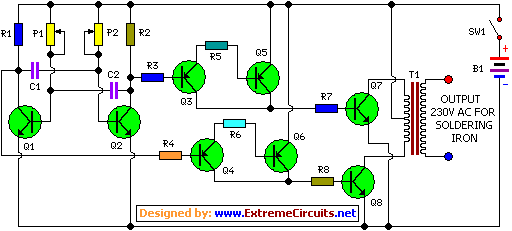
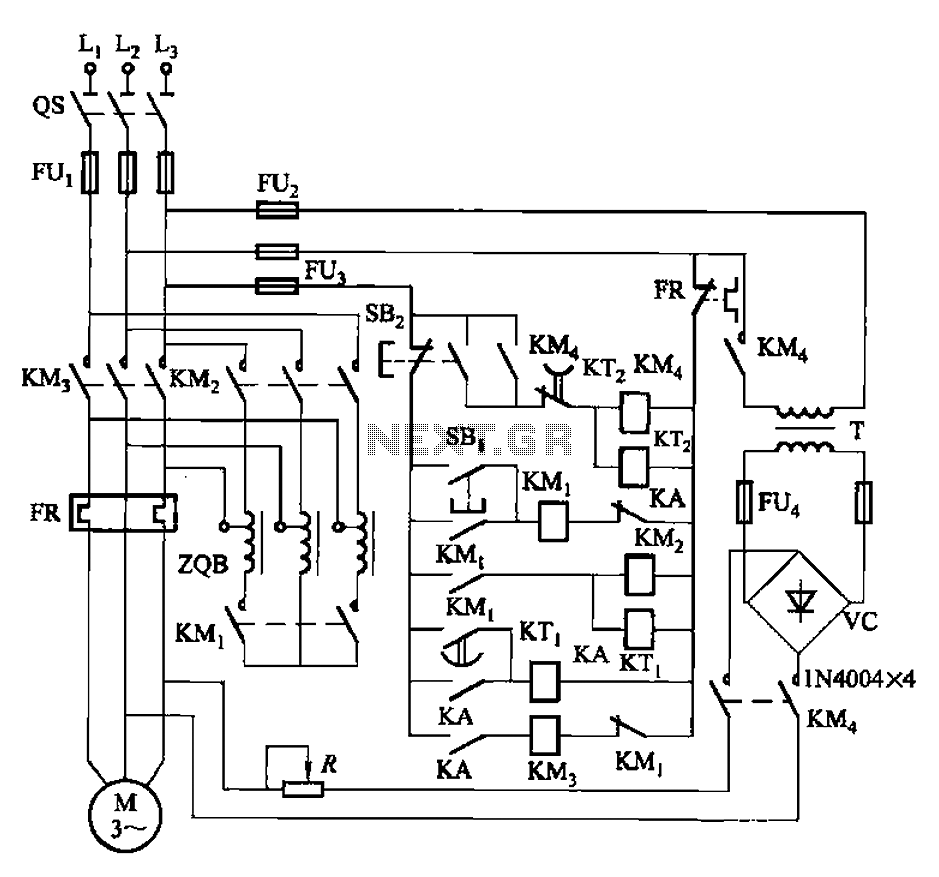
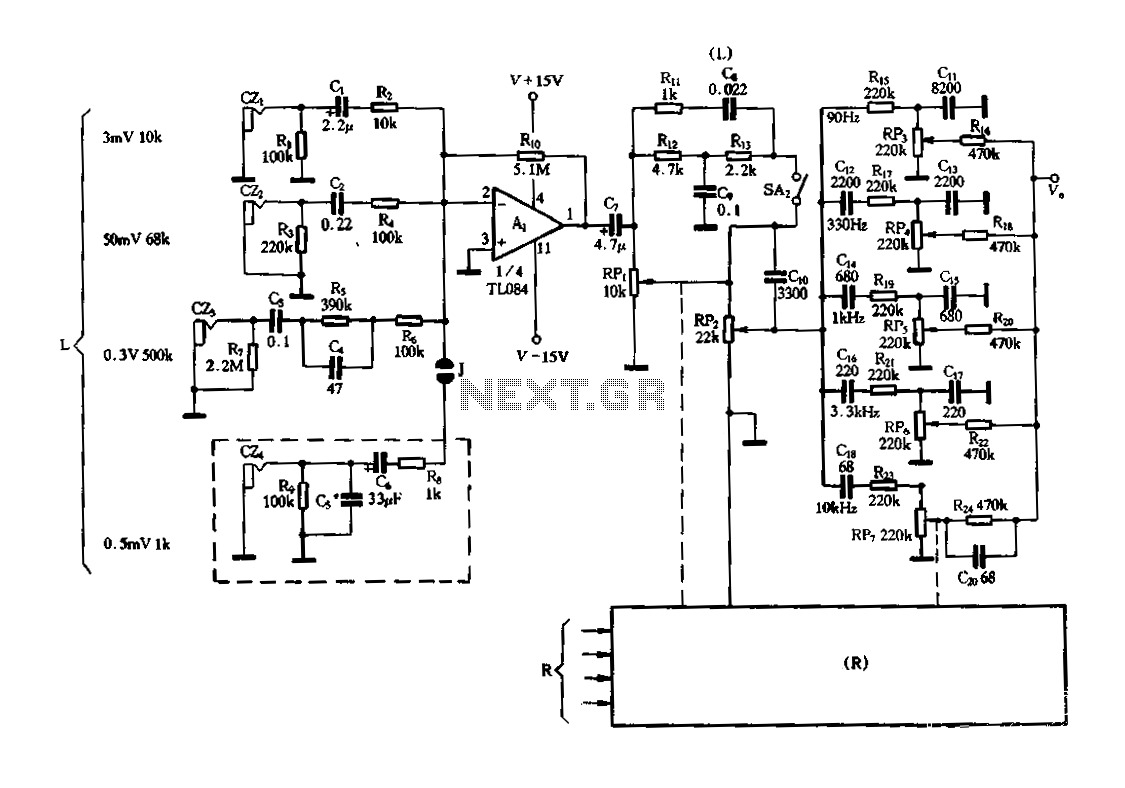
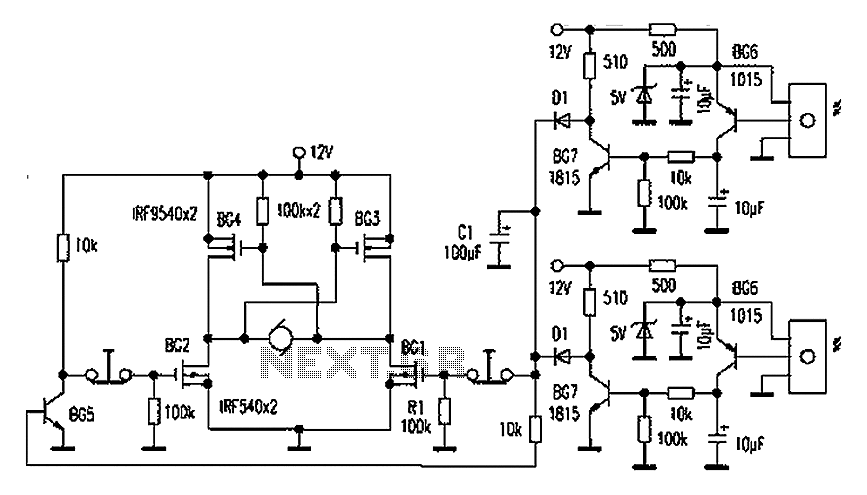
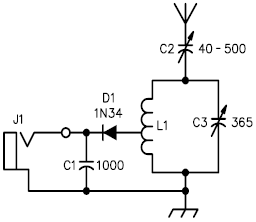
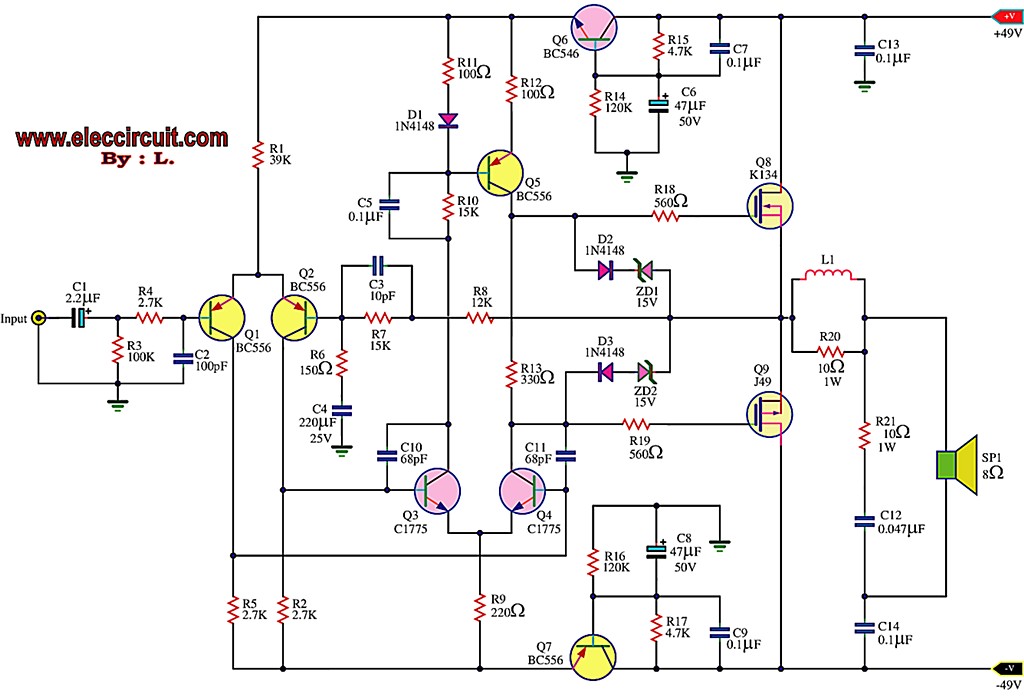
High-precision high-impedance instrument OPA2111 amplifier circuit

This document illustrates the configuration of the high-precision, high-impedance OPA2111 amplifier. The total voltage circuit is designed for a magnification of Av = 10 (1 + 2R2 / R1), achieving a total gain of 1000 times. A gain stage of 10 in the differential amplifier circuit is utilized to extend the input common-mode voltage range of the instrumentation amplifier to 10V.
The OPA2111 is a precision operational amplifier characterized by its low noise and high input impedance, making it suitable for applications requiring accurate signal amplification. The configuration described utilizes a differential amplifier setup, which is essential for rejecting common-mode signals while amplifying the desired differential signal.
In this circuit, the gain is determined by the resistors R1 and R2, with the formula for voltage gain being Av = 10 (1 + 2R2 / R1). This configuration allows for a significant amplification factor of 1000, which is beneficial in applications where signal levels are low and need to be boosted for further processing or analysis.
