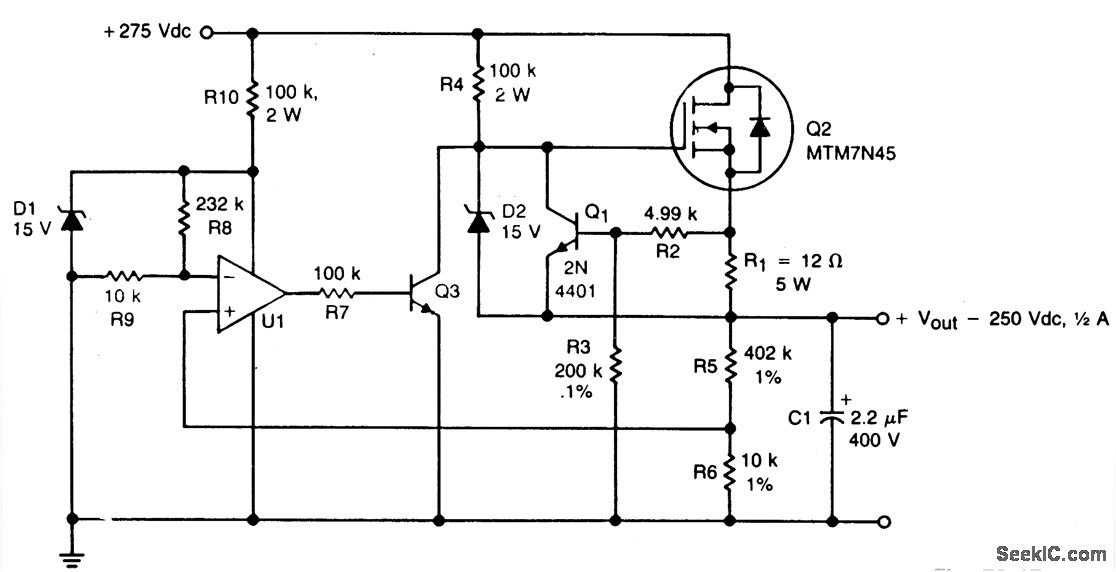
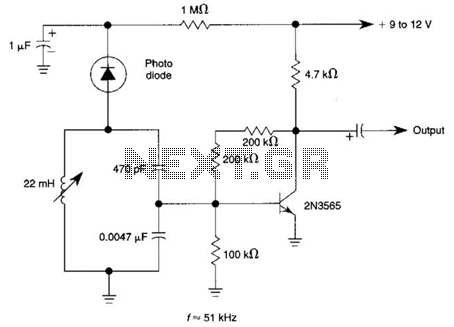
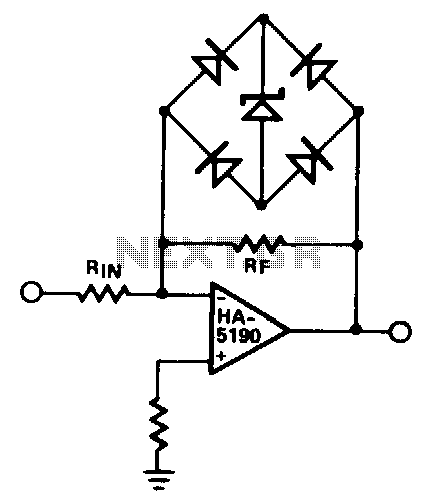
Zener diode increase regulator output
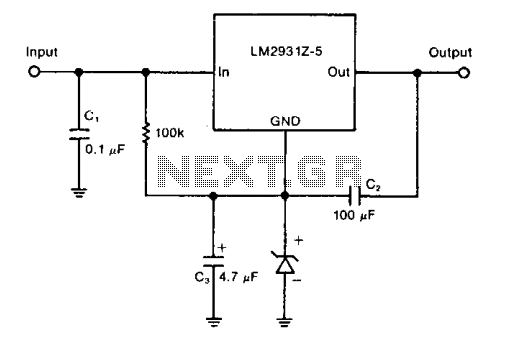
A zener diode in the ground lead of a fixed PNP regulator varies the voltage output of that device without a significant sacrifice in regulation. The technique also allows the regulator to operate with output voltages beyond its rated limit.
The circuit utilizes a Zener diode connected to the ground lead of a fixed PNP voltage regulator. This configuration enables the adjustment of the output voltage by effectively shifting the reference voltage seen by the regulator. The Zener diode's breakdown voltage determines the amount of voltage reduction, allowing for fine-tuning of the output voltage while maintaining stable regulation characteristics.
In addition to adjusting the output voltage, this method permits the regulator to function at output voltages that exceed its specified limits. This capability is particularly beneficial in applications requiring higher voltages than the regulator's nominal rating. The Zener diode ensures that the voltage remains within safe operating parameters, thereby preventing damage to the regulator and connected load.
When designing this circuit, it is crucial to select a Zener diode with an appropriate breakdown voltage that aligns with the desired output voltage range. Furthermore, the power rating of the Zener diode must be considered to avoid overheating during operation. The overall circuit design should also incorporate adequate bypass capacitors to filter any noise and stabilize the output voltage, ensuring reliable performance.
This configuration exemplifies a practical approach to enhancing the versatility of voltage regulators in electronic circuits, enabling them to accommodate a wider range of operational requirements without compromising their fundamental performance.A zener diode in the ground lead of a fixed pnp regulator varies the voltage output of that device without a significant sacrifice in regulation. The technique also allows the regulator to operate with output voltages beyond its rated limit.
The circuit utilizes a Zener diode connected to the ground lead of a fixed PNP voltage regulator. This configuration enables the adjustment of the output voltage by effectively shifting the reference voltage seen by the regulator. The Zener diode's breakdown voltage determines the amount of voltage reduction, allowing for fine-tuning of the output voltage while maintaining stable regulation characteristics.
In addition to adjusting the output voltage, this method permits the regulator to function at output voltages that exceed its specified limits. This capability is particularly beneficial in applications requiring higher voltages than the regulator's nominal rating. The Zener diode ensures that the voltage remains within safe operating parameters, thereby preventing damage to the regulator and connected load.
When designing this circuit, it is crucial to select a Zener diode with an appropriate breakdown voltage that aligns with the desired output voltage range. Furthermore, the power rating of the Zener diode must be considered to avoid overheating during operation. The overall circuit design should also incorporate adequate bypass capacitors to filter any noise and stabilize the output voltage, ensuring reliable performance.
This configuration exemplifies a practical approach to enhancing the versatility of voltage regulators in electronic circuits, enabling them to accommodate a wider range of operational requirements without compromising their fundamental performance.A zener diode in the ground lead of a fixed pnp regulator varies the voltage output of that device without a significant sacrifice in regulation. The technique also allows the regulator to operate with output voltages beyond its rated limit.