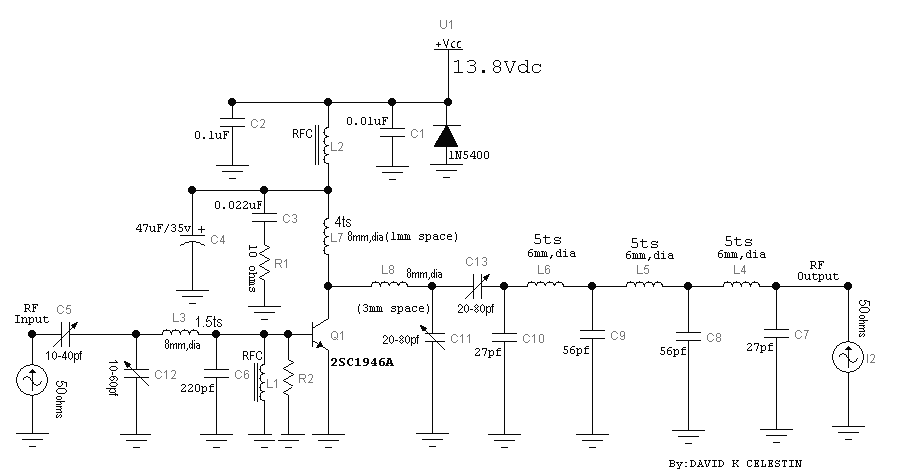
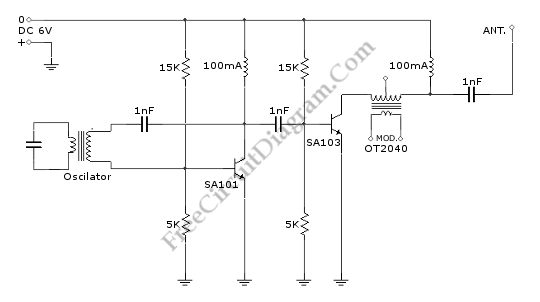
3 Transistor Headphone Amplifier
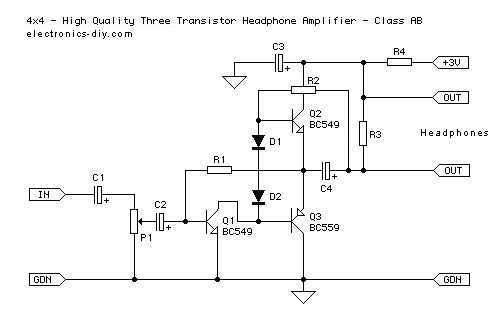
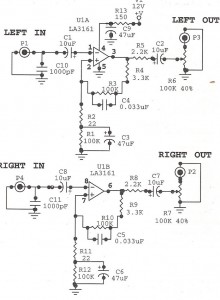
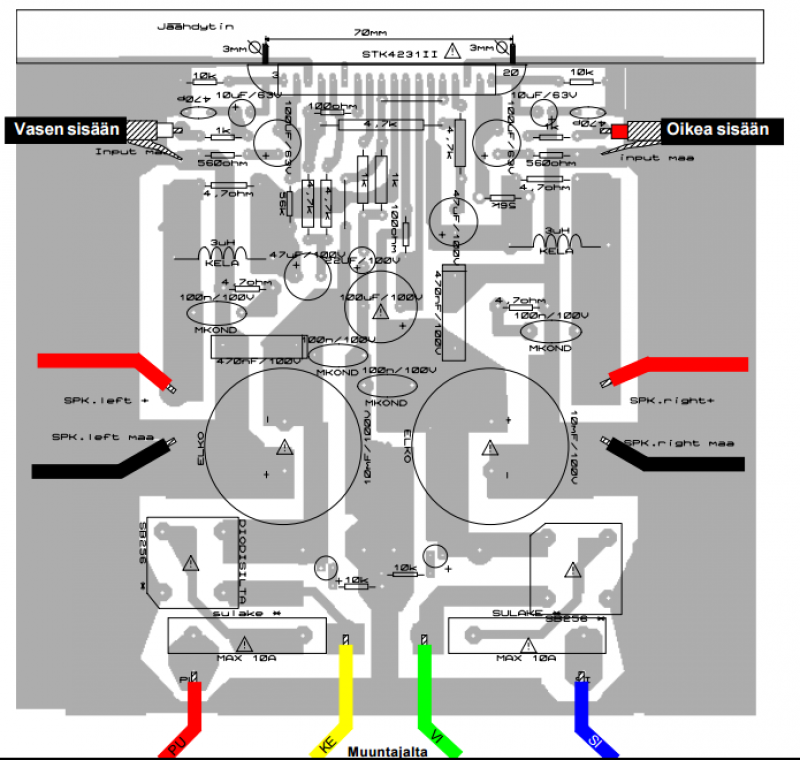
This is an improved version of a headphone amplifier I built many years ago. I wanted to share it because this simple circuit has done great service to me through all these years. It is very simple and reliable, hard to break, offers a lot of power, excellent sound quality, it is built with just a few simple parts and, more importantly, it has very little power consumption. Since I built this amplifier a long time ago, I decided to make an improved version now. The schematic has two protections added that aim at a similar purpose. The first protection, which consists of R4 and C3, simply reduces the noise while turning the amp ON.
