16 watt amplifier
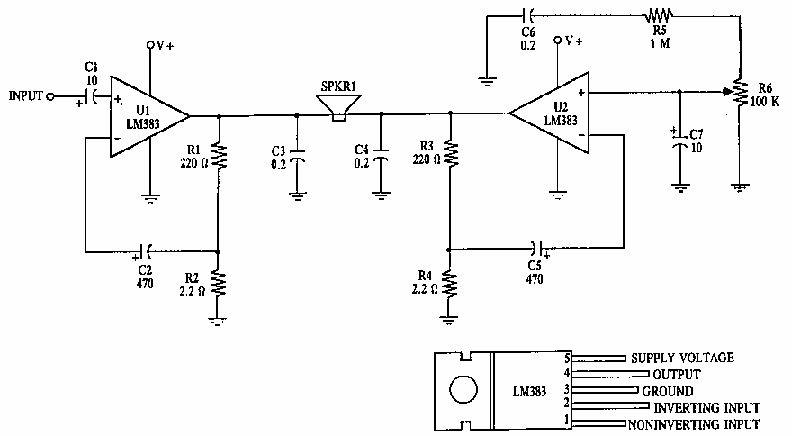
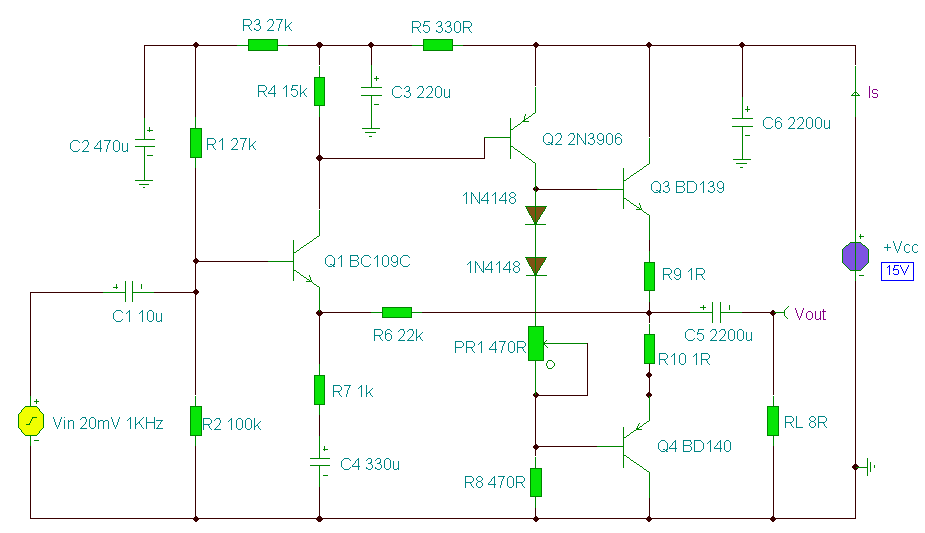
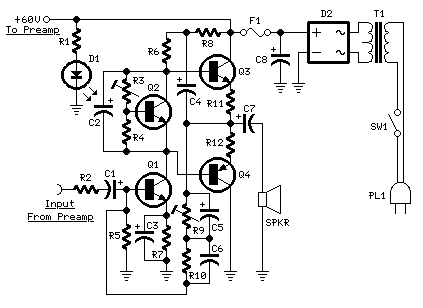
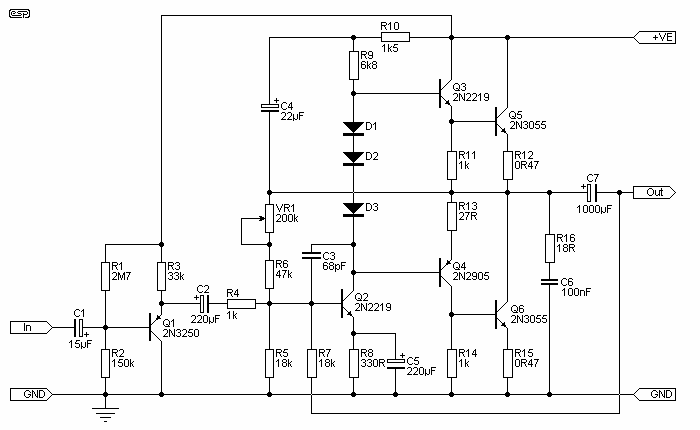
This circuit provides 16 watts of amplification. It is built using two LM383 power audio amplifiers. Use suitable heat sinks with the ICs. More: U1 U2 LM383 8 watt audio amplifier IC R1, R3 220 ohm resistor R2, R4 2.2 ohm resistor R5 1 megohm resistor R6 100k audio taper potentiometer C1, C7 10uf electrolytic capacitor C2, C5 470uf electrolytic capacitor C3, C4, C6 0.2uf ceramic capacitor
The circuit is designed to deliver a total output power of 16 watts, utilizing two LM383 integrated circuits, each capable of providing 8 watts of audio amplification. The LM383 is a power audio amplifier that is known for its reliability and efficiency in audio applications.
