100W 420-450Mhz push-pull linear amplifier
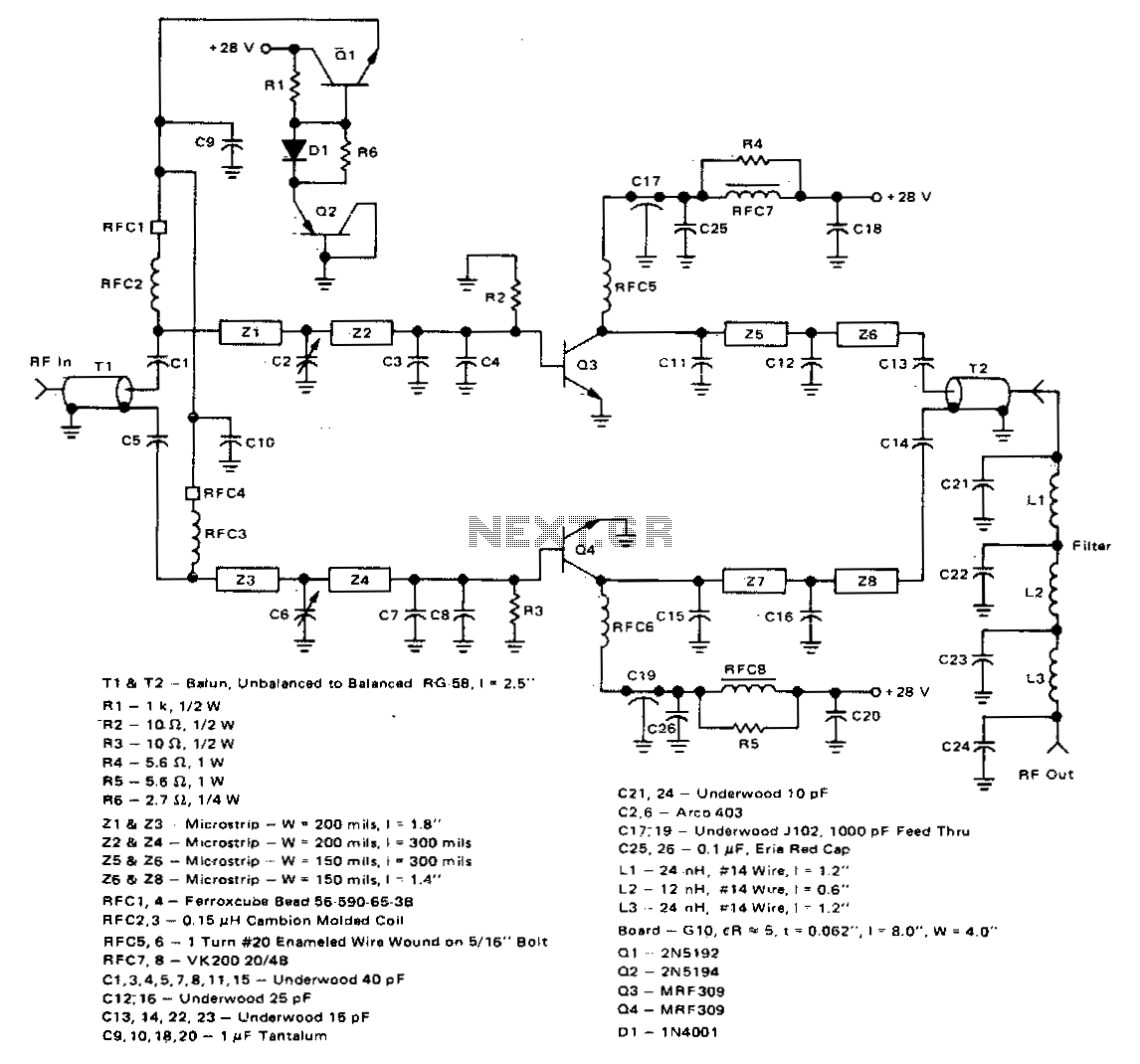
This 100-watt linear amplifier can be built using two MRF309 transistors in a push-pull configuration, requiring only 16 watts of drive power within the frequency range of 420 to 450 MHz. It operates from a 28-volt supply and achieves eight dB of power gain, providing excellent practical performance. Notable features include a maximum input SWR of 2:1, harmonic suppression exceeding -63 dB at 100 watts output, an efficiency greater than 40%, and circuit stability with a 3:1 collector mismatch across all phase angles.
