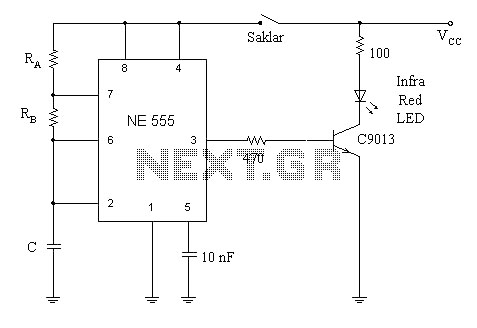
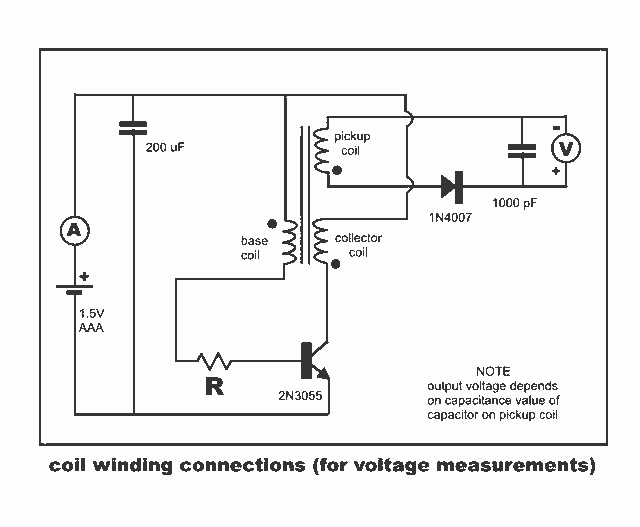
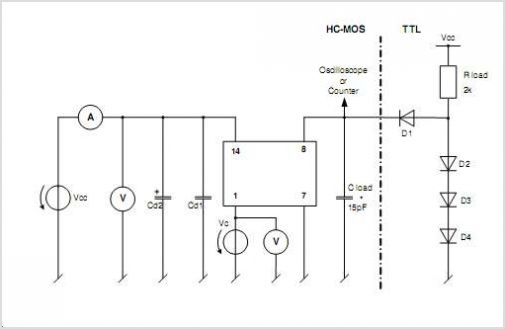
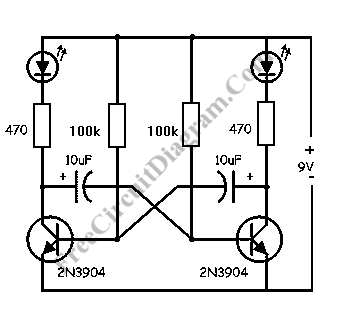
3170 IC For Telephone Remote Control Circuit
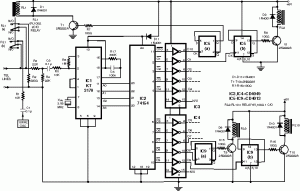
This circuit below shows a teleremote circuit that enables the switching on and off of appliances through telephone lines. It can be used.
The teleremote circuit operates by utilizing telephone lines to control electrical appliances remotely. The primary components of this circuit typically include a telephone line interface, a microcontroller or relay module, and the connected appliances.
When a user makes a call to the designated telephone number associated with the teleremote system, the circuit detects the incoming call. The microcontroller processes the call signals and interprets the commands based on the duration of the ring or specific tones sent by the caller. For instance, a short ring may signify a command to turn an appliance on, while a longer ring could indicate a command to turn it off.
The circuit may also incorporate a relay or solid-state switch to handle the high current required by electrical appliances. This ensures safe operation, as the microcontroller typically operates at low voltage levels. The relay acts as an intermediary, allowing the low-power control signal from the microcontroller to switch the higher power required by the appliance.
Additionally, the teleremote circuit can be enhanced with features such as feedback indicators, which inform the user of the current state of the appliance (on or off) through LED indicators or through a voice response system. This feedback can be crucial for users to confirm that their commands have been executed successfully.
Overall, this teleremote circuit design provides a convenient solution for remotely managing household appliances, leveraging existing telephone infrastructure for control and communication.This circuit bellow shows a teleremote circuit which enables switching ?on? and ?off? of appliances through telephone lines. Can be used . 🔗 External reference
The teleremote circuit operates by utilizing telephone lines to control electrical appliances remotely. The primary components of this circuit typically include a telephone line interface, a microcontroller or relay module, and the connected appliances.
When a user makes a call to the designated telephone number associated with the teleremote system, the circuit detects the incoming call. The microcontroller processes the call signals and interprets the commands based on the duration of the ring or specific tones sent by the caller. For instance, a short ring may signify a command to turn an appliance on, while a longer ring could indicate a command to turn it off.
The circuit may also incorporate a relay or solid-state switch to handle the high current required by electrical appliances. This ensures safe operation, as the microcontroller typically operates at low voltage levels. The relay acts as an intermediary, allowing the low-power control signal from the microcontroller to switch the higher power required by the appliance.
Additionally, the teleremote circuit can be enhanced with features such as feedback indicators, which inform the user of the current state of the appliance (on or off) through LED indicators or through a voice response system. This feedback can be crucial for users to confirm that their commands have been executed successfully.
Overall, this teleremote circuit design provides a convenient solution for remotely managing household appliances, leveraging existing telephone infrastructure for control and communication.This circuit bellow shows a teleremote circuit which enables switching ?on? and ?off? of appliances through telephone lines. Can be used . 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713