The headphone amplifier circuit is designed to provide high-quality audio amplification with minimal distortion and power consumption. The core components typically include transistors or operational amplifiers, resistors, capacitors, and power supply connections. The improved version of this amplifier introduces additional elements to enhance performance and protect the circuit from common issues.
The first protection circuit, comprising resistor R4 and capacitor C3, functions as a noise filter during the power-up phase. When the amplifier is turned on, there can be a transient spike in voltage, which may introduce noise into the audio output. The combination of R4 and C3 acts as a low-pass filter, smoothing out these transients and ensuring that the sound remains clear and free from pops or clicks. This is particularly important in audio applications, where even minor disturbances can significantly affect the listening experience.
In addition to the noise reduction feature, the amplifier's design emphasizes reliability and simplicity. The use of a minimal number of components not only reduces the potential points of failure but also simplifies the assembly process. The circuit can be powered by a low-voltage supply, which contributes to its efficiency and makes it suitable for portable applications.
The output stage of the amplifier is typically designed to drive headphones directly, providing sufficient power to achieve high sound levels without distortion. The choice of components, such as high-quality capacitors and resistors, further enhances the overall sound quality by minimizing signal degradation.
Overall, this headphone amplifier is a testament to effective circuit design, balancing performance, simplicity, and reliability. The improvements made in the latest version ensure that it continues to meet the demands of modern audio applications while maintaining the essential characteristics that have made it a reliable choice for many years.This is an improved version of headphone amplifier I`ve built many years ago. I wanted so much to share it with you because this simple circuit has done a great service to me through all these years. It is very simple and reliable, hard to break, offers a lot of power, excellent sound quality, it is built with just a few simple parts and more importantly it has a very little power consumption.
Since I built this amplifier a long time ago I decided to make an improved version now. The schematic has to protections added that aim at the similar purpose. First protection that consists of R4 and C3, simply reduces the noise while turning the amp ON 🔗 External reference
The headphone amplifier circuit is designed to provide high-quality audio amplification with minimal distortion and power consumption. The core components typically include transistors or operational amplifiers, resistors, capacitors, and power supply connections. The improved version of this amplifier introduces additional elements to enhance performance and protect the circuit from common issues.
The first protection circuit, comprising resistor R4 and capacitor C3, functions as a noise filter during the power-up phase. When the amplifier is turned on, there can be a transient spike in voltage, which may introduce noise into the audio output. The combination of R4 and C3 acts as a low-pass filter, smoothing out these transients and ensuring that the sound remains clear and free from pops or clicks. This is particularly important in audio applications, where even minor disturbances can significantly affect the listening experience.
In addition to the noise reduction feature, the amplifier's design emphasizes reliability and simplicity. The use of a minimal number of components not only reduces the potential points of failure but also simplifies the assembly process. The circuit can be powered by a low-voltage supply, which contributes to its efficiency and makes it suitable for portable applications.
The output stage of the amplifier is typically designed to drive headphones directly, providing sufficient power to achieve high sound levels without distortion. The choice of components, such as high-quality capacitors and resistors, further enhances the overall sound quality by minimizing signal degradation.
Overall, this headphone amplifier is a testament to effective circuit design, balancing performance, simplicity, and reliability. The improvements made in the latest version ensure that it continues to meet the demands of modern audio applications while maintaining the essential characteristics that have made it a reliable choice for many years.This is an improved version of headphone amplifier I`ve built many years ago. I wanted so much to share it with you because this simple circuit has done a great service to me through all these years. It is very simple and reliable, hard to break, offers a lot of power, excellent sound quality, it is built with just a few simple parts and more importantly it has a very little power consumption.
Since I built this amplifier a long time ago I decided to make an improved version now. The schematic has to protections added that aim at the similar purpose. First protection that consists of R4 and C3, simply reduces the noise while turning the amp ON 🔗 External reference