The differential amplifier stage enhances the common-mode voltage range, allowing the instrumentation amplifier to handle input signals that may vary significantly without distortion or loss of fidelity. By extending the common-mode input voltage range to 10V, the amplifier can effectively process signals from various sources, including sensors and transducers, which may operate within this voltage range.
Overall, the OPA2111 amplifier configuration presented is an effective solution for applications requiring high precision and high input impedance, ensuring accurate signal amplification while maintaining the integrity of the input signal.Shown for the high-precision, high-impedance instrument OPA2111 amplifier configuration. Total voltage circuit illustrated magnification Av = 10 (1 + 2R2 / R1) = 1000 times. A gain stage 10 of the differential amplifier circuit is to expand the instrumentation amplifiers input common-mode voltage range of 10V.
The OPA2111 is a precision operational amplifier characterized by its low noise and high input impedance, making it suitable for applications requiring accurate signal amplification. The configuration described utilizes a differential amplifier setup, which is essential for rejecting common-mode signals while amplifying the desired differential signal.
In this circuit, the gain is determined by the resistors R1 and R2, with the formula for voltage gain being Av = 10 (1 + 2R2 / R1). This configuration allows for a significant amplification factor of 1000, which is beneficial in applications where signal levels are low and need to be boosted for further processing or analysis.
The differential amplifier stage enhances the common-mode voltage range, allowing the instrumentation amplifier to handle input signals that may vary significantly without distortion or loss of fidelity. By extending the common-mode input voltage range to 10V, the amplifier can effectively process signals from various sources, including sensors and transducers, which may operate within this voltage range.
Overall, the OPA2111 amplifier configuration presented is an effective solution for applications requiring high precision and high input impedance, ensuring accurate signal amplification while maintaining the integrity of the input signal.Shown for the high-precision, high-impedance instrument OPA2111 amplifier configuration. Total voltage circuit illustrated magnification Av = 10 (1 + 2R2 / R1) = 1000 times. A gain stage 10 of the differential amplifier circuit is to expand the instrumentation amplifiers input common-mode voltage range of 10V.