1.2GHz Voltage Controlled Oscillator With Linear Modulation
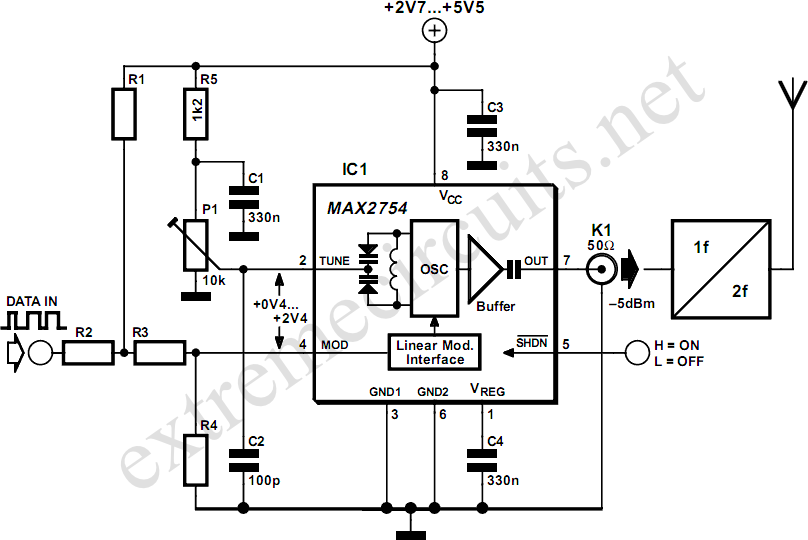
High-frequency voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs) are challenging to construct. Maxim has developed an integrated 1.2 GHz oscillator, the MAX2754. The center frequency is adjustable via the TUNE input, while a linear modulation input enables frequency modulation. This integrated circuit (IC) is housed in an 8-pin µMAX package, operates with a supply voltage between 2.7 V and 5.5 V, and consumes less than 2 mA of current. Both the TUNE and MOD inputs function over a control voltage range of +0.4 V to +2.4 V. The TUNE input allows the VCO frequency to be varied from 1050 MHz to 1270 MHz. In certain applications, a phase-locked loop (PLL) control voltage may be applied here to set the center frequency to a precise value. For ease of representation in the circuit diagram, a potentiometer is illustrated. The MOD input permits digital or analog modulation of the VCO, with a transfer slope of 500 kHz/V. The circuit example demonstrates the use of MOD for frequency shift keying (FSK) modulation. Resistors R1 to R4 adjust the data signal level to achieve a center value of +1.4 V and an amplitude that corresponds to the desired frequency deviation. A suggested set of resistor values for operation with a 5 V power supply includes: R1 = 480 Ω, R2 = 100 Ω, R3 = 220 Ω, and R4 = 270 Ω.
The MAX2754 VCO is designed to provide a compact solution for generating high-frequency signals, making it suitable for various RF applications. The TUNE input enables precise frequency adjustments, allowing designers to tailor the oscillator's output to specific requirements. The modulation capabilities via the MOD input facilitate the integration of the VCO into communication systems where frequency shift keying (FSK) is employed.
In practical applications, the use of a potentiometer for the TUNE input allows for manual tuning, which can be beneficial during the initial setup or testing phases. The recommended resistor values (R1 to R4) for the data signal conditioning ensure that the modulation input receives a properly biased signal, optimizing the performance of the VCO in a digital communication context. The transfer slope of 500 kHz/V indicates that for every volt applied to the MOD input, the output frequency will shift by 500 kHz, providing a clear relationship between the input control voltage and the frequency deviation.
Overall, the MAX2754's features, including low power consumption, wide frequency range, and versatile modulation capabilities, make it a valuable component for engineers designing RF circuits, particularly in applications requiring precise frequency control and modulation.Since high frequency voltage-controlled oscillators, or VCOs, are not easy to construct, Maxim ( has produced an integrated 1. 2GHz oscillator, the MAX2754. The center frequency is set using the TUNE input, and a linear modulation input allows the frequency to be modulated.
The IC is available in an 8-pin µMAX package, operates from a supply of be tween 2. 7 V and 5. 5 V, and draws a current of less than 2 mA. Both TUNE and MOD operate over control voltage range of +0. 4 V to +2. 4 V. TUNE allows the VCO frequency to be adjusted from 1050 MHz to 1270 MHz. In some applications a PLL control voltage will be applied here, allowing the center frequency to be set exactly to a desired value. For simplicity in the circuit diagram we have shown a potentiometer. The MOD input allows the VCO to be modulated in a digital or analogue fashion, with a transfer slope of 500 kHz/V.
In the circuit we have shown an example where MOD is used for frequency shift keying (FSK) modulation. Resistors R1 to R4 shift the level of the data signal so that it has a center value of +1. 4 V and an amplitude corresponding to the desired frequency deviation. One example set of values, suitable for use with a 5 V power supply, is as follows: R1 = 480 , R2 = 100 , R3 = 220 und R4 = 270 .
🔗 External reference
The MAX2754 VCO is designed to provide a compact solution for generating high-frequency signals, making it suitable for various RF applications. The TUNE input enables precise frequency adjustments, allowing designers to tailor the oscillator's output to specific requirements. The modulation capabilities via the MOD input facilitate the integration of the VCO into communication systems where frequency shift keying (FSK) is employed.
In practical applications, the use of a potentiometer for the TUNE input allows for manual tuning, which can be beneficial during the initial setup or testing phases. The recommended resistor values (R1 to R4) for the data signal conditioning ensure that the modulation input receives a properly biased signal, optimizing the performance of the VCO in a digital communication context. The transfer slope of 500 kHz/V indicates that for every volt applied to the MOD input, the output frequency will shift by 500 kHz, providing a clear relationship between the input control voltage and the frequency deviation.
Overall, the MAX2754's features, including low power consumption, wide frequency range, and versatile modulation capabilities, make it a valuable component for engineers designing RF circuits, particularly in applications requiring precise frequency control and modulation.Since high frequency voltage-controlled oscillators, or VCOs, are not easy to construct, Maxim ( has produced an integrated 1. 2GHz oscillator, the MAX2754. The center frequency is set using the TUNE input, and a linear modulation input allows the frequency to be modulated.
The IC is available in an 8-pin µMAX package, operates from a supply of be tween 2. 7 V and 5. 5 V, and draws a current of less than 2 mA. Both TUNE and MOD operate over control voltage range of +0. 4 V to +2. 4 V. TUNE allows the VCO frequency to be adjusted from 1050 MHz to 1270 MHz. In some applications a PLL control voltage will be applied here, allowing the center frequency to be set exactly to a desired value. For simplicity in the circuit diagram we have shown a potentiometer. The MOD input allows the VCO to be modulated in a digital or analogue fashion, with a transfer slope of 500 kHz/V.
In the circuit we have shown an example where MOD is used for frequency shift keying (FSK) modulation. Resistors R1 to R4 shift the level of the data signal so that it has a center value of +1. 4 V and an amplitude corresponding to the desired frequency deviation. One example set of values, suitable for use with a 5 V power supply, is as follows: R1 = 480 , R2 = 100 , R3 = 220 und R4 = 270 .
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713