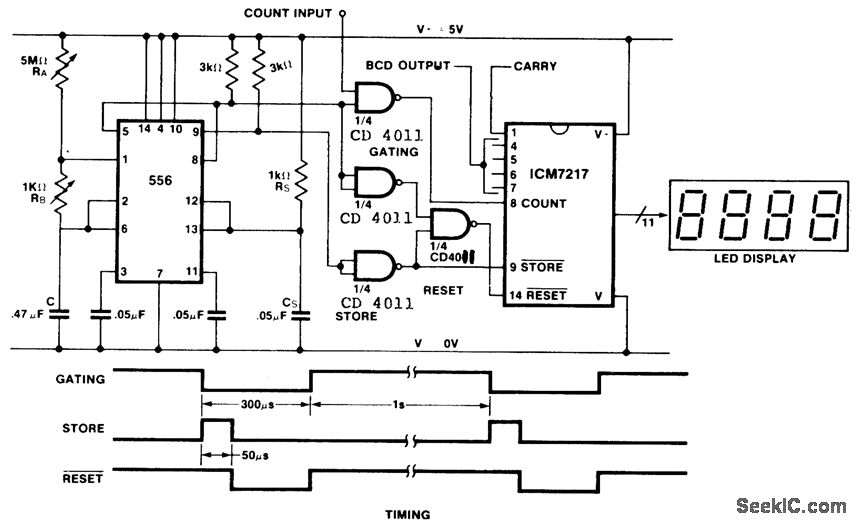
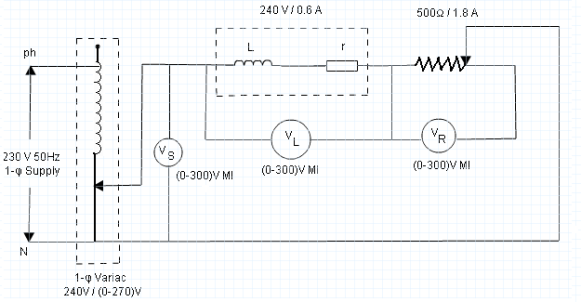
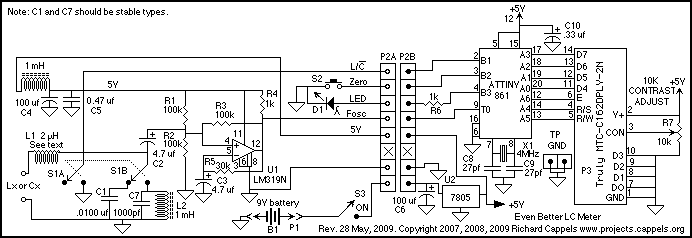
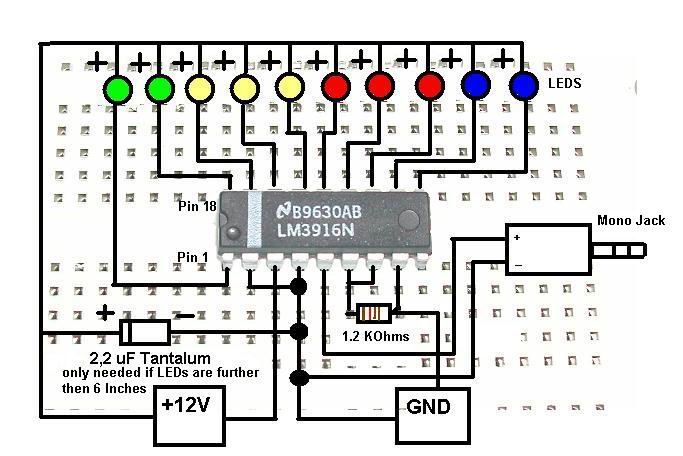
Field-strength meter

The antenna is made of approximately 20 cm of insulated stranded wire, which is adhered or affixed to the interior of a small plastic box. Additionally, the RF current is rectified using two diodes, and a 10 k potentiometer is included to allow for variable attenuation for the meter.
The described antenna system employs a compact design, utilizing insulated stranded wire approximately 20 cm in length. This wire is strategically arranged within a small plastic enclosure, which serves both to protect the antenna and to facilitate its installation. The choice of insulated stranded wire ensures flexibility and durability, making it suitable for various applications.
The RF current generated by the antenna is processed through a rectification stage involving two diodes. This configuration allows for the conversion of alternating current (AC) signals into direct current (DC), which is essential for further signal processing or measurement. The selection of diodes is critical; they should be chosen based on their forward voltage drop, reverse recovery time, and maximum current rating to ensure efficient rectification.
To provide adjustable output for measurement purposes, a 10 k potentiometer is integrated into the circuit. This component allows for variable attenuation, enabling the user to fine-tune the signal level before it is presented to the meter. The potentiometer's resistance value is suitable for applications where moderate signal levels are encountered, and it allows for a significant range of adjustment to accommodate varying input signal strengths.
Overall, this antenna system is designed for effective RF signal reception and measurement, with a focus on compactness and user adjustability. The combination of the antenna design, rectification stage, and attenuation control creates a versatile tool for various electronic applications.The antenna consists of about 20 cm of insulated stranded wire glued or taped around the inside of a small plastic box. RF current is rectified by two diodes, and a 10 k potentiometer provides variable attenuation for the meter. 🔗 External reference
The described antenna system employs a compact design, utilizing insulated stranded wire approximately 20 cm in length. This wire is strategically arranged within a small plastic enclosure, which serves both to protect the antenna and to facilitate its installation. The choice of insulated stranded wire ensures flexibility and durability, making it suitable for various applications.
The RF current generated by the antenna is processed through a rectification stage involving two diodes. This configuration allows for the conversion of alternating current (AC) signals into direct current (DC), which is essential for further signal processing or measurement. The selection of diodes is critical; they should be chosen based on their forward voltage drop, reverse recovery time, and maximum current rating to ensure efficient rectification.
To provide adjustable output for measurement purposes, a 10 k potentiometer is integrated into the circuit. This component allows for variable attenuation, enabling the user to fine-tune the signal level before it is presented to the meter. The potentiometer's resistance value is suitable for applications where moderate signal levels are encountered, and it allows for a significant range of adjustment to accommodate varying input signal strengths.
Overall, this antenna system is designed for effective RF signal reception and measurement, with a focus on compactness and user adjustability. The combination of the antenna design, rectification stage, and attenuation control creates a versatile tool for various electronic applications.The antenna consists of about 20 cm of insulated stranded wire glued or taped around the inside of a small plastic box. RF current is rectified by two diodes, and a 10 k potentiometer provides variable attenuation for the meter. 🔗 External reference