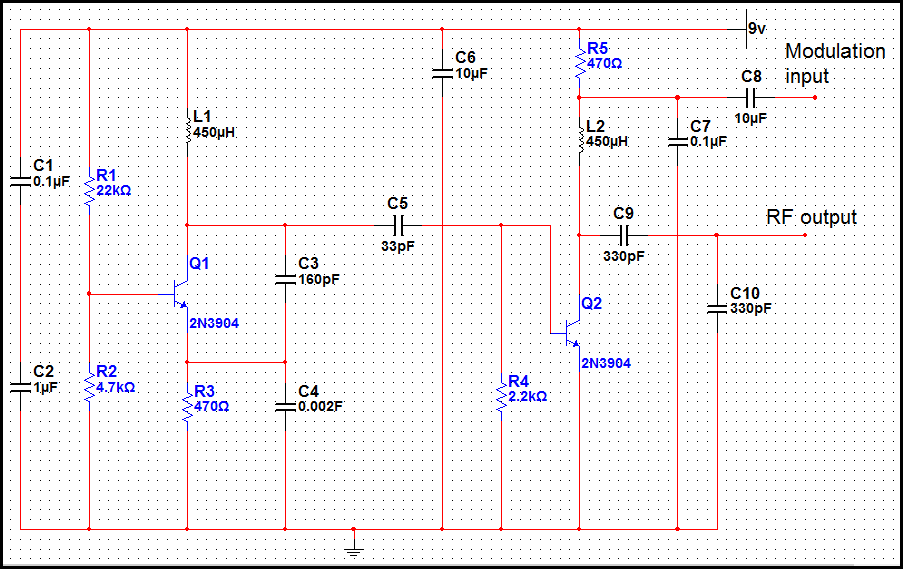
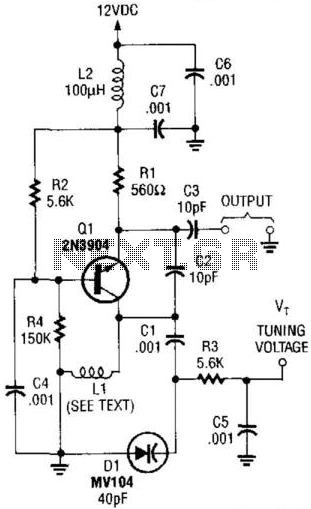
500 mW VHF Video Transmitter
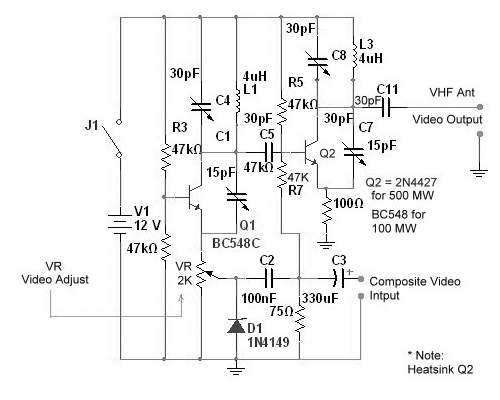
Tuned circuits consist of C4, L1, C8, L3, and two 15 pF trimmer capacitors positioned across the collectors and emitters of both transistors. Other NPN transistors such as BC54, 2N3642, and 2N3643 may also be suitable. The circuit is designed for simplicity, and no audio components have been included, as this would necessitate the addition of at least an RF coupling transformer. The primary application of this circuit is for security monitoring. When using a 2N4427 or a similar transistor for Q2 (output), a heat sink must be employed. The 2N4427 can deliver 1 Watt of RF at VHF frequencies, so it is essential to connect either a 50-75 Ohm dummy load or an antenna at all times before applying power.
The tuned circuit described utilizes a combination of capacitors and inductors to achieve resonance at a specific frequency, which is crucial for effective signal transmission and reception. The components C4, L1, C8, and L3 are carefully selected to form a resonant tank circuit, with the trimmer capacitors providing fine-tuning capabilities to adjust the circuit's operating frequency. This ensures optimal performance in the desired frequency range, particularly for security monitoring applications where reliability and precision are paramount.
