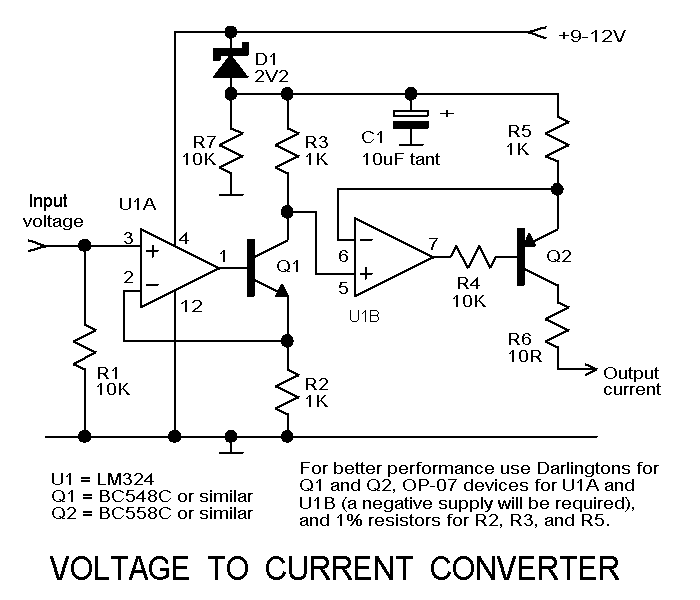
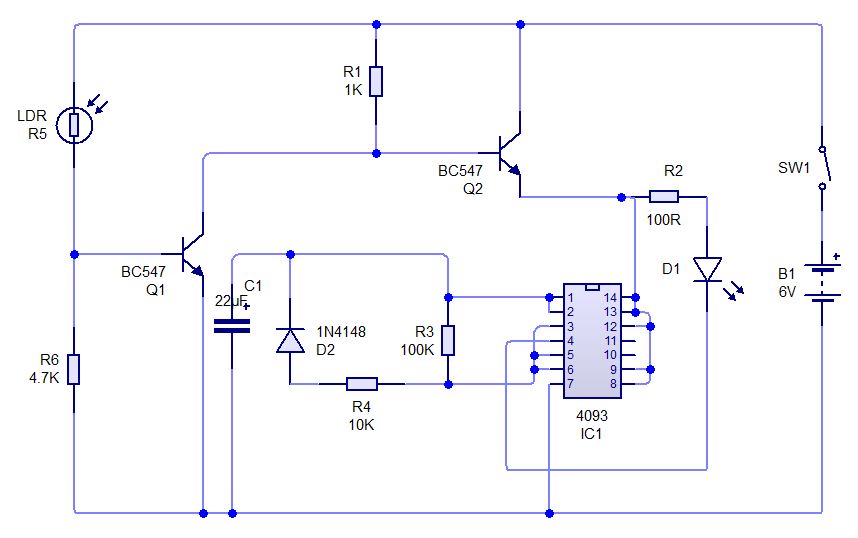
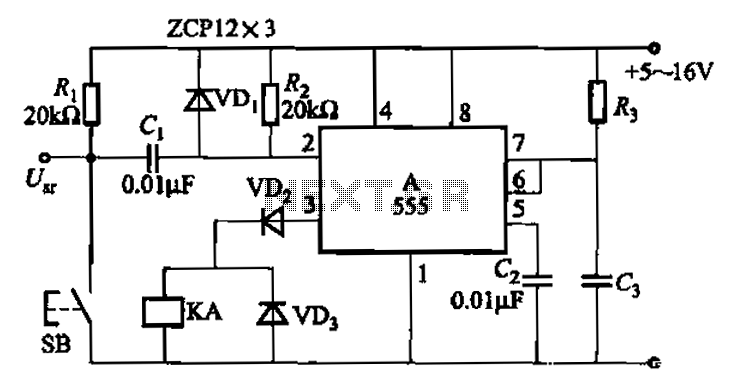
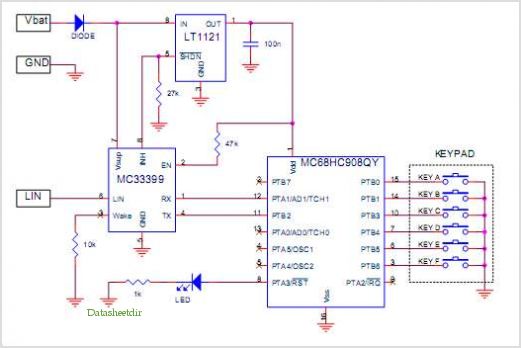
1.5V LED FLasher Using 3 Transistors
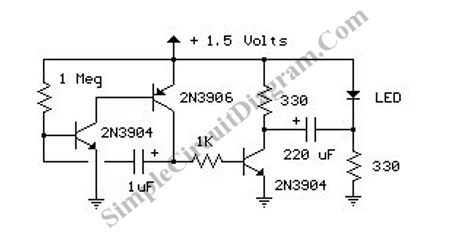
To make an LED function, a voltage source is required that exceeds the LED's forward bias voltage, which is typically greater than 1.5V (approximately 2V for red LEDs).
