18 stage led sequencer
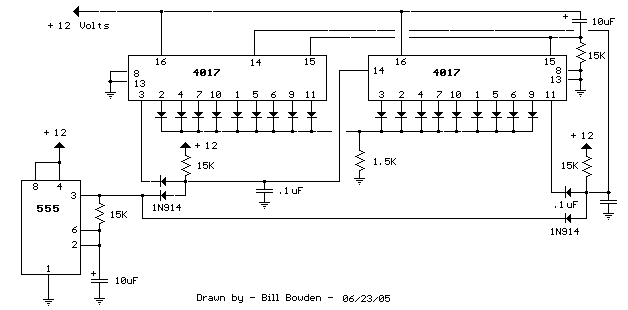
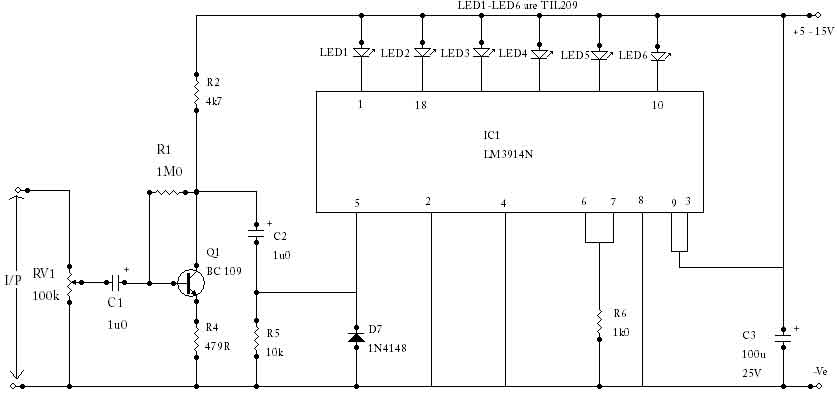
When power is applied, the 15K resistor and 10µF capacitor at pin 15 will reset the counters to a zero count, with pin 3 at +12V and all other outputs at zero. The two diodes (1N914) and a 15Ω resistor form an AND gate, allowing the clock pulse to be passed to the right side counter when the sequence starts.
The circuit described involves a reset mechanism for counters, utilizing a combination of passive and active components to ensure proper initialization upon power-up. The 15KΩ resistor and 10µF capacitor connected to pin 15 create a time constant that governs the duration of the reset signal. Upon application of power, the capacitor begins to charge through the resistor, causing the voltage at pin 15 to rise. This action effectively resets the counters, setting pin 3 to +12V while all other outputs are held at zero.
The inclusion of the two 1N914 diodes and a 15Ω resistor forms an AND gate configuration, which is critical for controlling the passage of the clock pulse to the right side counter. The diodes ensure that the clock pulse is only transmitted when both inputs are high, thus preventing erroneous counting due to noise or unintended signals. The 15Ω resistor limits the current flowing through the diodes, protecting them from potential damage and ensuring stable operation.
Overall, this circuit design is a typical example of using a combination of resistors, capacitors, and diodes to achieve reliable counter operation in digital electronics. The careful selection of component values and configurations allows for precise control over the timing and logical operations required for effective counting sequences.When power is applied, the 15K resistor and 10uF cap at pin 15 will reset the counters to the zero count where pin 3 is at +12 and all other outputs are at zero. The 2 diodes (1n914) and 15 resistor form a AND gate so the clock pulse will be passed to the right side counter when the sequence starts..
🔗 External reference
The circuit described involves a reset mechanism for counters, utilizing a combination of passive and active components to ensure proper initialization upon power-up. The 15KΩ resistor and 10µF capacitor connected to pin 15 create a time constant that governs the duration of the reset signal. Upon application of power, the capacitor begins to charge through the resistor, causing the voltage at pin 15 to rise. This action effectively resets the counters, setting pin 3 to +12V while all other outputs are held at zero.
The inclusion of the two 1N914 diodes and a 15Ω resistor forms an AND gate configuration, which is critical for controlling the passage of the clock pulse to the right side counter. The diodes ensure that the clock pulse is only transmitted when both inputs are high, thus preventing erroneous counting due to noise or unintended signals. The 15Ω resistor limits the current flowing through the diodes, protecting them from potential damage and ensuring stable operation.
Overall, this circuit design is a typical example of using a combination of resistors, capacitors, and diodes to achieve reliable counter operation in digital electronics. The careful selection of component values and configurations allows for precise control over the timing and logical operations required for effective counting sequences.When power is applied, the 15K resistor and 10uF cap at pin 15 will reset the counters to the zero count where pin 3 is at +12 and all other outputs are at zero. The 2 diodes (1n914) and 15 resistor form a AND gate so the clock pulse will be passed to the right side counter when the sequence starts..
🔗 External reference