12 Volt Lead Acid Battery Meter Led
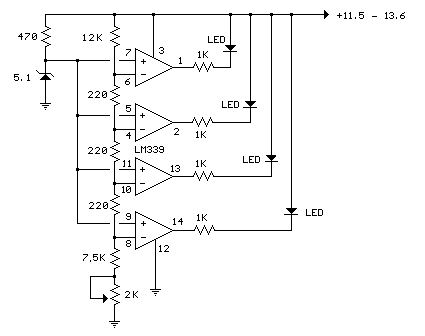
In the circuit below, a quad voltage comparator (LM339) is utilized as a simple bar graph meter to indicate the charge condition of a 12-volt lead-acid battery. A 5-volt reference voltage is connected to each of the positive inputs of the four comparators, while the negative inputs are connected to successive points along a voltage divider. The LEDs will illuminate when the voltage at the negative input exceeds the reference voltage. Calibration can be performed by adjusting the 2K potentiometer so that all four LEDs light up when the battery voltage reaches 12.7 volts, indicating a full charge without any load on the battery. At 11.7 volts, the LEDs should be off, signaling a dead battery. Each LED represents an approximate 25% change in charge condition or 300 millivolts; therefore, three LEDs indicate 75%, two LEDs indicate 50%, and so forth. The actual voltages will depend on temperature conditions and battery type, such as wet cell or gel cell.
The circuit employs the LM339 quad voltage comparator, which consists of four independent, high-speed voltage comparators. The comparators are configured to compare the voltage levels from the battery and a reference voltage. The reference voltage is established at 5 volts, serving as a threshold for the comparators. The voltage divider, composed of resistors, divides the battery voltage into smaller voltages that are fed into the negative inputs of the comparators.
When the battery voltage exceeds the reference voltage at the negative input, the output of the comparator goes low, turning on the corresponding LED. This configuration allows for a visual representation of the battery's charge status, with each LED indicating a specific range of battery voltage. The calibration process involves adjusting a potentiometer to ensure that the system accurately reflects the battery's state of charge.
The use of a 2K potentiometer provides a means to fine-tune the threshold levels at which the LEDs activate. This is crucial for ensuring that the bar graph meter accurately reflects the battery's voltage levels. The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating temperature compensation, which would adjust the reference voltage based on the ambient temperature, thereby improving accuracy across different operating conditions.
In practical applications, this circuit can be used in various battery-powered devices to monitor battery health, providing users with a simple and effective means to assess battery status. The design is flexible enough to accommodate different types of lead-acid batteries, ensuring broad applicability. Additional considerations may include implementing protection circuits to prevent over-discharge of the battery, which could extend the battery's lifespan and maintain its performance.In the circuit below, a quad voltage comparator (LM339) is used as a simple bar graph meter to indicate the charge condition of a 12 volt, lead acid battery. A 5 volt reference voltage is connected to each of the (+) inputs of the four comparators and the (-) inputs are connected to successive points along a voltage divider.
The LEDs will illumina te when the voltage at the negative (-) input exceeds the reference voltage. Calibration can be done by adjusting the 2K potentiometer so that all four LEDs illuminate when the battery voltage is 12. 7 volts, indicating full charge with no load on the battery. At 11. 7 volts, the LEDs should be off indicating a dead battery. Each LED represents an approximate 25% change in charge condition or 300 millivolts, so that 3 LEDs indicate 75%, 2 LEDs indicate 50%, etc.
The actual voltages will depend on temperature conditions and battery type, wet cell, gel cell etc. Additional information on battery maintenance can be found at: 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs the LM339 quad voltage comparator, which consists of four independent, high-speed voltage comparators. The comparators are configured to compare the voltage levels from the battery and a reference voltage. The reference voltage is established at 5 volts, serving as a threshold for the comparators. The voltage divider, composed of resistors, divides the battery voltage into smaller voltages that are fed into the negative inputs of the comparators.
When the battery voltage exceeds the reference voltage at the negative input, the output of the comparator goes low, turning on the corresponding LED. This configuration allows for a visual representation of the battery's charge status, with each LED indicating a specific range of battery voltage. The calibration process involves adjusting a potentiometer to ensure that the system accurately reflects the battery's state of charge.
The use of a 2K potentiometer provides a means to fine-tune the threshold levels at which the LEDs activate. This is crucial for ensuring that the bar graph meter accurately reflects the battery's voltage levels. The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating temperature compensation, which would adjust the reference voltage based on the ambient temperature, thereby improving accuracy across different operating conditions.
In practical applications, this circuit can be used in various battery-powered devices to monitor battery health, providing users with a simple and effective means to assess battery status. The design is flexible enough to accommodate different types of lead-acid batteries, ensuring broad applicability. Additional considerations may include implementing protection circuits to prevent over-discharge of the battery, which could extend the battery's lifespan and maintain its performance.In the circuit below, a quad voltage comparator (LM339) is used as a simple bar graph meter to indicate the charge condition of a 12 volt, lead acid battery. A 5 volt reference voltage is connected to each of the (+) inputs of the four comparators and the (-) inputs are connected to successive points along a voltage divider.
The LEDs will illumina te when the voltage at the negative (-) input exceeds the reference voltage. Calibration can be done by adjusting the 2K potentiometer so that all four LEDs illuminate when the battery voltage is 12. 7 volts, indicating full charge with no load on the battery. At 11. 7 volts, the LEDs should be off indicating a dead battery. Each LED represents an approximate 25% change in charge condition or 300 millivolts, so that 3 LEDs indicate 75%, 2 LEDs indicate 50%, etc.
The actual voltages will depend on temperature conditions and battery type, wet cell, gel cell etc. Additional information on battery maintenance can be found at: 🔗 External reference