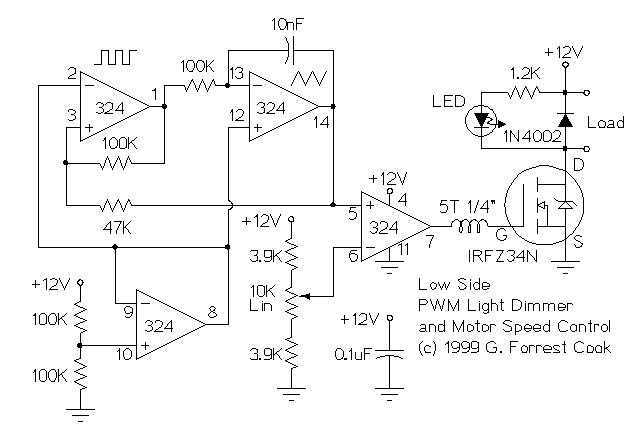
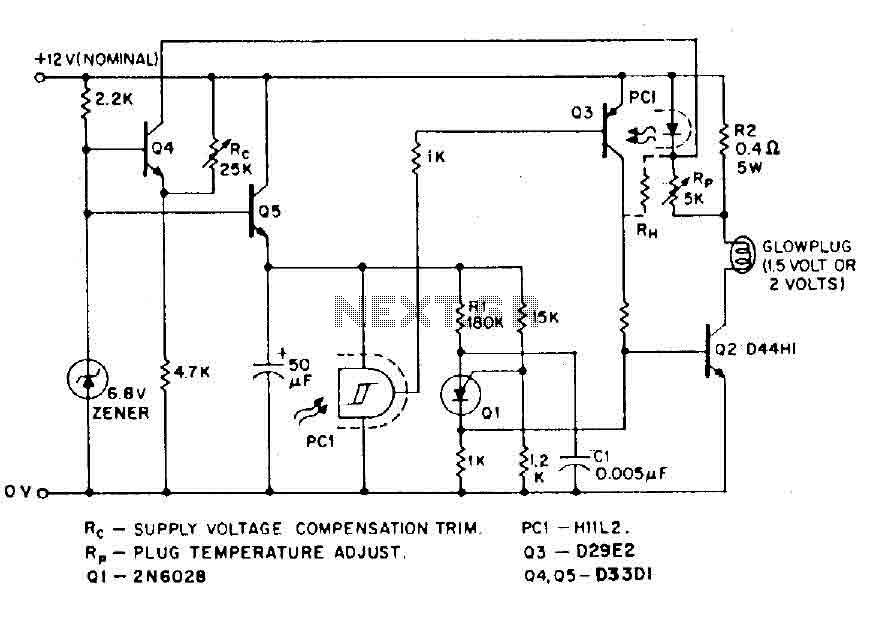
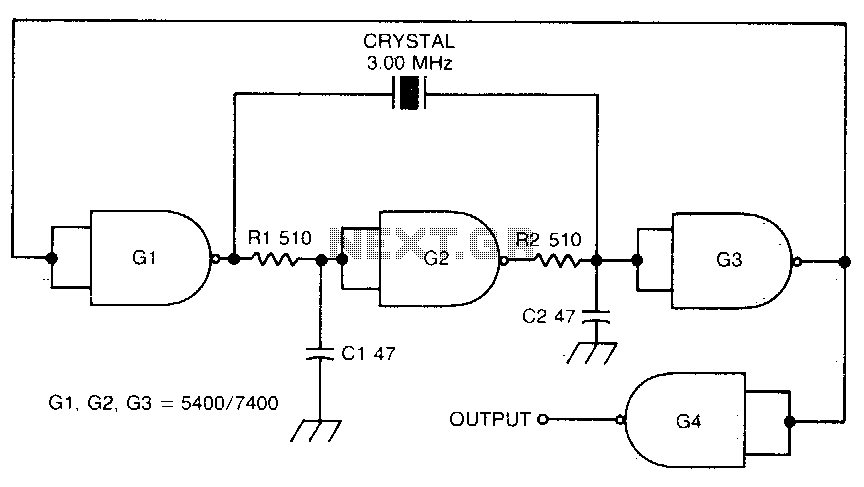
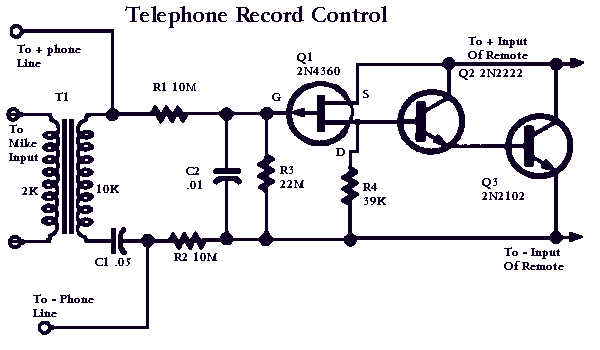
High-power motor control circuit summary
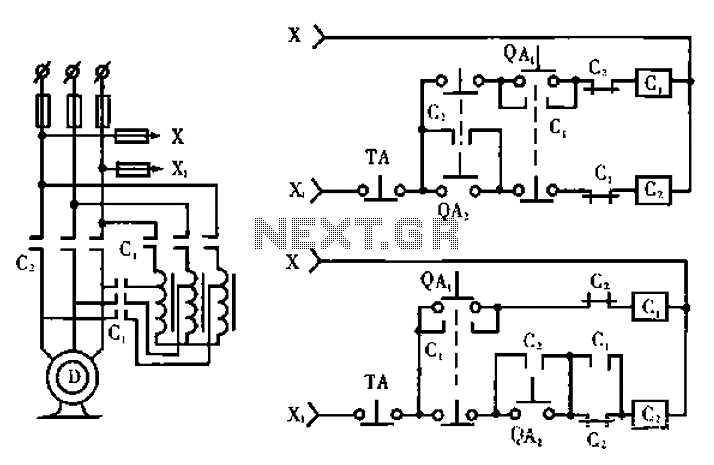
The circuit operates with relevant components highlighted in the manual's draw mode. Figure A presents a circuit schematic, while Figure B illustrates a typical conventional secondary circuit layout. Figure E showcases an improved secondary circuit schematic diagram that incorporates mandatory program features. Initially, the conventional secondary circuit, as depicted in Figure B, appears to function well, a fact familiar to many operators. However, variations in operator quality can lead to issues, particularly if an operator mistakenly presses the start button. According to the principle illustrated in Figure B, pressing the QAz start button initiates the device based on a predefined procedure. However, improper use can cause the contactor C to engage, resulting in a direct start condition. This situation can lead to excessive starting current, potentially damaging the equipment. Therefore, the circuit design in Figure C has been developed to effectively prevent such accidents.
