Current-tampering circuit
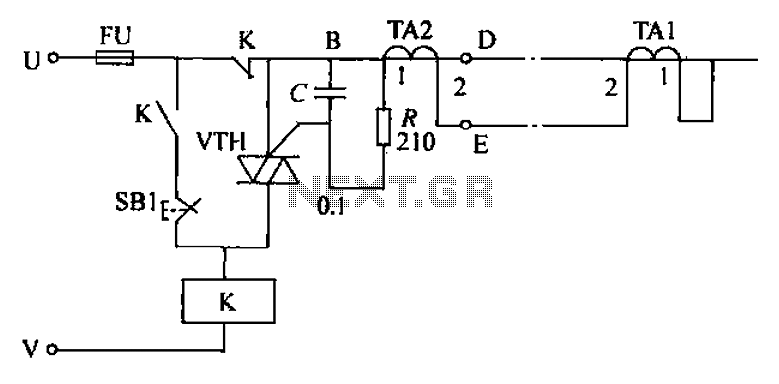
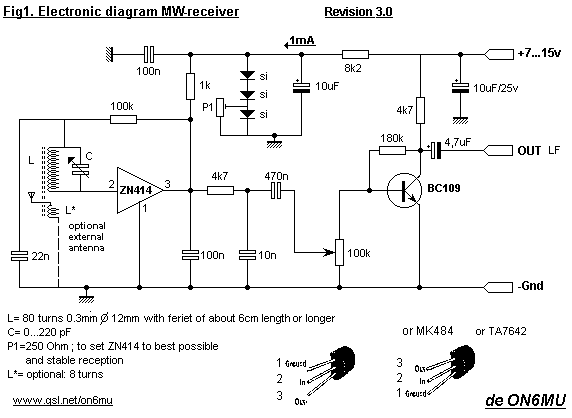
The circuit's current exceeds the load carried by the rated current meter, prompting the user to immediately cut off the power supply to address the overload. Pressing the reset button restores power, making the system simple, convenient, and practical. In the circuit diagram, an AC relay (K) is controlled by a Triac (VTH). The terminals TA1 and TA2 are of the same phase; when the current flows through the wire segment BD, the current meter reading is equal. The induced voltage across TA1 and TA2 on the secondary side is equal as well. When there is no voltage between the terminals of TA1 and TA2, VTH remains off, leading to the release of relay K, which has normally closed contacts for the user's power supply. However, in the event of power theft, the current through the wire segment BD becomes unequal, causing the induced voltages across TA1 and TA2 to trigger VTH into conduction. This action pulls in relay K, cutting off the user's power supply circuit. While relay K is engaged, it remains energized. Electrical control personnel can then open the rear cover and press the reset button (SB); if K does not release, the user can restore power. The VTH trigger circuit (C) includes anti-interference measures to prevent device malfunctions. The resistor (R) limits the trigger current to protect the VTH trigger circuit. For component selection, relay K can be an AC 220V JQX-4 type small power relay, where several normally closed contacts can be arranged in parallel to increase load capacity. The VTH can be a 3CTSIB model. The parameters for TA1 and TA2 should be closely matched to avoid malfunctions under high current conditions. For construction, a toroidal core is preferable for the transformer, allowing the power cord to pass through as the primary side, with approximately one hundred turns of appropriate wire wrapped around as the secondary side.
The described circuit effectively monitors current flow and provides a safety mechanism to disconnect the power supply in case of overload or theft. The use of a Triac (VTH) for control allows for efficient switching, while the relay (K) serves as a reliable means of cutting off power. The system is designed to be user-friendly, with a reset button that enables the restoration of power once the overload condition has been addressed.
The choice of components, particularly the relay and the transformer, is crucial for ensuring the circuit operates reliably under various load conditions. The JQX-4 relay is suitable for handling moderate loads and can be configured to enhance its capacity through parallel connections of its contacts. The 3CTSIB Triac is selected for its ability to handle AC loads effectively, providing a robust solution for the control mechanism.
The design emphasizes safety and ease of use, with the anti-interference measures incorporated into the trigger circuit to prevent false triggering due to electrical noise. This is especially important in environments where electrical fluctuations may occur. Additionally, the precise matching of TA1 and TA2 parameters is essential to maintain the integrity of the current sensing mechanism, ensuring that the system can accurately detect overload conditions without false alarms.
