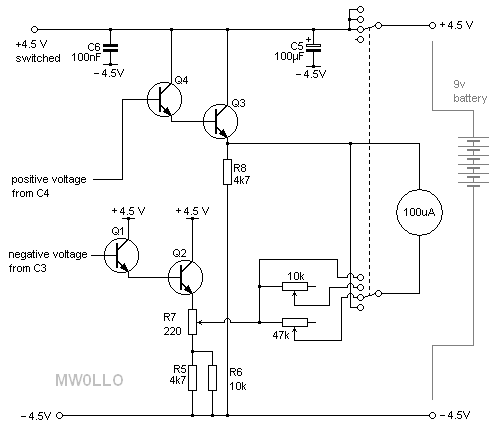
40 meter Direct Conversion Receiver
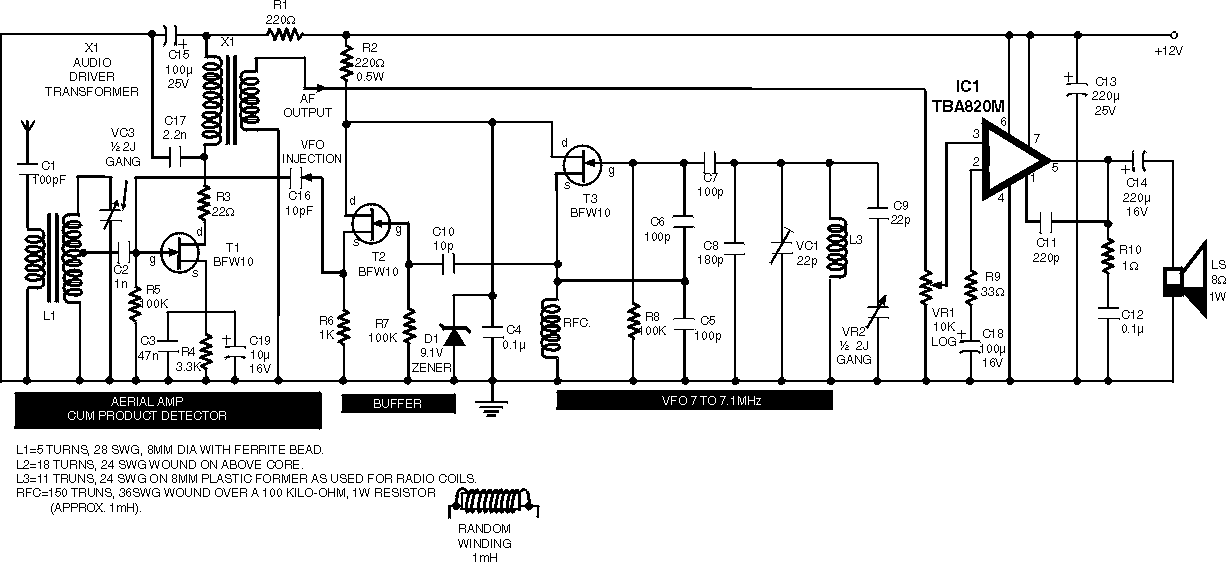
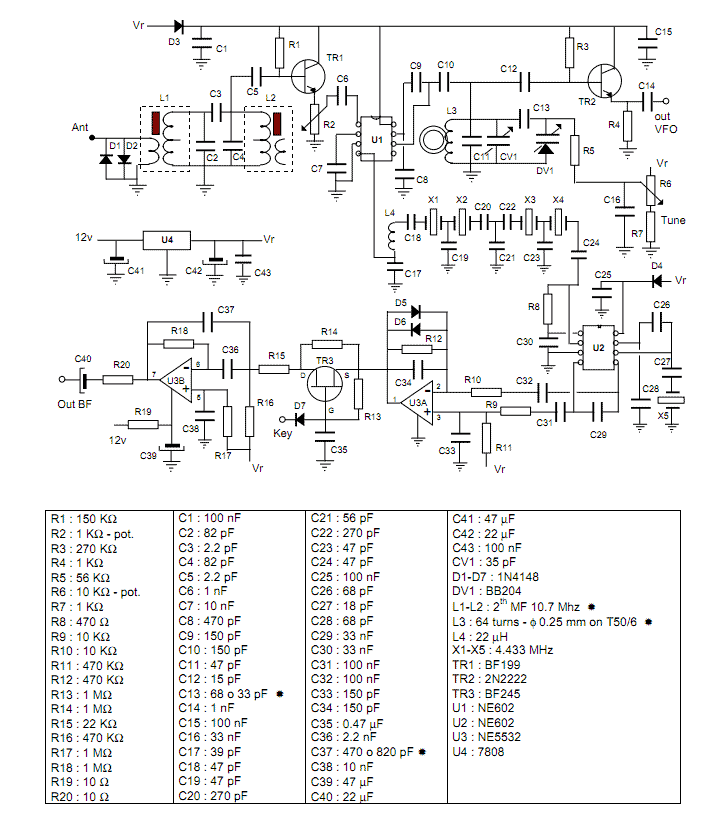
40-meter Direct Conversion Receiver. Using the circuit of a 40-meter band direct-conversion receiver described here, one can listen to amateur radio QSO signals in both CW and SSB modes.
