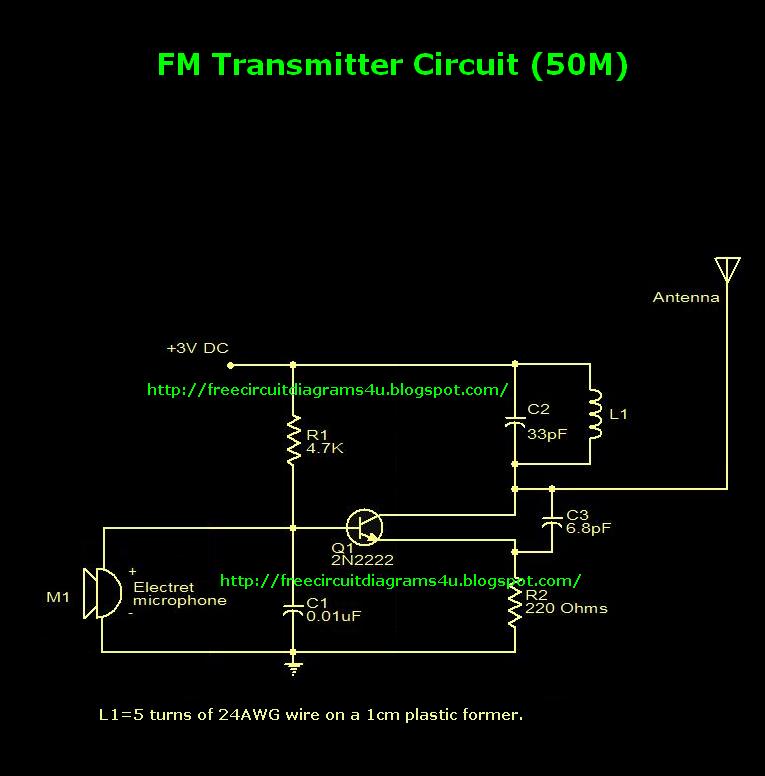
Low Power FM Transmitter
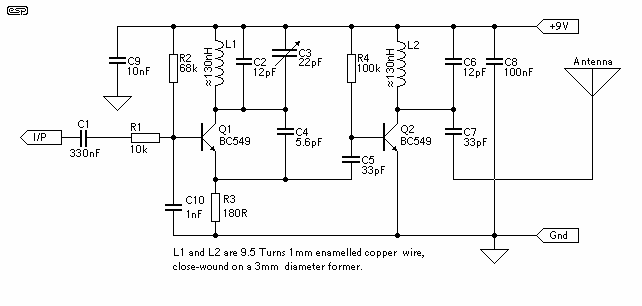
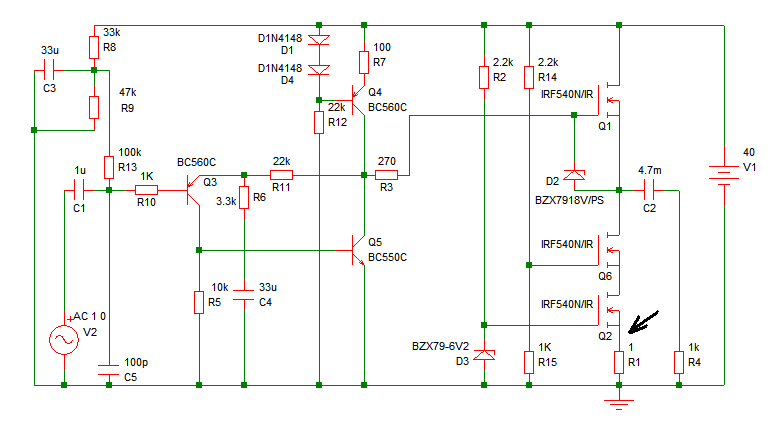
The circuit of the transmitter is shown in Figure 1, and as you can see it is quite simple. The first stage is the oscillator, and is tuned with the variable capacitor. Select an unused frequency, and carefully adjust C3 until the background noise stops (you have to disable the FM receiver's mute circuit to hear this). Because the trimmer cap is very sensitive, make the final frequency adjustment on the receiver. When assembling the circuit, make sure the rotor of C3 is connected to the +9V supply. This ensures that there will be minimal frequency disturbance when the screwdriver touches the adjustment shaft. You can use a small piece of non copper-clad circuit board to make a screwdriver - this will not alter the frequency. The frequency stability is improved considerably by adding a capacitor from the base of Q1 to ground. This ensures that the transistor operates in true common base at RF.
