required current specifications.
The adjustment of the common mode input voltage is a critical aspect of this design, allowing it to be finely tuned within a range of 1.25 V to 3.5 V. This feature enhances the circuit's performance by accommodating variations in the input signal conditions, thus ensuring stable operation under diverse scenarios.
In practical applications, these current sources can be utilized in sensor interfaces, signal conditioning, or as part of a larger analog system where precise current regulation is necessary. The ability to bridge excitation with adjustable common mode voltage ensures that the circuit can maintain optimal performance across a variety of environmental and operational conditions.
Overall, the integration of these current sources within a single chip simplifies design processes and enhances reliability, making it a valuable component in modern electronic systems. As shown, the two current sources inside the chip (1 foot and 14 feet out) bridge excitation, the output of each current source is 0.2mA (XTR114) or 0.5A (XTR112). With RCM adj usted common mode input voltage, so that is 1.25 ~ 3.5V.
The circuit features two distinct current sources designed to deliver precise excitation levels for various applications. The XTR114 current source outputs a nominal current of 0.2 mA, while the XTR112 is capable of providing a higher output of 0.5 A. This versatility allows for adaptability in different circuit configurations, depending on the required current specifications.
The adjustment of the common mode input voltage is a critical aspect of this design, allowing it to be finely tuned within a range of 1.25 V to 3.5 V. This feature enhances the circuit's performance by accommodating variations in the input signal conditions, thus ensuring stable operation under diverse scenarios.
In practical applications, these current sources can be utilized in sensor interfaces, signal conditioning, or as part of a larger analog system where precise current regulation is necessary. The ability to bridge excitation with adjustable common mode voltage ensures that the circuit can maintain optimal performance across a variety of environmental and operational conditions.
Overall, the integration of these current sources within a single chip simplifies design processes and enhances reliability, making it a valuable component in modern electronic systems. As shown, the two current sources inside the chip (1 foot and 14 feet out) bridge excitation, the output of each current source is 0.2mA (XTR114) or 0.5A (XTR112). With RCM adj usted common mode input voltage, so that is 1.25 ~ 3.5V.