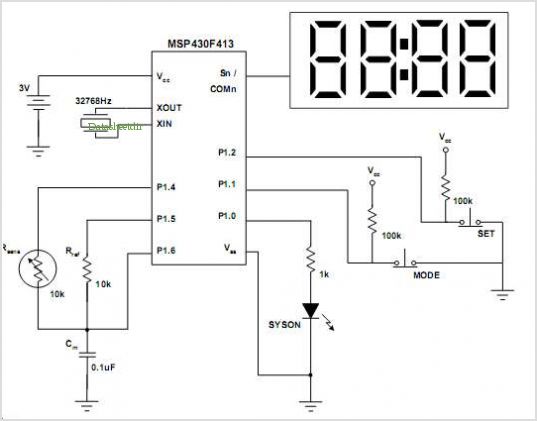
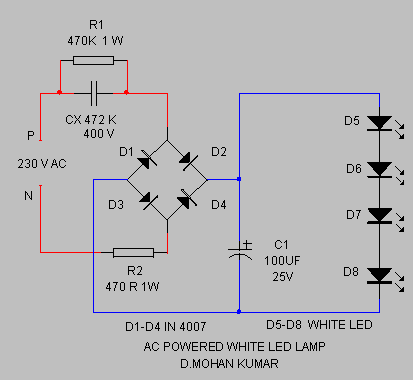
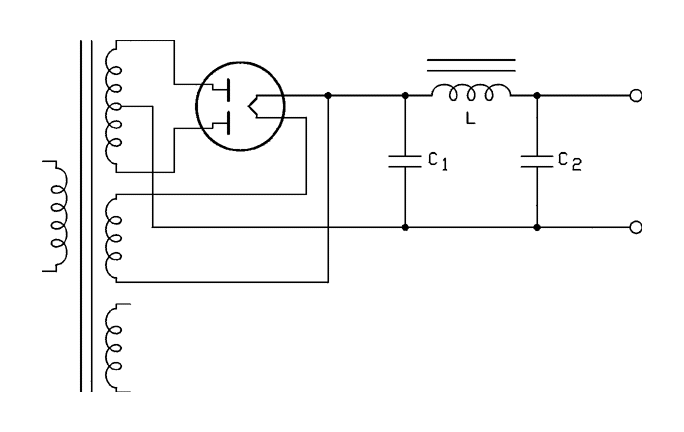
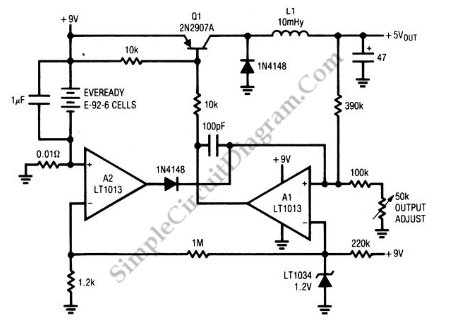
48V Phantom (Microphone) Power Supply
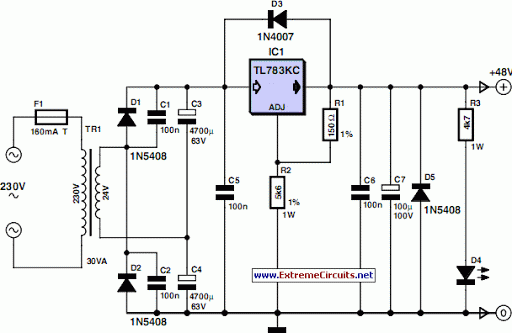
48 V phantom powering has become the standard for professional condenser microphones. The supply (or rather bias) voltage is applied over both wires of the microphone cable.
Phantom power is a method used to provide power to condenser microphones through the same cables that carry the audio signal. This technique allows for a simplified setup, eliminating the need for separate power sources. Typically, the voltage is supplied at 48 volts, although some devices may operate at lower voltages such as 12 V or 24 V.
In a standard configuration, the phantom power is delivered through the two signal wires of a balanced audio cable, usually XLR connectors. The voltage is applied equally to both wires, with the microphone itself being designed to utilize this power for its internal preamplifier, which is essential for converting sound waves into an electrical signal.
The presence of phantom power does not affect dynamic microphones, which do not require external power to operate. However, when connecting a condenser microphone, it is crucial to ensure that the phantom power is enabled on the audio interface or mixer to avoid any signal issues.
Proper implementation of phantom power includes using high-quality cables and connectors to minimize noise and interference. Additionally, it is advisable to check the specifications of both the microphone and the audio equipment to ensure compatibility and prevent potential damage.
Overall, 48 V phantom power is a reliable and efficient method for powering professional condenser microphones, facilitating high-quality audio capture in various applications, including studio recordings, live performances, and broadcasting.48 V ‘phantom powering has become the standard for professional condenser microphones. The supply (or rather bias) voltage is applied over both wires of.. 🔗 External reference
Phantom power is a method used to provide power to condenser microphones through the same cables that carry the audio signal. This technique allows for a simplified setup, eliminating the need for separate power sources. Typically, the voltage is supplied at 48 volts, although some devices may operate at lower voltages such as 12 V or 24 V.
In a standard configuration, the phantom power is delivered through the two signal wires of a balanced audio cable, usually XLR connectors. The voltage is applied equally to both wires, with the microphone itself being designed to utilize this power for its internal preamplifier, which is essential for converting sound waves into an electrical signal.
The presence of phantom power does not affect dynamic microphones, which do not require external power to operate. However, when connecting a condenser microphone, it is crucial to ensure that the phantom power is enabled on the audio interface or mixer to avoid any signal issues.
Proper implementation of phantom power includes using high-quality cables and connectors to minimize noise and interference. Additionally, it is advisable to check the specifications of both the microphone and the audio equipment to ensure compatibility and prevent potential damage.
Overall, 48 V phantom power is a reliable and efficient method for powering professional condenser microphones, facilitating high-quality audio capture in various applications, including studio recordings, live performances, and broadcasting.48 V ‘phantom powering has become the standard for professional condenser microphones. The supply (or rather bias) voltage is applied over both wires of.. 🔗 External reference