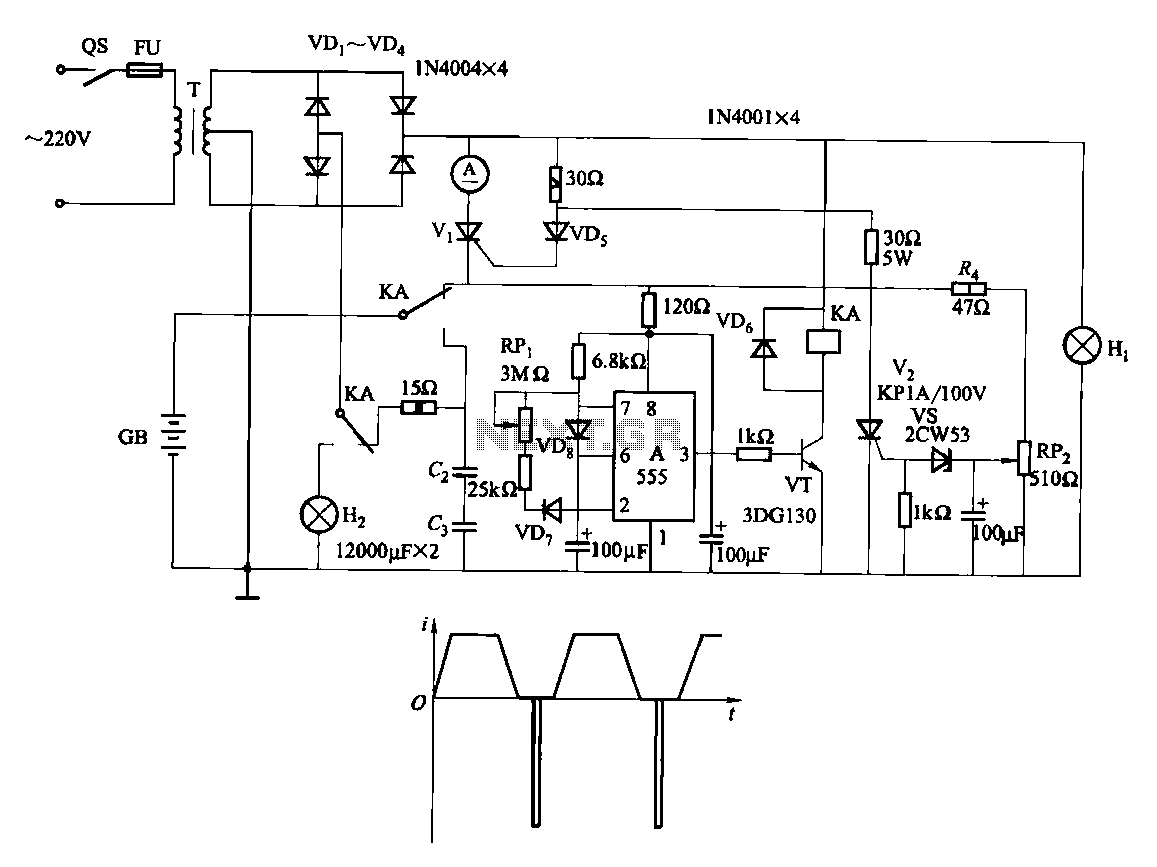
ZMDIZSSC1856 double-channel intellectual battery manages the solution

The ZSSC1856 from ZMDI Company is a double-channel ADC integrated with an embedded MCU, composed of two chips packaged in a PQFN32 5x5mm format. The system's basic chip, the System Basis Chip (SBC), incorporates high voltage circuits, a LIN transceiver, and peripheral hardware, including 18 ADCs that perform numerical filtering on the input stage. The microcontroller unit (MCU) includes the core, memory, and additional peripheral hardware. Communication between the MCU and SBC is facilitated through an SPI interface. The normal operating current ranges from 10mA to 20mA, while the low-power consumption mode is less than 100µA. This device is primarily used for measuring batteries in automotive, industrial, and medical applications that require accurate battery monitoring. The text outlines the key features of the ZSSC1856, including block diagrams of the SBC's digital part and the MCU, as well as typical application circuits. The ZSSC1856 consists of two silicon dies in one package, stacked within a PQFN32 5x5mm configuration. The SBC includes high voltage circuits, an analog input stage with peripheral blocks, ADCs, digital filtering, and a LIN transceiver. The MCU contains the microcontroller core, memory, and several peripheral blocks. Communication is managed through an SPI interface, with internal nodes such as TXD, RXD, IRQN, CSN, SPI_CLK, MOSI, MISO, MCU_CLK, MCU_RSTN, and RAM_PROTN controlled by firmware. Users can access these internal nodes via the LIN interface and/or external JTAG pins (TDO, TDI, TRSTN, TMS, TCK). One input channel measures the battery current (IBAT) using the voltage drop across an external shunt resistor, while the second channel measures battery voltage (VBAT) and temperature. An integrated flash memory allows for customer-specific software, such as algorithms for calculating battery state. During Sleep Mode (e.g., when the engine is off), the system conducts periodic measurements to monitor battery discharge. Measurement cycles are software-controlled and include various wake-up conditions. The ZSSC1856 is optimized for ultra-low power consumption, drawing 100µA or less in this mode, making it suitable for industrial and medical applications that require precise monitoring of battery state of charge (SOC), state of health (SOH), and state of function (SOF), such as in emergency lighting, uninterruptible power supplies, hospital equipment, and alarm systems.
