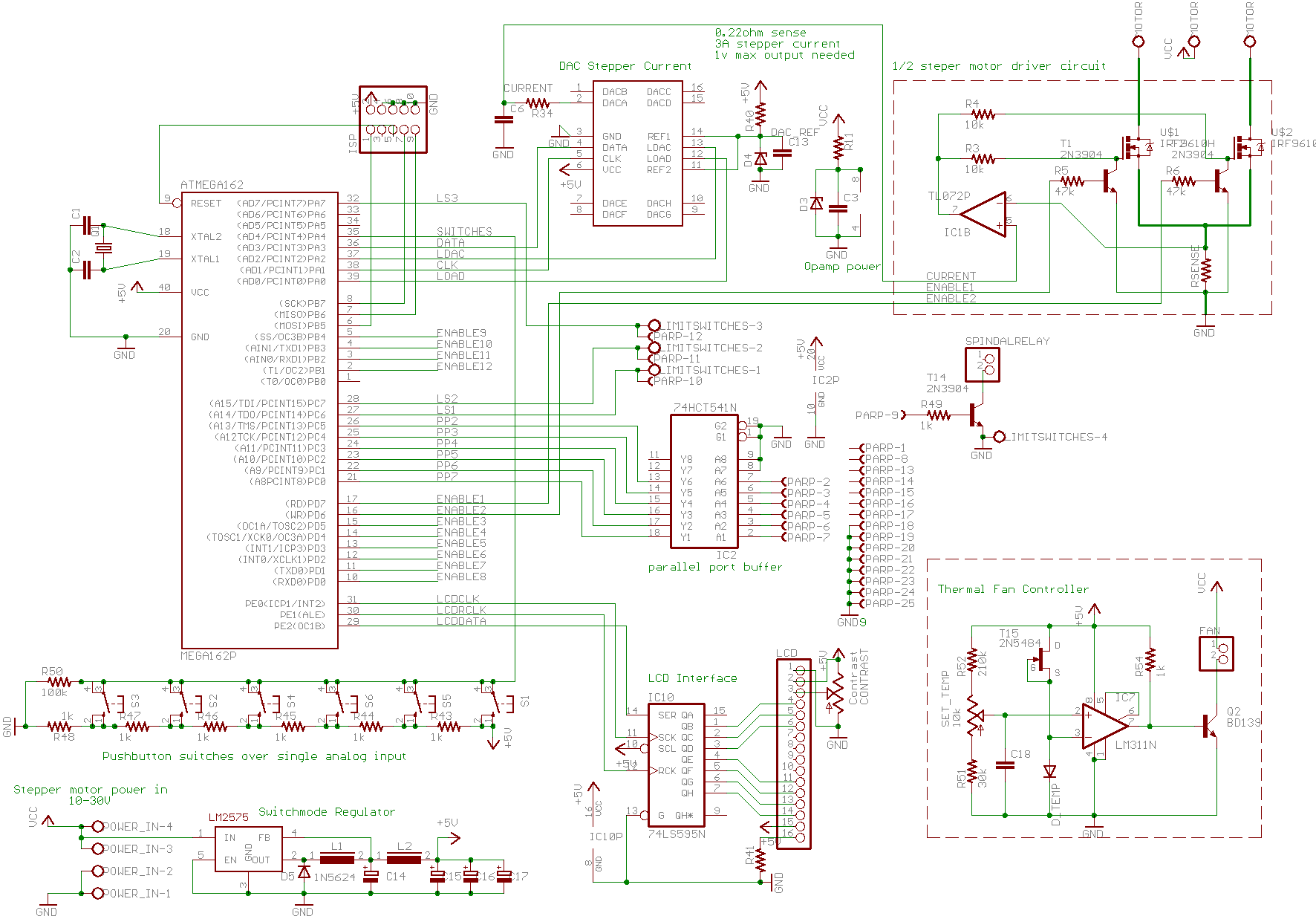
5-Volt RelayCircuit for Controlling AC Current
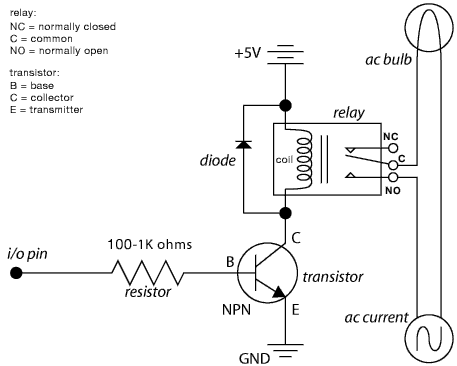
The schematic illustrates the Relay Wiring Circuit Diagram used to control an air conditioner or other high-current devices via a microcontroller.
The relay wiring circuit serves as an interface between low-voltage microcontroller signals and high-voltage appliances, such as air conditioners. This circuit typically consists of a relay module, which includes an electromagnetic switch capable of handling high current. The microcontroller outputs a control signal, often a digital HIGH or LOW, to the relay's input, activating or deactivating the relay coil.
When the microcontroller sends a HIGH signal to the relay, current flows through the relay coil, creating a magnetic field that closes the switch contacts. This action connects the high-voltage power supply to the load—in this case, the air conditioner—allowing it to operate. Conversely, when the microcontroller outputs a LOW signal, the relay coil is de-energized, the magnetic field collapses, and the switch contacts open, disconnecting the power supply from the load.
To ensure safe operation, the circuit may include protective components such as diodes across the relay coil to prevent back EMF when the relay is switched off, as well as fuses or circuit breakers to protect against overcurrent situations. Additionally, opto-isolators may be used to provide electrical isolation between the microcontroller and the high-voltage circuit, enhancing safety and reducing the risk of damage to sensitive components.
The schematic should clearly indicate the connections between the microcontroller, relay module, power supply, and load, along with any necessary components for protection and isolation. Proper labeling of each component and connection will facilitate understanding and implementation of the circuit, ensuring reliable control of high-current devices.The following schematic shows the Relay Wiring Circuit Diagram for controlling an Air Conditioner or other higher high-current device from a microcontroller.. 🔗 External reference
The relay wiring circuit serves as an interface between low-voltage microcontroller signals and high-voltage appliances, such as air conditioners. This circuit typically consists of a relay module, which includes an electromagnetic switch capable of handling high current. The microcontroller outputs a control signal, often a digital HIGH or LOW, to the relay's input, activating or deactivating the relay coil.
When the microcontroller sends a HIGH signal to the relay, current flows through the relay coil, creating a magnetic field that closes the switch contacts. This action connects the high-voltage power supply to the load—in this case, the air conditioner—allowing it to operate. Conversely, when the microcontroller outputs a LOW signal, the relay coil is de-energized, the magnetic field collapses, and the switch contacts open, disconnecting the power supply from the load.
To ensure safe operation, the circuit may include protective components such as diodes across the relay coil to prevent back EMF when the relay is switched off, as well as fuses or circuit breakers to protect against overcurrent situations. Additionally, opto-isolators may be used to provide electrical isolation between the microcontroller and the high-voltage circuit, enhancing safety and reducing the risk of damage to sensitive components.
The schematic should clearly indicate the connections between the microcontroller, relay module, power supply, and load, along with any necessary components for protection and isolation. Proper labeling of each component and connection will facilitate understanding and implementation of the circuit, ensuring reliable control of high-current devices.The following schematic shows the Relay Wiring Circuit Diagram for controlling an Air Conditioner or other higher high-current device from a microcontroller.. 🔗 External reference