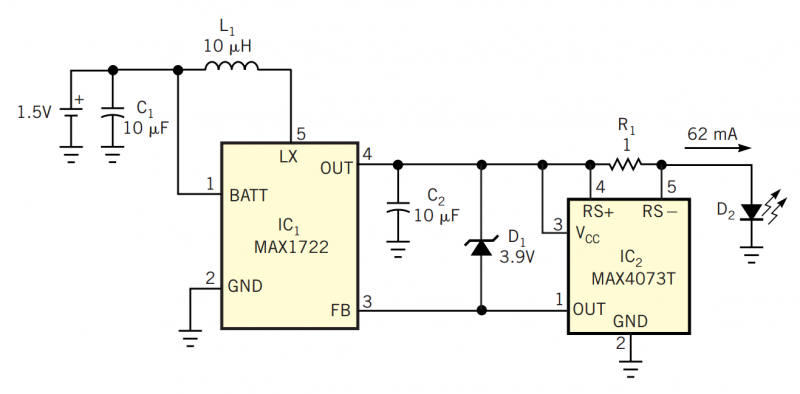
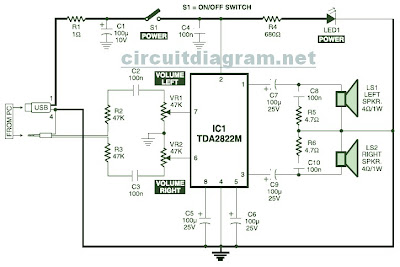
0-50v 2a Bench Power Supply
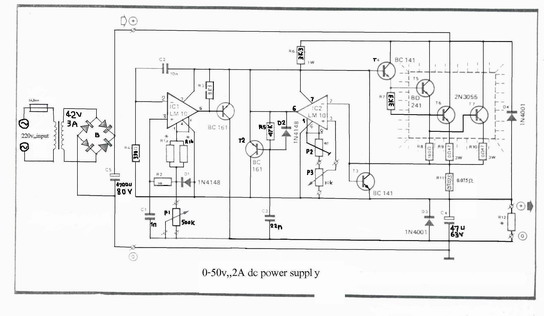
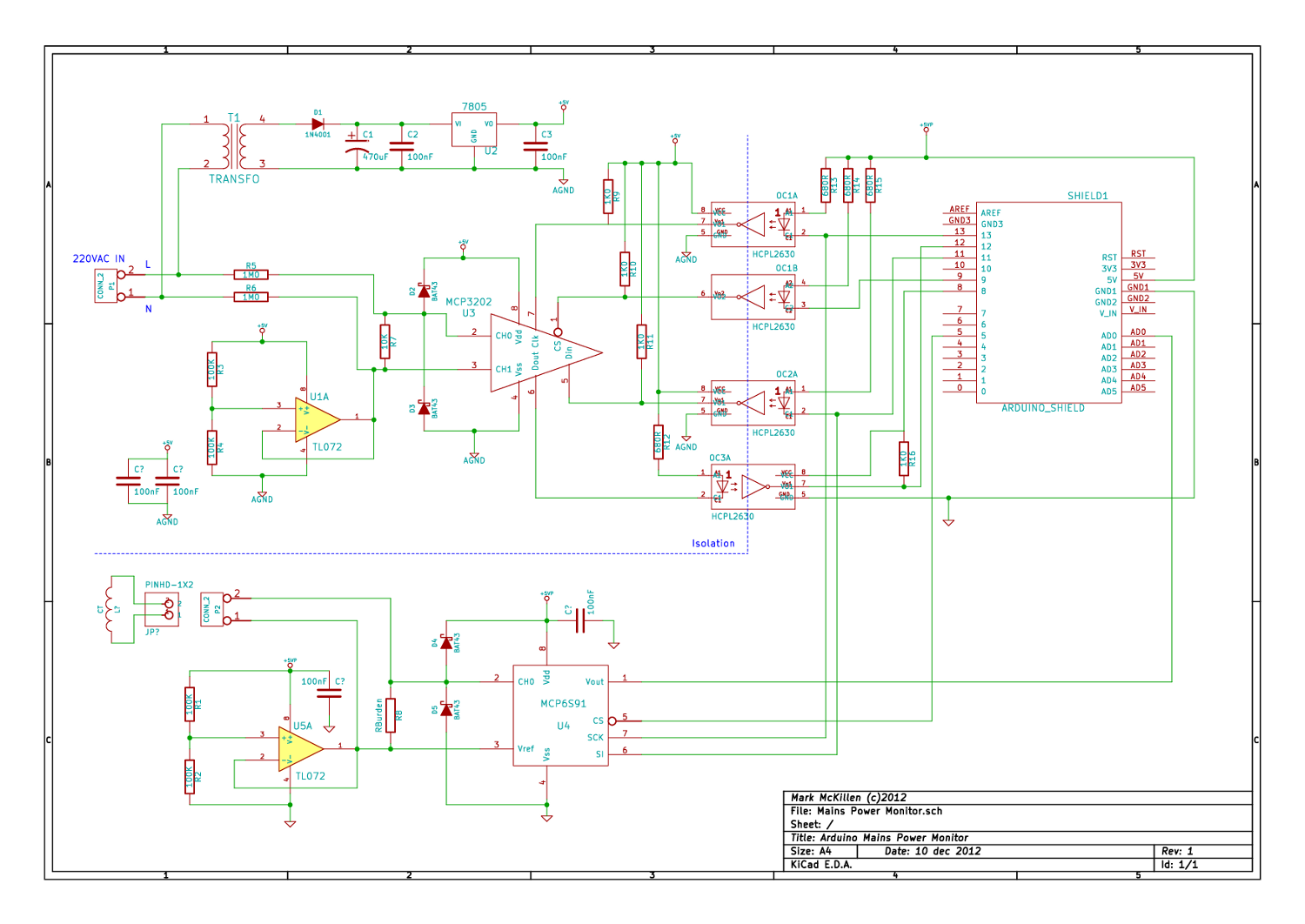
A variable power supply designed for laboratory use. It utilizes two integrated circuits (ICs) to provide adjustable output voltage and current.
This variable power supply is engineered to meet the diverse needs of laboratory applications, offering flexibility in output voltage and current levels. The use of two integrated circuits allows for precise control over the power supply's performance characteristics.
The schematic typically includes a transformer to step down the AC mains voltage, followed by a rectifier circuit to convert the AC voltage to DC. The two ICs serve distinct roles: one IC may be responsible for voltage regulation, while the other manages current regulation. This dual-IC configuration ensures that the power supply can maintain stable output under varying load conditions.
Additional components such as capacitors are included to filter out noise and provide stability to the output voltage. Potentiometers may be integrated into the design to allow users to easily adjust the output voltage and current settings.
Protection features, such as fuses or circuit breakers, are also essential to safeguard both the power supply and connected devices from overcurrent or short-circuit conditions. Visual indicators, such as LED lights, can be incorporated to provide real-time feedback on the operational status of the power supply.
