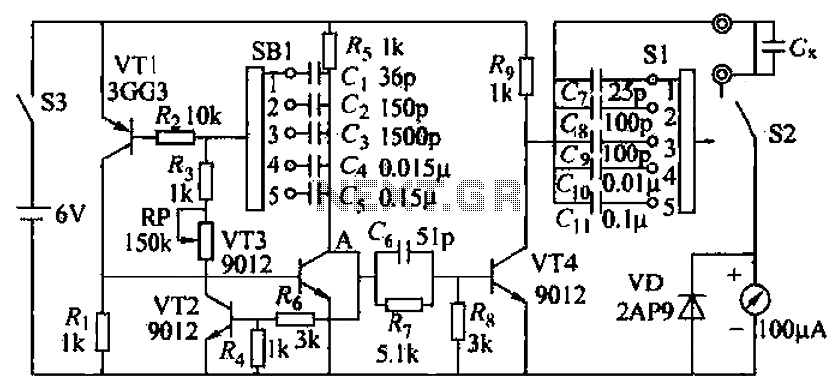
Synchronous RS flip-flop circuit structure and symbols
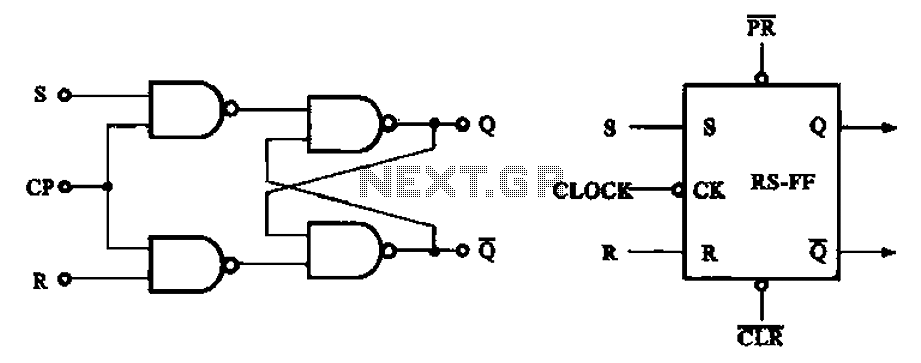
The asynchronous RS flip-flop mentioned earlier is not synchronized with the system clock signal. In contrast, the synchronous RS flip-flop incorporates synchronization, allowing it to operate in conjunction with the clock signal. Figure (a) illustrates the circuit configuration of the synchronous RS flip-flop, which utilizes two inputs, two NAND gates, and includes a clock input (CP). The circuit symbol is depicted in Figure (b).
The synchronous RS flip-flop is a fundamental building block in digital electronics, providing a means to store a single bit of data while being controlled by a clock signal. This configuration helps eliminate the race conditions and unstable states that can occur in asynchronous designs.
The circuit is typically composed of two NAND gates configured as a bistable multivibrator. The inputs are designated as R (reset) and S (set), which control the state of the flip-flop. The addition of the clock input (CP) ensures that changes in the output state occur only on a specific edge of the clock signal, typically the rising edge.
When the clock input is high, the states of the R and S inputs are evaluated. If S is high and R is low, the output Q will be set to high (1), indicating that the flip-flop is in the set state. Conversely, if R is high and S is low, the output Q will be reset to low (0), indicating that the flip-flop is in the reset state. If both inputs are low, the output retains its previous state, demonstrating the memory characteristic of the flip-flop.
The circuit symbol for the synchronous RS flip-flop typically includes the two input terminals (S and R), the clock input (CP), and the output terminal (Q). The design ensures that the output only changes when the clock signal transitions, facilitating reliable timing and control in sequential circuits.
Overall, the synchronous RS flip-flop is essential for applications requiring precise timing and control in digital systems, such as counters, registers, and memory units. Its ability to synchronize with a clock signal allows for more predictable behavior in complex circuits.Aforementioned asynchronous RS flip-flop is not synchronized with the system clock signal synchronous RS flip-flop is the addition of the synchronization can be synchronized wi th the clock signal work. Figure (a) shows the circuit configuration of synchronous RS flip-flop, it will use two inputs, two NAND gates, and adds a clock input (CP), the circuit symbol shown in Figure (b), show
The synchronous RS flip-flop is a fundamental building block in digital electronics, providing a means to store a single bit of data while being controlled by a clock signal. This configuration helps eliminate the race conditions and unstable states that can occur in asynchronous designs.
The circuit is typically composed of two NAND gates configured as a bistable multivibrator. The inputs are designated as R (reset) and S (set), which control the state of the flip-flop. The addition of the clock input (CP) ensures that changes in the output state occur only on a specific edge of the clock signal, typically the rising edge.
When the clock input is high, the states of the R and S inputs are evaluated. If S is high and R is low, the output Q will be set to high (1), indicating that the flip-flop is in the set state. Conversely, if R is high and S is low, the output Q will be reset to low (0), indicating that the flip-flop is in the reset state. If both inputs are low, the output retains its previous state, demonstrating the memory characteristic of the flip-flop.
The circuit symbol for the synchronous RS flip-flop typically includes the two input terminals (S and R), the clock input (CP), and the output terminal (Q). The design ensures that the output only changes when the clock signal transitions, facilitating reliable timing and control in sequential circuits.
Overall, the synchronous RS flip-flop is essential for applications requiring precise timing and control in digital systems, such as counters, registers, and memory units. Its ability to synchronize with a clock signal allows for more predictable behavior in complex circuits.Aforementioned asynchronous RS flip-flop is not synchronized with the system clock signal synchronous RS flip-flop is the addition of the synchronization can be synchronized wi th the clock signal work. Figure (a) shows the circuit configuration of synchronous RS flip-flop, it will use two inputs, two NAND gates, and adds a clock input (CP), the circuit symbol shown in Figure (b), show