Overall, this circuit provides a comprehensive solution for monitoring and controlling electrical loads, with a focus on user safety and operational reliability. Circuit current is greater than the load carried by the rated current meter, the user immediately cut off the power supply to be subtracted overload, press the reset button to restore power, production of simple, convenient and feasible. Circuit shown in FIG. AC relay K is controlled by the Triac VTH. TA1 and TA2 end phase of the same name, in the pass when crossing the wire segment BD current meter current equal, TA1 and TA2 induced voltage equal to the secondary side. TA1 and TA2 1 no voltage between terminals, VTH is not turned on. K release, K normally closed contacts for power users. However, in the case of stealing, BD segment of a wire through the current meter current unequal, TA and TA2] two secondary side voltage induced errand VTH trigger conduction.
K pull its normally closed contacts cut off the users power supply circuit; while K is closed, so that K stays energized. Electrical control officers to be opened and open the rear cover, press the reset button after SB, K is not released, the user restore power.
VTH trigger circuit C has anti-interference effect, device malfunction fat only; R trigger current role is limited to avoid damage to the VTH trigger knot. Component selection: Relay K optional AC 220V JQX-4 type of small power relays, the normally 6ij several contacts in parallel can be increased load capacity.
VTH available 3CTSIB. rAl and TA2 parameters should be very consistent, otherwise malfunction when the current is large. Production time - core toroidal core is preferably selected, the power cord can pass therethrough as the primary side, with the appropriate wire wrap around one hundred turns as the secondary side.
The described circuit effectively monitors current flow and provides a safety mechanism to disconnect the power supply in case of overload or theft. The use of a Triac (VTH) for control allows for efficient switching, while the relay (K) serves as a reliable means of cutting off power. The system is designed to be user-friendly, with a reset button that enables the restoration of power once the overload condition has been addressed.
The choice of components, particularly the relay and the transformer, is crucial for ensuring the circuit operates reliably under various load conditions. The JQX-4 relay is suitable for handling moderate loads and can be configured to enhance its capacity through parallel connections of its contacts. The 3CTSIB Triac is selected for its ability to handle AC loads effectively, providing a robust solution for the control mechanism.
The design emphasizes safety and ease of use, with the anti-interference measures incorporated into the trigger circuit to prevent false triggering due to electrical noise. This is especially important in environments where electrical fluctuations may occur. Additionally, the precise matching of TA1 and TA2 parameters is essential to maintain the integrity of the current sensing mechanism, ensuring that the system can accurately detect overload conditions without false alarms.
Overall, this circuit provides a comprehensive solution for monitoring and controlling electrical loads, with a focus on user safety and operational reliability. Circuit current is greater than the load carried by the rated current meter, the user immediately cut off the power supply to be subtracted overload, press the reset button to restore power, production of simple, convenient and feasible. Circuit shown in FIG. AC relay K is controlled by the Triac VTH. TA1 and TA2 end phase of the same name, in the pass when crossing the wire segment BD current meter current equal, TA1 and TA2 induced voltage equal to the secondary side. TA1 and TA2 1 no voltage between terminals, VTH is not turned on. K release, K normally closed contacts for power users. However, in the case of stealing, BD segment of a wire through the current meter current unequal, TA and TA2] two secondary side voltage induced errand VTH trigger conduction.
K pull its normally closed contacts cut off the users power supply circuit; while K is closed, so that K stays energized. Electrical control officers to be opened and open the rear cover, press the reset button after SB, K is not released, the user restore power.
VTH trigger circuit C has anti-interference effect, device malfunction fat only; R trigger current role is limited to avoid damage to the VTH trigger knot. Component selection: Relay K optional AC 220V JQX-4 type of small power relays, the normally 6ij several contacts in parallel can be increased load capacity.
VTH available 3CTSIB. rAl and TA2 parameters should be very consistent, otherwise malfunction when the current is large. Production time - core toroidal core is preferably selected, the power cord can pass therethrough as the primary side, with the appropriate wire wrap around one hundred turns as the secondary side.