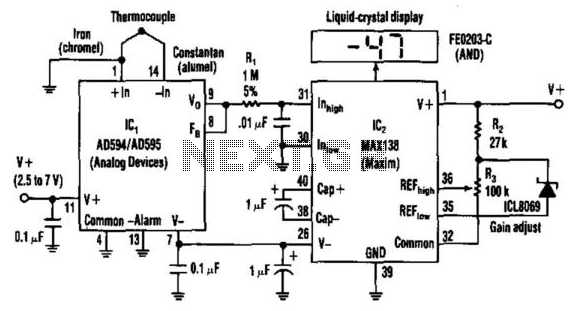
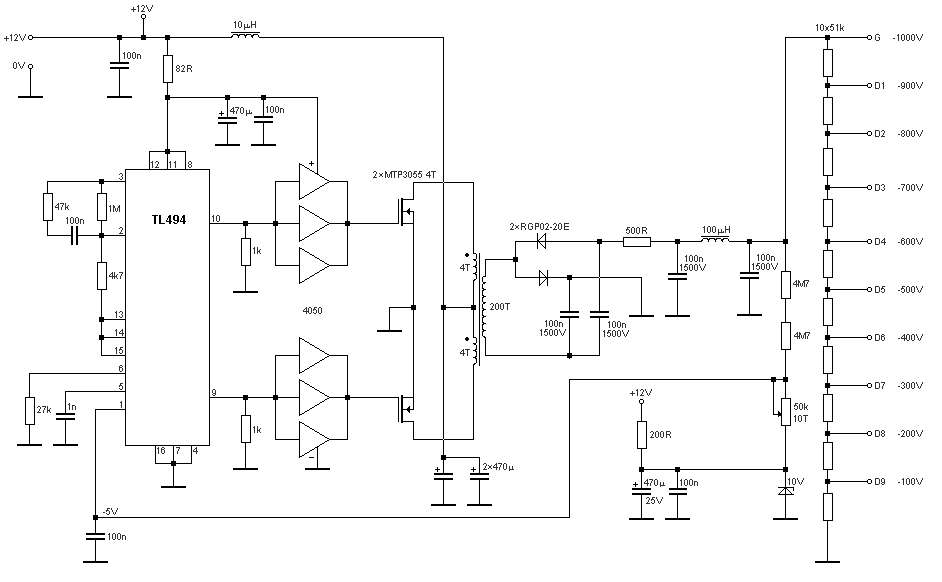
10000Vdc Supply
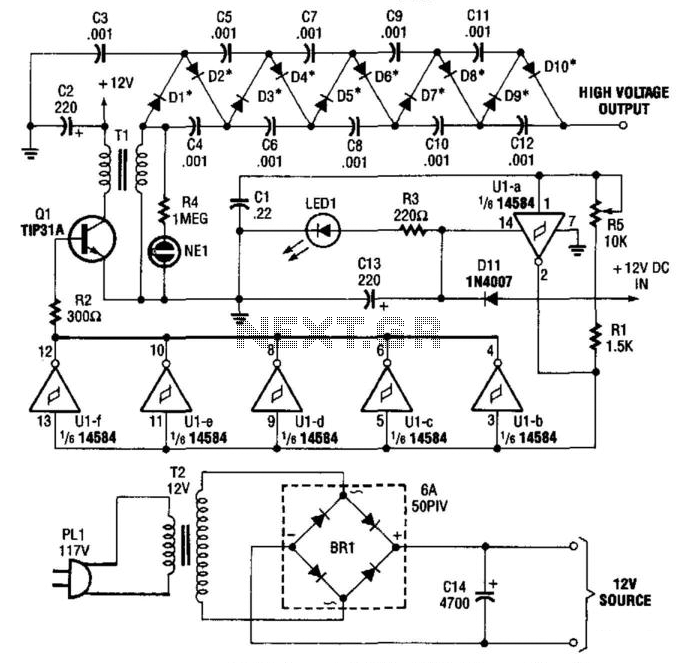
A CMOS oscillator (U1A) drives U1B through U1F, which in turn drives Q1, generating a 12-Vpp square wave across the primary of T1. This square wave is applied to a rectifier-multiplier circuit consisting of diodes D1 through D10 (each comprising two 1N4007 diodes in series) and capacitors C3 through C12. Approximately 10 kV is available.
The circuit described features a CMOS oscillator (U1A) that serves as the primary frequency generator. This oscillator produces a square wave output, which is characterized by its 12-V peak-to-peak (Vpp) amplitude. The output from U1A is fed into multiple stages (U1B through U1F), which function as amplifiers or buffers to ensure the signal maintains its integrity while driving the next stage of the circuit.
The amplified square wave is then used to energize a transformer (T1). The primary winding of T1 receives the square wave input, and due to the transformer's inductive properties, it generates a higher voltage in the secondary winding. This is a critical step for applications requiring high-voltage outputs.
The output from the transformer is then directed to a rectifier-multiplier circuit composed of diodes D1 through D10, where each diode is arranged in series pairs of 1N4007. This configuration is designed to efficiently convert the alternating current (AC) square wave into a direct current (DC) voltage. The rectification process is augmented by the use of capacitors C3 through C12, which are strategically placed to smooth and store the resultant DC voltage.
The combination of the rectifier and multiplier stages allows the circuit to achieve an output voltage of approximately 10 kV. This high-voltage output is suitable for various applications, including but not limited to, high-voltage power supplies, ionization devices, and other electronic applications requiring significant voltage levels. The careful selection of components and their arrangement within the circuit ensures reliability and performance in high-voltage scenarios. A CMOS oscillator (U1A) drives. U1B through U1F, which drives Ql, which generates a 12-Vpp square wave across the primary of Tl. This square wave is applied to a rectifier-multiplier circuit consisting of Dl through D10 (each is two 1N4007 diodes in series) and C3 through C12. About 10 kV is available. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described features a CMOS oscillator (U1A) that serves as the primary frequency generator. This oscillator produces a square wave output, which is characterized by its 12-V peak-to-peak (Vpp) amplitude. The output from U1A is fed into multiple stages (U1B through U1F), which function as amplifiers or buffers to ensure the signal maintains its integrity while driving the next stage of the circuit.
The amplified square wave is then used to energize a transformer (T1). The primary winding of T1 receives the square wave input, and due to the transformer's inductive properties, it generates a higher voltage in the secondary winding. This is a critical step for applications requiring high-voltage outputs.
The output from the transformer is then directed to a rectifier-multiplier circuit composed of diodes D1 through D10, where each diode is arranged in series pairs of 1N4007. This configuration is designed to efficiently convert the alternating current (AC) square wave into a direct current (DC) voltage. The rectification process is augmented by the use of capacitors C3 through C12, which are strategically placed to smooth and store the resultant DC voltage.
The combination of the rectifier and multiplier stages allows the circuit to achieve an output voltage of approximately 10 kV. This high-voltage output is suitable for various applications, including but not limited to, high-voltage power supplies, ionization devices, and other electronic applications requiring significant voltage levels. The careful selection of components and their arrangement within the circuit ensures reliability and performance in high-voltage scenarios. A CMOS oscillator (U1A) drives. U1B through U1F, which drives Ql, which generates a 12-Vpp square wave across the primary of Tl. This square wave is applied to a rectifier-multiplier circuit consisting of Dl through D10 (each is two 1N4007 diodes in series) and C3 through C12. About 10 kV is available. 🔗 External reference