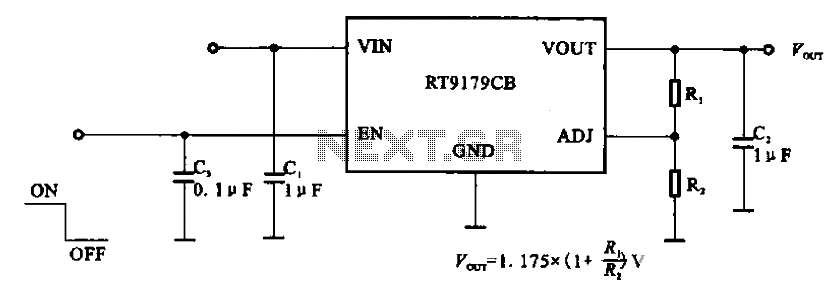
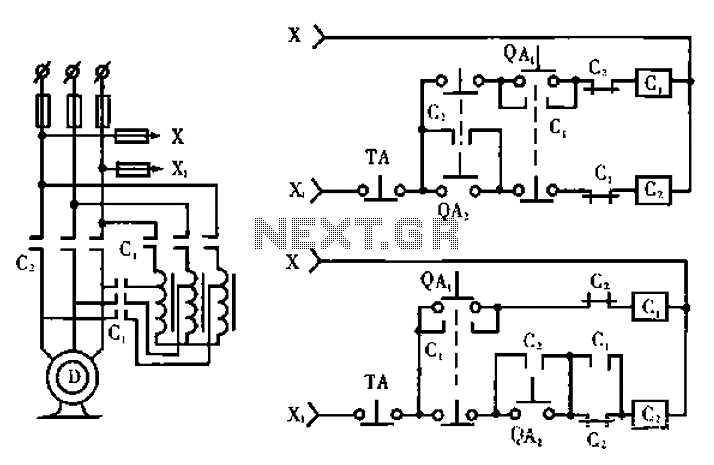
±15V or ±12V Output Switch-Mode Power Supply Has Wide Input-Voltage Range
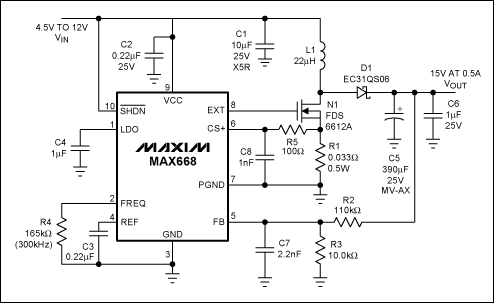
A switch-mode power supply provides ±15V or ±12V at 0.5A output from a 4.5V to 12V input. The wide input voltage range allows flexibility to be powered from a regulated DC voltage.
The switch-mode power supply (SMPS) described operates within a versatile input range of 4.5V to 12V, making it suitable for various applications where power supply flexibility is required. The output voltage options of ±15V or ±12V cater to different circuit requirements, providing a maximum output current of 0.5A.
The design of the SMPS typically includes several key components such as an input filter, a switching transistor, a transformer, a rectifier, and an output filter. The input filter is essential for reducing voltage spikes and electromagnetic interference from the power source. The switching transistor, often a MOSFET, rapidly turns on and off to control the energy transfer to the transformer, which steps up or steps down the voltage as needed.
The transformer is a critical component that isolates the output from the input and helps in voltage conversion. Following the transformer, a rectifier converts the AC voltage back to DC. This stage may utilize diodes or synchronous rectification for improved efficiency. Finally, the output filter smooths the rectified voltage, ensuring that the output is stable and free from ripple.
The wide input voltage range of the SMPS allows it to be powered from various regulated DC sources, making it adaptable for use in different environments and applications. This versatility is particularly beneficial in portable devices, industrial equipment, and communication systems, where power supply requirements may vary significantly.
Overall, the switch-mode power supply design emphasizes efficiency, compactness, and adaptability, making it an essential component in modern electronic systems.A switch-mode power supply provides ±15V or ±12V @ 0.5A output from a 4.5V to 12V input Wide input voltage range allows flexibility to be powered from a regulated DC voltage.. 🔗 External reference
The switch-mode power supply (SMPS) described operates within a versatile input range of 4.5V to 12V, making it suitable for various applications where power supply flexibility is required. The output voltage options of ±15V or ±12V cater to different circuit requirements, providing a maximum output current of 0.5A.
The design of the SMPS typically includes several key components such as an input filter, a switching transistor, a transformer, a rectifier, and an output filter. The input filter is essential for reducing voltage spikes and electromagnetic interference from the power source. The switching transistor, often a MOSFET, rapidly turns on and off to control the energy transfer to the transformer, which steps up or steps down the voltage as needed.
The transformer is a critical component that isolates the output from the input and helps in voltage conversion. Following the transformer, a rectifier converts the AC voltage back to DC. This stage may utilize diodes or synchronous rectification for improved efficiency. Finally, the output filter smooths the rectified voltage, ensuring that the output is stable and free from ripple.
The wide input voltage range of the SMPS allows it to be powered from various regulated DC sources, making it adaptable for use in different environments and applications. This versatility is particularly beneficial in portable devices, industrial equipment, and communication systems, where power supply requirements may vary significantly.
Overall, the switch-mode power supply design emphasizes efficiency, compactness, and adaptability, making it an essential component in modern electronic systems.A switch-mode power supply provides ±15V or ±12V @ 0.5A output from a 4.5V to 12V input Wide input voltage range allows flexibility to be powered from a regulated DC voltage.. 🔗 External reference