HIGH PERFORMANCE VIDEO MIXER
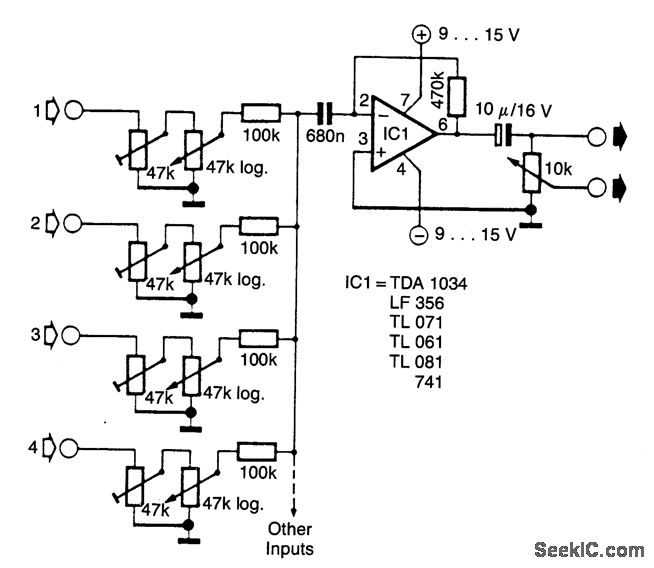
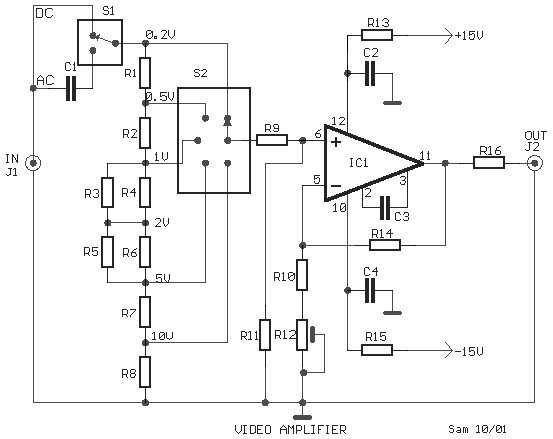
This circuit combines horizontal synchronization (H sync), vertical synchronization (V sync), and the actual video signal. Transistor T2 is responsible for mixing the synchronization signals, while transistor T1 functions as an emitter-follower. Typical bandwidths for this circuit can reach up to 25 MHz.
The described circuit is a fundamental component in video processing, particularly in the context of analog video systems. The integration of H sync, V sync, and video signals is crucial for maintaining proper synchronization between the displayed image and the video source.
Transistor T2 plays a pivotal role in the mixing process, where it combines the synchronization signals to ensure that the timing of the video display aligns accurately with the incoming video data. This mixing is essential for preventing issues such as tearing or misalignment in the displayed image.
Transistor T1, acting as an emitter-follower, provides a high input impedance and low output impedance, which is beneficial for buffering the mixed signal. This configuration allows the circuit to drive subsequent stages without loading down the previous stage, thus preserving signal integrity. The emitter-follower configuration is advantageous in applications where signal isolation is necessary, and it helps to maintain the fidelity of the video signal.
The circuit's bandwidth capability of up to 25 MHz indicates its suitability for standard video resolutions, making it effective for various applications including television broadcasting and video conferencing systems. The design considerations for achieving this bandwidth include careful selection of components and layout to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect performance.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a critical aspect of video signal processing, where synchronization and signal integrity are paramount for delivering high-quality video output.This circuit mixes H synch. V synch. and actual video. T2 mixes the synch, while T1 serves as an emitter-follower. Bandwidths of up to 25 MHz are typical for this circuit. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a fundamental component in video processing, particularly in the context of analog video systems. The integration of H sync, V sync, and video signals is crucial for maintaining proper synchronization between the displayed image and the video source.
Transistor T2 plays a pivotal role in the mixing process, where it combines the synchronization signals to ensure that the timing of the video display aligns accurately with the incoming video data. This mixing is essential for preventing issues such as tearing or misalignment in the displayed image.
Transistor T1, acting as an emitter-follower, provides a high input impedance and low output impedance, which is beneficial for buffering the mixed signal. This configuration allows the circuit to drive subsequent stages without loading down the previous stage, thus preserving signal integrity. The emitter-follower configuration is advantageous in applications where signal isolation is necessary, and it helps to maintain the fidelity of the video signal.
The circuit's bandwidth capability of up to 25 MHz indicates its suitability for standard video resolutions, making it effective for various applications including television broadcasting and video conferencing systems. The design considerations for achieving this bandwidth include careful selection of components and layout to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect performance.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a critical aspect of video signal processing, where synchronization and signal integrity are paramount for delivering high-quality video output.This circuit mixes H synch. V synch. and actual video. T2 mixes the synch, while T1 serves as an emitter-follower. Bandwidths of up to 25 MHz are typical for this circuit. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713