Overall, this variable power supply is a versatile tool for experimental setups, testing, and prototyping, catering to a wide range of electronic devices and circuits in laboratory environments.Variable power supply for laboratories. With two ICs can take different output voltage and amperage 🔗 External reference
This variable power supply is engineered to meet the diverse needs of laboratory applications, offering flexibility in output voltage and current levels. The use of two integrated circuits allows for precise control over the power supply's performance characteristics.
The schematic typically includes a transformer to step down the AC mains voltage, followed by a rectifier circuit to convert the AC voltage to DC. The two ICs serve distinct roles: one IC may be responsible for voltage regulation, while the other manages current regulation. This dual-IC configuration ensures that the power supply can maintain stable output under varying load conditions.
Additional components such as capacitors are included to filter out noise and provide stability to the output voltage. Potentiometers may be integrated into the design to allow users to easily adjust the output voltage and current settings.
Protection features, such as fuses or circuit breakers, are also essential to safeguard both the power supply and connected devices from overcurrent or short-circuit conditions. Visual indicators, such as LED lights, can be incorporated to provide real-time feedback on the operational status of the power supply.
Overall, this variable power supply is a versatile tool for experimental setups, testing, and prototyping, catering to a wide range of electronic devices and circuits in laboratory environments.Variable power supply for laboratories. With two ICs can take different output voltage and amperage 🔗 External reference