The choice of NPN transistors, such as the BC54 and 2N3642, offers flexibility in component selection, allowing for variations based on availability and performance characteristics. These transistors are known for their suitability in RF applications, providing sufficient gain and frequency response for the circuit's needs.
The absence of audio components simplifies the design, focusing on RF signal processing. This streamlined approach is beneficial for security monitoring systems, where audio signals are not required, and the emphasis is on detecting and transmitting RF signals effectively. The mention of the RF coupling transformer highlights the potential for expansion should audio capabilities be needed in future iterations of the design.
The use of the 2N4427 transistor for the output stage (Q2) is noteworthy due to its capability to handle high power levels, specifically up to 1 Watt at VHF frequencies. The recommendation for a heat sink is critical, as high-power transistors can generate significant heat during operation, which, if not dissipated, could lead to thermal runaway and eventual failure of the component. Connecting a dummy load or antenna is essential for safe operation; without it, the circuit may experience undesired behavior or damage when powered on.
In summary, this tuned circuit design is well-suited for security monitoring applications, leveraging a straightforward architecture and robust components to achieve effective RF performance while maintaining the option for future enhancements.Tuned circuits consist of C4, L1, C8, L3, and the two 15 pF trimmer capacitors across the collectors and emitters of both transistors. Other NPN transistors like BC54, 2N3642, 43, etc should also work. The circuit is designed for simplicity, so No Audio has been included as this would involve adding at least an RF coupling transformer.
The main use for this circuit is for Security Monitoring . If you use a 2N4427 or similar transistor for Q2 (output), you must use a heat sink. The 2N4427 is capable of delivering 1 Watt of RF at VHF frequencies so be sure that either a 50-75 Ohm dummy load or antenna is connected at all times before applying power. 🔗 External reference
The tuned circuit described utilizes a combination of capacitors and inductors to achieve resonance at a specific frequency, which is crucial for effective signal transmission and reception. The components C4, L1, C8, and L3 are carefully selected to form a resonant tank circuit, with the trimmer capacitors providing fine-tuning capabilities to adjust the circuit's operating frequency. This ensures optimal performance in the desired frequency range, particularly for security monitoring applications where reliability and precision are paramount.
The choice of NPN transistors, such as the BC54 and 2N3642, offers flexibility in component selection, allowing for variations based on availability and performance characteristics. These transistors are known for their suitability in RF applications, providing sufficient gain and frequency response for the circuit's needs.
The absence of audio components simplifies the design, focusing on RF signal processing. This streamlined approach is beneficial for security monitoring systems, where audio signals are not required, and the emphasis is on detecting and transmitting RF signals effectively. The mention of the RF coupling transformer highlights the potential for expansion should audio capabilities be needed in future iterations of the design.
The use of the 2N4427 transistor for the output stage (Q2) is noteworthy due to its capability to handle high power levels, specifically up to 1 Watt at VHF frequencies. The recommendation for a heat sink is critical, as high-power transistors can generate significant heat during operation, which, if not dissipated, could lead to thermal runaway and eventual failure of the component. Connecting a dummy load or antenna is essential for safe operation; without it, the circuit may experience undesired behavior or damage when powered on.
In summary, this tuned circuit design is well-suited for security monitoring applications, leveraging a straightforward architecture and robust components to achieve effective RF performance while maintaining the option for future enhancements.Tuned circuits consist of C4, L1, C8, L3, and the two 15 pF trimmer capacitors across the collectors and emitters of both transistors. Other NPN transistors like BC54, 2N3642, 43, etc should also work. The circuit is designed for simplicity, so No Audio has been included as this would involve adding at least an RF coupling transformer.
The main use for this circuit is for Security Monitoring . If you use a 2N4427 or similar transistor for Q2 (output), you must use a heat sink. The 2N4427 is capable of delivering 1 Watt of RF at VHF frequencies so be sure that either a 50-75 Ohm dummy load or antenna is connected at all times before applying power. 🔗 External reference