In this configuration, U1 and U2 represent the two LM383 amplifiers, which are the heart of the circuit. Each amplifier requires proper thermal management; therefore, it is essential to attach suitable heat sinks to the ICs to prevent overheating during operation.
Resistors R1 and R3 are both 220 ohms, and they are likely used for biasing or feedback purposes within the amplifiers. Resistors R2 and R4, with a value of 2.2 ohms, may serve as current sensing or load resistors, contributing to the stability and performance of the output stage. R5, a 1 megohm resistor, is typically used in audio circuits for input impedance matching or as part of the feedback network to set the gain of the amplifier.
The circuit includes a 100k audio taper potentiometer, R6, which allows for volume control. This potentiometer is essential for user interaction, enabling the adjustment of the output level based on the desired listening volume.
Capacitors play a crucial role in audio circuits for coupling and decoupling signals. Capacitors C1 and C7 are 10 µF electrolytic capacitors, which may be used for coupling the audio signal to the amplifiers, ensuring that only the AC component of the audio signal passes while blocking any DC offset. Capacitors C2 and C5, rated at 470 µF, are likely used for power supply decoupling, providing stability and filtering against voltage fluctuations. Finally, C3, C4, and C6 are 0.2 µF ceramic capacitors, which may be employed for high-frequency bypassing, ensuring that high-frequency noise does not affect the performance of the amplifiers.
The overall design emphasizes audio fidelity and stability, suitable for various audio amplification applications. Proper layout and component selection are critical to achieving the desired performance and reliability in the final circuit implementation.This circuit provides 16 watts of amplification. it is built using two LM383 power audio amplifiers. use suitable heat sinks with the ic`s. U1 U2 LM383 8 watt audio amplifier ic R1, R3 220 ohm resistor R2, R4 2.2 ohm resistor R5 1 megohm resistor R6 100k audio taper potentiometer C1, C7 10uf electrolytic capacitor C2, C5 470uf electrolytic capacitor C3, C4, C6 0.2uf ceramic capacitor 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed to deliver a total output power of 16 watts, utilizing two LM383 integrated circuits, each capable of providing 8 watts of audio amplification. The LM383 is a power audio amplifier that is known for its reliability and efficiency in audio applications.
In this configuration, U1 and U2 represent the two LM383 amplifiers, which are the heart of the circuit. Each amplifier requires proper thermal management; therefore, it is essential to attach suitable heat sinks to the ICs to prevent overheating during operation.
Resistors R1 and R3 are both 220 ohms, and they are likely used for biasing or feedback purposes within the amplifiers. Resistors R2 and R4, with a value of 2.2 ohms, may serve as current sensing or load resistors, contributing to the stability and performance of the output stage. R5, a 1 megohm resistor, is typically used in audio circuits for input impedance matching or as part of the feedback network to set the gain of the amplifier.
The circuit includes a 100k audio taper potentiometer, R6, which allows for volume control. This potentiometer is essential for user interaction, enabling the adjustment of the output level based on the desired listening volume.
Capacitors play a crucial role in audio circuits for coupling and decoupling signals. Capacitors C1 and C7 are 10 µF electrolytic capacitors, which may be used for coupling the audio signal to the amplifiers, ensuring that only the AC component of the audio signal passes while blocking any DC offset. Capacitors C2 and C5, rated at 470 µF, are likely used for power supply decoupling, providing stability and filtering against voltage fluctuations. Finally, C3, C4, and C6 are 0.2 µF ceramic capacitors, which may be employed for high-frequency bypassing, ensuring that high-frequency noise does not affect the performance of the amplifiers.
The overall design emphasizes audio fidelity and stability, suitable for various audio amplification applications. Proper layout and component selection are critical to achieving the desired performance and reliability in the final circuit implementation.This circuit provides 16 watts of amplification. it is built using two LM383 power audio amplifiers. use suitable heat sinks with the ic`s. U1 U2 LM383 8 watt audio amplifier ic R1, R3 220 ohm resistor R2, R4 2.2 ohm resistor R5 1 megohm resistor R6 100k audio taper potentiometer C1, C7 10uf electrolytic capacitor C2, C5 470uf electrolytic capacitor C3, C4, C6 0.2uf ceramic capacitor 🔗 External reference