The transmitter circuit described is a straightforward design primarily focused on frequency generation through an oscillator. The oscillator is the first stage, which utilizes a variable capacitor (C3) for tuning. This capacitor allows the user to select a specific frequency by adjusting its capacitance. The process involves selecting an unused frequency and fine-tuning the capacitor until the background noise ceases, which is crucial for effective operation. It is important to disable the mute function of the FM receiver during this adjustment to clearly hear the changes in noise levels.
To ensure stable operation during tuning, it is critical that the rotor of the variable capacitor (C3) is connected to a +9V power supply. This connection minimizes frequency fluctuations that may occur when handling the tuning mechanism, such as when a screwdriver is used for adjustments. A practical tip for making adjustments is to use a non copper-clad circuit board piece as a screwdriver, as this material will not influence the frequency being generated.
Additionally, to enhance frequency stability, a capacitor should be connected from the base of transistor Q1 to ground. This configuration promotes the operation of the transistor in a true common base mode at radio frequencies (RF), which significantly improves the circuit's overall performance and reliability. The careful assembly and tuning of this transmitter circuit will lead to efficient frequency generation suitable for various applications in RF communication.The circuit of the transmitter is shown in Figure 1, and as you can see it is quite simple. The first stage is the oscillator, and is tuned with the variable capacitor. Select an unused frequency, and carefully adjust C3 until the background noise stops (you have to disable the FM receiver`s mute circuit to hear this). Because the trimmer cap is very sensitive, make the final frequency adjustment on the receiver. When assembling the circuit, make sure the rotor of C3 is connected to the +9V supply. This ensures that there will be minimal frequency disturbance when the screwdriver touches the adjustment shaft.
You can use a small piece of non copper-clad circuit board to make a screwdriver - this will not alter the frequency. The frequency stability is improved considerably by adding a capacitor from the base of Q1 to ground.
This ensures that the transistor operates in true common base at RF. 🔗 External reference
The transmitter circuit described is a straightforward design primarily focused on frequency generation through an oscillator. The oscillator is the first stage, which utilizes a variable capacitor (C3) for tuning. This capacitor allows the user to select a specific frequency by adjusting its capacitance. The process involves selecting an unused frequency and fine-tuning the capacitor until the background noise ceases, which is crucial for effective operation. It is important to disable the mute function of the FM receiver during this adjustment to clearly hear the changes in noise levels.
To ensure stable operation during tuning, it is critical that the rotor of the variable capacitor (C3) is connected to a +9V power supply. This connection minimizes frequency fluctuations that may occur when handling the tuning mechanism, such as when a screwdriver is used for adjustments. A practical tip for making adjustments is to use a non copper-clad circuit board piece as a screwdriver, as this material will not influence the frequency being generated.
Additionally, to enhance frequency stability, a capacitor should be connected from the base of transistor Q1 to ground. This configuration promotes the operation of the transistor in a true common base mode at radio frequencies (RF), which significantly improves the circuit's overall performance and reliability. The careful assembly and tuning of this transmitter circuit will lead to efficient frequency generation suitable for various applications in RF communication.The circuit of the transmitter is shown in Figure 1, and as you can see it is quite simple. The first stage is the oscillator, and is tuned with the variable capacitor. Select an unused frequency, and carefully adjust C3 until the background noise stops (you have to disable the FM receiver`s mute circuit to hear this). Because the trimmer cap is very sensitive, make the final frequency adjustment on the receiver. When assembling the circuit, make sure the rotor of C3 is connected to the +9V supply. This ensures that there will be minimal frequency disturbance when the screwdriver touches the adjustment shaft.
You can use a small piece of non copper-clad circuit board to make a screwdriver - this will not alter the frequency. The frequency stability is improved considerably by adding a capacitor from the base of Q1 to ground.
This ensures that the transistor operates in true common base at RF. 🔗 External reference