The ZSSC1856 device is designed to provide accurate and efficient battery monitoring solutions across various applications. The integration of the SBC and MCU into a single package not only saves space but also enhances performance by reducing interconnect delays and improving signal integrity. The high voltage circuits within the SBC are essential for interfacing with automotive battery systems, ensuring that the device can handle the demands of high voltage environments. The dual-channel ADC capability allows simultaneous measurement of critical parameters, such as battery current and voltage, which is vital for effective battery management systems.
The SPI interface facilitates fast and reliable communication between the MCU and SBC, enabling quick data transfer and command execution. This is particularly important in applications where timely responses to battery status are critical. The firmware-controlled internal nodes enhance flexibility, allowing users to customize the operation of the device according to specific application requirements.
The ability to measure battery temperature alongside voltage and current is a significant advantage, as temperature can greatly affect battery performance and longevity. The integrated flash memory supports the implementation of custom algorithms, enabling users to optimize battery state calculations and improve overall system efficiency.
The ultra-low power consumption feature of the ZSSC1856 is particularly beneficial in applications where power availability is limited, such as in medical devices or portable equipment. The periodic measurement capability during Sleep Mode ensures that battery health is continuously monitored without significant power draw, thus extending the operational life of the device.
Overall, the ZSSC1856 is a versatile and efficient solution for advanced battery monitoring applications, combining high-performance features with low power consumption to meet the demands of modern electronic systems.ZSSC1856 of ZMDI Company is the double-channel ADC of integrating embedded MCU, made up of two chips, PQFN32 5x5mm capsulates. Basic chip SBC of the system Having included the high tension circuit, LIN transceiver and including the peripheral hardware, 18 ADCs, the numerical filtering inclusive really imitates the input stage.
MCU chip includes MCU kernel, the memorizer and some peripheral hardware. The communication of MCU and SBC is dealt with by SPI interface. The normal modal electric current is 10mA-20mA, the low power consumption mode is smaller than 100uA, the intellectual battery mainly used in the car is measured, industry and medical application in need of accurate battery. This text has introduced ZSSC1856 key feature, the block-diagram, SBC digital part and MCU some block-diagrams and typical application circuit.
The ZSSC1856 consists of two silicon dies in one package. The dies are assembled as stacked dies in a PQFN32 5x5mm package. The System Basis Chip SBC contains the high voltage circuits, the analog input stage including peripheral blocks, the ADCs, the digital filtering, and the LIN-transceiver. The microcontroller chip MCU contains the microcontroller core, memories, and some peripheral blocks.
Communication between the MCU and the SBC is handled by an SPI interface. Internal nodes connecting the MCU and the SBC i. e. , TXD, RXD, IRQN, CSN, SPI_CLK, MOSI, MISO, MCU_CLK, MCU_RSTN, and RAM_PROTN are controlled by firmware. Users can access the internal nodes via the LIN interface and/or external JTAG pins i. e. , TDO, TDI, TRSTN, TMS, and TCK. One of the two input channels measures the battery current IBAT via the voltage drop at the external shunt resistor.