The 100-watt linear amplifier designed with two MRF309 transistors in a push-pull configuration presents a robust solution for RF amplification. The use of MRF309 transistors is advantageous due to their high-frequency capabilities and power-handling characteristics, making them suitable for applications within the specified frequency range of 420 to 450 MHz.
The amplifier requires a modest input drive of only 16 watts, which is efficient for achieving the desired output power of 100 watts. This low drive requirement helps in minimizing the overall power consumption and heat generation, contributing to a more reliable operation.
Operating at a supply voltage of 28 volts, the amplifier achieves a power gain of eight dB. This level of gain is sufficient for many RF applications, ensuring that the output signal is significantly amplified while maintaining signal integrity. The design also incorporates features that enhance performance, such as a maximum input standing wave ratio (SWR) of 2:1, which indicates good impedance matching and minimizes signal reflections that could lead to inefficiencies.
Harmonic suppression is another critical specification, with the amplifier providing suppression levels greater than -63 dB at the 100-watt output level. This feature is essential for reducing unwanted emissions and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards for spectral purity in RF transmission.
Furthermore, the amplifier exhibits an efficiency greater than 40%, indicating that a substantial portion of the input power is converted to output power, which is crucial for minimizing operational costs and thermal management. The circuit also demonstrates stability under varying load conditions, with the ability to handle a 3:1 collector mismatch at all phase angles. This characteristic is particularly important in real-world applications where load conditions may fluctuate, ensuring reliable and consistent performance of the amplifier across its operating range.
Overall, this linear amplifier design combines efficiency, power gain, and stability, making it suitable for various RF applications.This 100 watt linear amplifier may be constructed using two MRF309 transistors in push-pull, requiring only 16 watts drive from 420 to 450 MHz Operating from a 28 volt supply, eight dB of power gain is achieved along with excellent practical performance featuring: maximum input SWR of 2:1, harmonic suppression more than—63 dB below 100 watts output, efficiency greater than 40%, circuit stability with a 3:1 collector mismatch at all phase angles. 🔗 External reference
The 100-watt linear amplifier designed with two MRF309 transistors in a push-pull configuration presents a robust solution for RF amplification. The use of MRF309 transistors is advantageous due to their high-frequency capabilities and power-handling characteristics, making them suitable for applications within the specified frequency range of 420 to 450 MHz.
The amplifier requires a modest input drive of only 16 watts, which is efficient for achieving the desired output power of 100 watts. This low drive requirement helps in minimizing the overall power consumption and heat generation, contributing to a more reliable operation.
Operating at a supply voltage of 28 volts, the amplifier achieves a power gain of eight dB. This level of gain is sufficient for many RF applications, ensuring that the output signal is significantly amplified while maintaining signal integrity. The design also incorporates features that enhance performance, such as a maximum input standing wave ratio (SWR) of 2:1, which indicates good impedance matching and minimizes signal reflections that could lead to inefficiencies.
Harmonic suppression is another critical specification, with the amplifier providing suppression levels greater than -63 dB at the 100-watt output level. This feature is essential for reducing unwanted emissions and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards for spectral purity in RF transmission.
Furthermore, the amplifier exhibits an efficiency greater than 40%, indicating that a substantial portion of the input power is converted to output power, which is crucial for minimizing operational costs and thermal management. The circuit also demonstrates stability under varying load conditions, with the ability to handle a 3:1 collector mismatch at all phase angles. This characteristic is particularly important in real-world applications where load conditions may fluctuate, ensuring reliable and consistent performance of the amplifier across its operating range.
Overall, this linear amplifier design combines efficiency, power gain, and stability, making it suitable for various RF applications.This 100 watt linear amplifier may be constructed using two MRF309 transistors in push-pull, requiring only 16 watts drive from 420 to 450 MHz Operating from a 28 volt supply, eight dB of power gain is achieved along with excellent practical performance featuring: maximum input SWR of 2:1, harmonic suppression more than—63 dB below 100 watts output, efficiency greater than 40%, circuit stability with a 3:1 collector mismatch at all phase angles. 🔗 External reference