32768 hz quartz oscillator
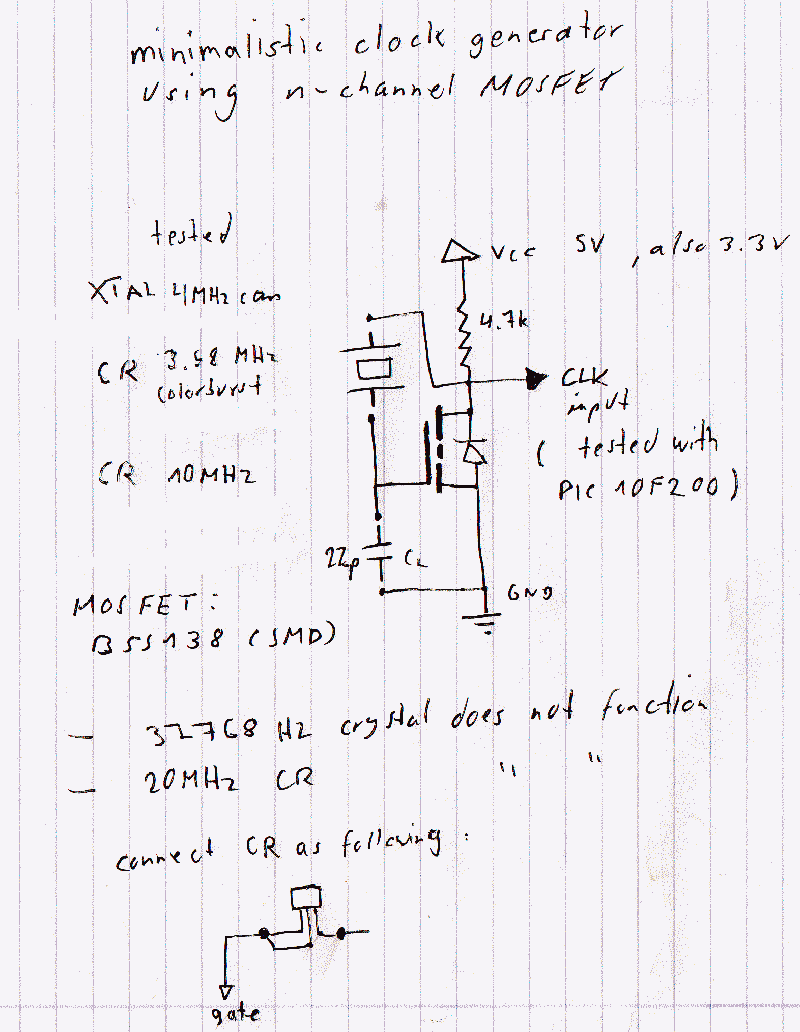
This is the first post discussing a watch crystal oscillator for a PIC microcontroller. The intention is to avoid the use of logic gates in the circuit.
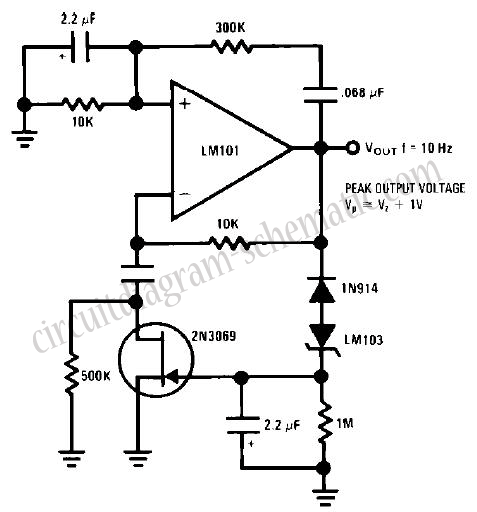
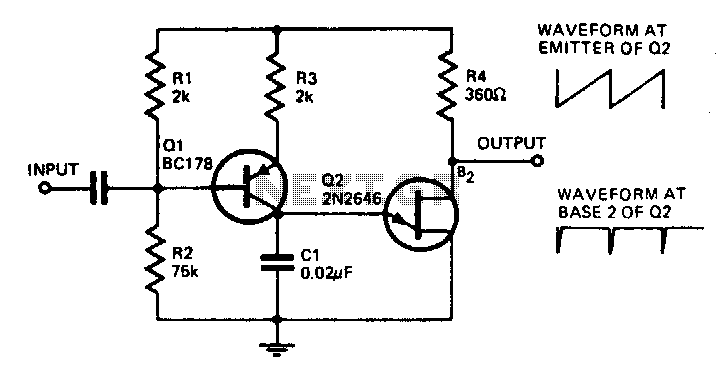
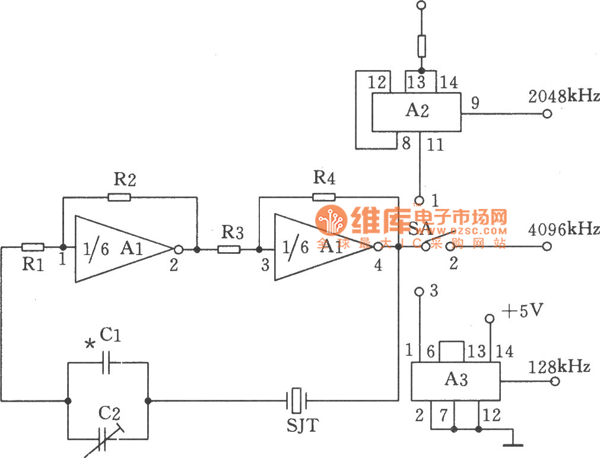
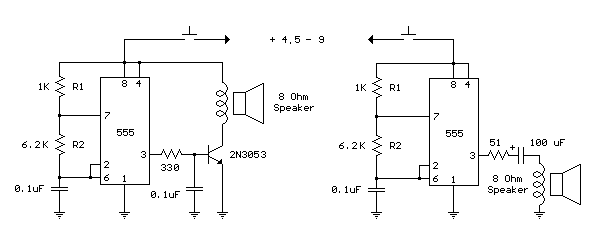
A watch crystal oscillator is a fundamental component used in various electronic applications, particularly in microcontroller circuits, to provide a stable clock signal. In the context of a PIC microcontroller, the oscillator circuit can be designed using a quartz crystal, which is known for its precise frequency stability.
The circuit typically involves connecting a quartz crystal between the oscillator pins of the PIC microcontroller. The crystal's resonant frequency determines the clock speed of the microcontroller, which is crucial for timing and synchronization in digital circuits. The configuration may include load capacitors connected to the crystal terminals to ensure proper operation and frequency stability.
In this design, since the use of logic gates is avoided, the oscillator function relies solely on the internal oscillator capabilities of the PIC microcontroller, which can utilize the external crystal for generating the necessary clock signal. This approach simplifies the circuit and reduces component count, enhancing reliability and minimizing potential failure points.
The typical values for the load capacitors can be calculated based on the crystal specifications and the microcontroller's requirements, ensuring that the circuit operates within the desired frequency range. It is essential to refer to the specific PIC microcontroller datasheet for accurate pin configurations and recommended capacitor values to optimize performance.
Overall, the implementation of a watch crystal oscillator in a PIC microcontroller circuit is a straightforward yet effective method to achieve precise timing without the complexity introduced by additional logic gates.hi this my 1st post here. topic is a watch crystal oscillator for PIC (microcontroller). i do not want to use logic gates. here the circuit (a thread.. 🔗 External reference