The 40-meter direct conversion receiver is designed to facilitate the reception of amateur radio communications, specifically in the 7 MHz frequency range, which is popular for both CW (Continuous Wave) and SSB (Single Sideband) modes. This receiver operates by converting the incoming RF (radio frequency) signals directly to audio frequencies, allowing for easier processing and listening.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: an RF amplifier, a mixer, a local oscillator, and an audio amplifier. The RF amplifier boosts the weak signals received by the antenna, ensuring that they are strong enough for further processing. The mixer then combines the amplified RF signal with a signal from the local oscillator, which is tuned to the desired frequency. This mixing process produces an intermediate frequency (IF) that is lower than the original RF signal, making it easier to filter and amplify.
In CW mode, the receiver can demodulate the on-off keying of the signal, while in SSB mode, it can extract the audio information from the modulated carrier wave. The audio output can be connected to headphones or a speaker for listening. Additional features may include adjustable filters to improve selectivity and reduce interference from adjacent frequencies, as well as volume controls for the audio output.
This direct conversion method is favored for its simplicity and effectiveness, making it a popular choice among amateur radio enthusiasts for building their own receivers. The design can be further enhanced with additional components such as automatic gain control (AGC) to maintain consistent audio levels and improved sensitivity, contributing to an overall better reception experience.40 meter Direct Conversion Receiver. Using the circuit of 40-metre band direct-conversion receiver descr- ibed here, one can listen to amateur radio QSO signals in CW as well as in SSB mode in. 🔗 External reference
The 40-meter direct conversion receiver is designed to facilitate the reception of amateur radio communications, specifically in the 7 MHz frequency range, which is popular for both CW (Continuous Wave) and SSB (Single Sideband) modes. This receiver operates by converting the incoming RF (radio frequency) signals directly to audio frequencies, allowing for easier processing and listening.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: an RF amplifier, a mixer, a local oscillator, and an audio amplifier. The RF amplifier boosts the weak signals received by the antenna, ensuring that they are strong enough for further processing. The mixer then combines the amplified RF signal with a signal from the local oscillator, which is tuned to the desired frequency. This mixing process produces an intermediate frequency (IF) that is lower than the original RF signal, making it easier to filter and amplify.
In CW mode, the receiver can demodulate the on-off keying of the signal, while in SSB mode, it can extract the audio information from the modulated carrier wave. The audio output can be connected to headphones or a speaker for listening. Additional features may include adjustable filters to improve selectivity and reduce interference from adjacent frequencies, as well as volume controls for the audio output.
This direct conversion method is favored for its simplicity and effectiveness, making it a popular choice among amateur radio enthusiasts for building their own receivers. The design can be further enhanced with additional components such as automatic gain control (AGC) to maintain consistent audio levels and improved sensitivity, contributing to an overall better reception experience.40 meter Direct Conversion Receiver. Using the circuit of 40-metre band direct-conversion receiver descr- ibed here, one can listen to amateur radio QSO signals in CW as well as in SSB mode in. 🔗 External reference