The schematic circuit design presented in Figure C incorporates several protective features aimed at enhancing operational safety and reliability. The circuit utilizes a combination of relays, timers, and interlocks to ensure that the device only starts under the correct conditions.
The circuit begins with the QAz start button, which is connected to a relay that only energizes if certain preconditions are met. This includes checks for the operational state of the machine and the status of other safety interlocks. If these conditions are satisfied, the relay activates, allowing current to flow through the main contactor C, which then engages the motor or load.
To prevent accidental engagement, the circuit includes a delay timer that ensures the motor does not start immediately upon pressing the start button. This delay allows operators to confirm that all safety measures are in place before the machine begins operation. Additionally, the design features a stop button that can interrupt the power supply to the relay, ensuring that the machine can be safely deactivated at any time.
Furthermore, the circuit employs overload protection mechanisms, which monitor the current draw of the motor. If the current exceeds a predefined threshold, the overload relay will trip, disconnecting power to the motor and preventing damage. This feature is crucial in maintaining the longevity of the equipment and ensuring safe operation.
In summary, the circuit design shown in Figure C not only improves upon the conventional secondary circuit by incorporating mandatory safety features but also addresses the potential risks associated with operator error. By implementing these enhancements, the circuit ensures a more reliable and safer operational environment for electrical devices. Circuit works (only the relevant parts of the manual draw mode): Figure a shows a circuit schematic circuit; Fig. B Typical electricity as conventional secondary circuit road; Fig e shows the improved, with the mandatory nature of the program secondary circuit schematic diagram. Firstly deficiencies of conventional secondary circuit, the circuit in Figure b form, it seems perfectly reasonable, it works we are all familiar.
However, many operators, the quality varies, assuming that the operator of a small mistake by running the button to start the device. B from FIG principle, the press QAz run button, so the device is based on the procedure after the first press starts running through QA, start button, but more than misuse, can make the run contactor C: pull into the work state, becoming a direct start, this time starting current cause great damage to the equipment.
For this reason we designed the circuit shown in Figure c, before it can completely prevent the occurrence of accidents.
The schematic circuit design presented in Figure C incorporates several protective features aimed at enhancing operational safety and reliability. The circuit utilizes a combination of relays, timers, and interlocks to ensure that the device only starts under the correct conditions.
The circuit begins with the QAz start button, which is connected to a relay that only energizes if certain preconditions are met. This includes checks for the operational state of the machine and the status of other safety interlocks. If these conditions are satisfied, the relay activates, allowing current to flow through the main contactor C, which then engages the motor or load.
To prevent accidental engagement, the circuit includes a delay timer that ensures the motor does not start immediately upon pressing the start button. This delay allows operators to confirm that all safety measures are in place before the machine begins operation. Additionally, the design features a stop button that can interrupt the power supply to the relay, ensuring that the machine can be safely deactivated at any time.
Furthermore, the circuit employs overload protection mechanisms, which monitor the current draw of the motor. If the current exceeds a predefined threshold, the overload relay will trip, disconnecting power to the motor and preventing damage. This feature is crucial in maintaining the longevity of the equipment and ensuring safe operation.
In summary, the circuit design shown in Figure C not only improves upon the conventional secondary circuit by incorporating mandatory safety features but also addresses the potential risks associated with operator error. By implementing these enhancements, the circuit ensures a more reliable and safer operational environment for electrical devices. Circuit works (only the relevant parts of the manual draw mode): Figure a shows a circuit schematic circuit; Fig. B Typical electricity as conventional secondary circuit road; Fig e shows the improved, with the mandatory nature of the program secondary circuit schematic diagram. Firstly deficiencies of conventional secondary circuit, the circuit in Figure b form, it seems perfectly reasonable, it works we are all familiar.
However, many operators, the quality varies, assuming that the operator of a small mistake by running the button to start the device. B from FIG principle, the press QAz run button, so the device is based on the procedure after the first press starts running through QA, start button, but more than misuse, can make the run contactor C: pull into the work state, becoming a direct start, this time starting current cause great damage to the equipment.
For this reason we designed the circuit shown in Figure c, before it can completely prevent the occurrence of accidents.