The second channel measures the battery voltage VBAT and the temperature. An integrated flash memory is provided for customer-specific soft-ware; e. g. , dedicated algorithms for calculating the battery state. During Sleep Mode e. g. , engine off, the system makes periodic measurements to monitor the dis-charge of the battery. Measurement cycles are controlled by the software and include various wake-up conditions. The ZSSC1856 is optimized for ultra-low power consumption and draws only 100 A or less in this mode. Industrial and medical applica-tions requiring precise battery SOC, SOH and SOF monitoring; e. g. , emergency lighting, uninter-ruptable power supplies, hospital equipment, alarm systems, and more. 🔗 External reference
The ZSSC1856 device is designed to provide accurate and efficient battery monitoring solutions across various applications. The integration of the SBC and MCU into a single package not only saves space but also enhances performance by reducing interconnect delays and improving signal integrity. The high voltage circuits within the SBC are essential for interfacing with automotive battery systems, ensuring that the device can handle the demands of high voltage environments. The dual-channel ADC capability allows simultaneous measurement of critical parameters, such as battery current and voltage, which is vital for effective battery management systems.
The SPI interface facilitates fast and reliable communication between the MCU and SBC, enabling quick data transfer and command execution. This is particularly important in applications where timely responses to battery status are critical. The firmware-controlled internal nodes enhance flexibility, allowing users to customize the operation of the device according to specific application requirements.
The ability to measure battery temperature alongside voltage and current is a significant advantage, as temperature can greatly affect battery performance and longevity. The integrated flash memory supports the implementation of custom algorithms, enabling users to optimize battery state calculations and improve overall system efficiency.
The ultra-low power consumption feature of the ZSSC1856 is particularly beneficial in applications where power availability is limited, such as in medical devices or portable equipment. The periodic measurement capability during Sleep Mode ensures that battery health is continuously monitored without significant power draw, thus extending the operational life of the device.
Overall, the ZSSC1856 is a versatile and efficient solution for advanced battery monitoring applications, combining high-performance features with low power consumption to meet the demands of modern electronic systems.ZSSC1856 of ZMDI Company is the double-channel ADC of integrating embedded MCU, made up of two chips, PQFN32 5x5mm capsulates. Basic chip SBC of the system Having included the high tension circuit, LIN transceiver and including the peripheral hardware, 18 ADCs, the numerical filtering inclusive really imitates the input stage.
MCU chip includes MCU kernel, the memorizer and some peripheral hardware. The communication of MCU and SBC is dealt with by SPI interface. The normal modal electric current is 10mA-20mA, the low power consumption mode is smaller than 100uA, the intellectual battery mainly used in the car is measured, industry and medical application in need of accurate battery. This text has introduced ZSSC1856 key feature, the block-diagram, SBC digital part and MCU some block-diagrams and typical application circuit.
The ZSSC1856 consists of two silicon dies in one package. The dies are assembled as stacked dies in a PQFN32 5x5mm package. The System Basis Chip SBC contains the high voltage circuits, the analog input stage including peripheral blocks, the ADCs, the digital filtering, and the LIN-transceiver. The microcontroller chip MCU contains the microcontroller core, memories, and some peripheral blocks.
Communication between the MCU and the SBC is handled by an SPI interface. Internal nodes connecting the MCU and the SBC i. e. , TXD, RXD, IRQN, CSN, SPI_CLK, MOSI, MISO, MCU_CLK, MCU_RSTN, and RAM_PROTN are controlled by firmware. Users can access the internal nodes via the LIN interface and/or external JTAG pins i. e. , TDO, TDI, TRSTN, TMS, and TCK. One of the two input channels measures the battery current IBAT via the voltage drop at the external shunt resistor.
The second channel measures the battery voltage VBAT and the temperature. An integrated flash memory is provided for customer-specific soft-ware; e. g. , dedicated algorithms for calculating the battery state. During Sleep Mode e. g. , engine off, the system makes periodic measurements to monitor the dis-charge of the battery. Measurement cycles are controlled by the software and include various wake-up conditions. The ZSSC1856 is optimized for ultra-low power consumption and draws only 100 A or less in this mode. Industrial and medical applica-tions requiring precise battery SOC, SOH and SOF monitoring; e. g. , emergency lighting, uninter-ruptable power supplies, hospital equipment, alarm systems, and more. 🔗 External reference