A watch crystal oscillator is a fundamental component used in various electronic applications, particularly in microcontroller circuits, to provide a stable clock signal. In the context of a PIC microcontroller, the oscillator circuit can be designed using a quartz crystal, which is known for its precise frequency stability.
The circuit typically involves connecting a quartz crystal between the oscillator pins of the PIC microcontroller. The crystal's resonant frequency determines the clock speed of the microcontroller, which is crucial for timing and synchronization in digital circuits. The configuration may include load capacitors connected to the crystal terminals to ensure proper operation and frequency stability.
In this design, since the use of logic gates is avoided, the oscillator function relies solely on the internal oscillator capabilities of the PIC microcontroller, which can utilize the external crystal for generating the necessary clock signal. This approach simplifies the circuit and reduces component count, enhancing reliability and minimizing potential failure points.
The typical values for the load capacitors can be calculated based on the crystal specifications and the microcontroller's requirements, ensuring that the circuit operates within the desired frequency range. It is essential to refer to the specific PIC microcontroller datasheet for accurate pin configurations and recommended capacitor values to optimize performance.
Overall, the implementation of a watch crystal oscillator in a PIC microcontroller circuit is a straightforward yet effective method to achieve precise timing without the complexity introduced by additional logic gates.hi this my 1st post here. topic is a watch crystal oscillator for PIC (microcontroller). i do not want to use logic gates. here the circuit (a thread.. 🔗 External reference