To effectively operate an LED, it is essential to provide a voltage source that meets or exceeds the forward bias voltage of the LED. This forward bias voltage is the minimum voltage required for the LED to conduct electricity and emit light. For standard red LEDs, this forward voltage is around 2V, although it can vary slightly depending on the specific LED model and manufacturer.
When designing a circuit to power an LED, it is important to include a current-limiting resistor in series with the LED. This resistor protects the LED from excessive current, which can lead to thermal failure and permanent damage. The value of the resistor can be calculated using Ohm's Law, taking into account the supply voltage (Vs), the forward voltage of the LED (Vf), and the desired forward current (If) through the LED.
The formula for calculating the resistor value (R) is as follows:
R = (Vs - Vf) / If
Where:
- R is the resistance in ohms (Ω),
- Vs is the supply voltage in volts (V),
- Vf is the forward voltage of the LED in volts (V),
- If is the desired forward current in amperes (A).
For example, if a 9V power supply is used to power a red LED with a forward voltage of 2V and a desired current of 20mA (0.02A), the resistor value would be calculated as:
R = (9V - 2V) / 0.02A = 350Ω
In this case, a standard resistor value of 360Ω could be used, which would provide adequate current limiting for the LED.
It is also important to consider the power rating of the resistor. The power dissipated by the resistor can be calculated using the formula:
P = I^2 * R
Where P is the power in watts (W), I is the current in amperes (A), and R is the resistance in ohms (Ω). For the previous example, the power dissipated by the resistor would be:
P = (0.02A)^2 * 360Ω = 0.144W
A resistor with a power rating of at least 0.25W would be suitable for this application, providing a safe margin above the calculated power dissipation.
In summary, to successfully operate an LED, it is crucial to select an appropriate voltage source that exceeds the LED's forward bias voltage, incorporate a current-limiting resistor to protect the LED from excess current, and ensure that the resistor's power rating is adequate for the application.To make LED works, you need a voltage source that is higher than the LED`s forward bias voltage, and it`s higher that 1.5V (around 2V for red LEDs).. 🔗 External reference
To effectively operate an LED, it is essential to provide a voltage source that meets or exceeds the forward bias voltage of the LED. This forward bias voltage is the minimum voltage required for the LED to conduct electricity and emit light. For standard red LEDs, this forward voltage is around 2V, although it can vary slightly depending on the specific LED model and manufacturer.
When designing a circuit to power an LED, it is important to include a current-limiting resistor in series with the LED. This resistor protects the LED from excessive current, which can lead to thermal failure and permanent damage. The value of the resistor can be calculated using Ohm's Law, taking into account the supply voltage (Vs), the forward voltage of the LED (Vf), and the desired forward current (If) through the LED.
The formula for calculating the resistor value (R) is as follows:
R = (Vs - Vf) / If
Where:
- R is the resistance in ohms (Ω),
- Vs is the supply voltage in volts (V),
- Vf is the forward voltage of the LED in volts (V),
- If is the desired forward current in amperes (A).
For example, if a 9V power supply is used to power a red LED with a forward voltage of 2V and a desired current of 20mA (0.02A), the resistor value would be calculated as:
R = (9V - 2V) / 0.02A = 350Ω
In this case, a standard resistor value of 360Ω could be used, which would provide adequate current limiting for the LED.
It is also important to consider the power rating of the resistor. The power dissipated by the resistor can be calculated using the formula:
P = I^2 * R
Where P is the power in watts (W), I is the current in amperes (A), and R is the resistance in ohms (Ω). For the previous example, the power dissipated by the resistor would be:
P = (0.02A)^2 * 360Ω = 0.144W
A resistor with a power rating of at least 0.25W would be suitable for this application, providing a safe margin above the calculated power dissipation.
In summary, to successfully operate an LED, it is crucial to select an appropriate voltage source that exceeds the LED's forward bias voltage, incorporate a current-limiting resistor to protect the LED from excess current, and ensure that the resistor's power rating is adequate for the application.To make LED works, you need a voltage source that is higher than the LED`s forward bias voltage, and it`s higher that 1.5V (around 2V for red LEDs).. 🔗 External reference