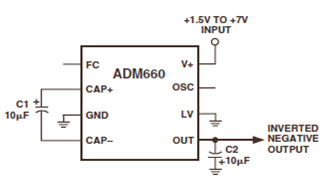
500W 12V to 220V inverter
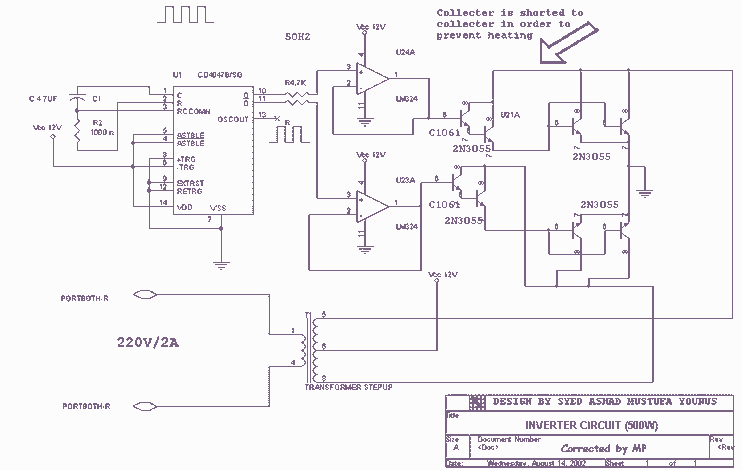
Using this circuit you can convert the 12V dc into the 220V Ac. In this circuit, 4047 is used to generate the square wave of 50Hz and amplify the current and then amplify the voltage by using the step transformer. How to calculate transformer rating The basic formula is P=VI and between input output of the transformer we have Power input = Power output.
For example, if we want a 220W output at 220V then we need 1A at the output. Then at the input, we must have at least 18.3V at 12V because: 12V*18.3 = 220V*1. So you have to wind the step-up transformer 12V to 220V but input winding must be capable to bear 20A.
The circuit described utilizes a 4047 astable multivibrator to generate a square wave signal at 50Hz, which is essential for converting the direct current (DC) from a 12V source into alternating current (AC) at 220V. The 4047 IC is configured in an astable mode, producing a continuous square wave output. This output signal is then used to drive a transistor or a power amplifier stage, which increases the current necessary to drive the transformer.
The transformer used in this circuit is a step-up transformer, which is designed to convert the low voltage (12V) input to a high voltage (220V) output. The transformer’s turns ratio is critical for ensuring that the output voltage is achieved. The formula for calculating the transformer rating is based on the principle of power conservation, where the power input (P_in) equals the power output (P_out). The relationship can be expressed as P = VI, where V is voltage and I is current.
In this case, to achieve a desired output of 220W at 220V, the output current required is 1A. To determine the necessary input voltage, the equation can be rearranged to find the minimum input voltage needed at 12V. The calculation shows that to maintain power balance, the input must be at least 18.3V, which is derived from the equation: 12V * 18.3 = 220V * 1A. Therefore, the transformer must be designed with a primary winding that can handle 20A to ensure it is capable of sustaining the current during operation.
When designing the transformer, attention must be paid to the wire gauge and the number of turns in both the primary and secondary windings to ensure efficiency and minimize losses. The core material of the transformer should also be selected to handle the frequency of operation (50Hz) and to reduce core losses. Proper heat dissipation mechanisms should be considered, especially for the transistor or amplifier stage, to prevent overheating during prolonged use. Overall, this circuit is a practical implementation of DC to AC conversion techniques suitable for various applications requiring a 220V AC supply from a 12V DC source.Using this circuit you can convert the 12V dc in to the 220V Ac. In this circuit 4047 is use to generate the square wave of 50hz and amplify the current and then amplify the voltage by using the step transformer. How to calculate transformer rating The basic formula is P=VI and between input output of the transformer we have Power input = Power output.
For example if we want a 220W output at 220V then we need 1A at the output. Then at the input we must have at least 18.3V at 12V because: 12V*18.3 = 220v*1. So you have to wind the step up transformer 12v to 220v but input winding must be capable to bear 20A. 🔗 External reference
For example, if we want a 220W output at 220V then we need 1A at the output. Then at the input, we must have at least 18.3V at 12V because: 12V*18.3 = 220V*1. So you have to wind the step-up transformer 12V to 220V but input winding must be capable to bear 20A.
The circuit described utilizes a 4047 astable multivibrator to generate a square wave signal at 50Hz, which is essential for converting the direct current (DC) from a 12V source into alternating current (AC) at 220V. The 4047 IC is configured in an astable mode, producing a continuous square wave output. This output signal is then used to drive a transistor or a power amplifier stage, which increases the current necessary to drive the transformer.
The transformer used in this circuit is a step-up transformer, which is designed to convert the low voltage (12V) input to a high voltage (220V) output. The transformer’s turns ratio is critical for ensuring that the output voltage is achieved. The formula for calculating the transformer rating is based on the principle of power conservation, where the power input (P_in) equals the power output (P_out). The relationship can be expressed as P = VI, where V is voltage and I is current.
In this case, to achieve a desired output of 220W at 220V, the output current required is 1A. To determine the necessary input voltage, the equation can be rearranged to find the minimum input voltage needed at 12V. The calculation shows that to maintain power balance, the input must be at least 18.3V, which is derived from the equation: 12V * 18.3 = 220V * 1A. Therefore, the transformer must be designed with a primary winding that can handle 20A to ensure it is capable of sustaining the current during operation.
When designing the transformer, attention must be paid to the wire gauge and the number of turns in both the primary and secondary windings to ensure efficiency and minimize losses. The core material of the transformer should also be selected to handle the frequency of operation (50Hz) and to reduce core losses. Proper heat dissipation mechanisms should be considered, especially for the transistor or amplifier stage, to prevent overheating during prolonged use. Overall, this circuit is a practical implementation of DC to AC conversion techniques suitable for various applications requiring a 220V AC supply from a 12V DC source.Using this circuit you can convert the 12V dc in to the 220V Ac. In this circuit 4047 is use to generate the square wave of 50hz and amplify the current and then amplify the voltage by using the step transformer. How to calculate transformer rating The basic formula is P=VI and between input output of the transformer we have Power input = Power output.
For example if we want a 220W output at 220V then we need 1A at the output. Then at the input we must have at least 18.3V at 12V because: 12V*18.3 = 220v*1. So you have to wind the step up transformer 12v to 220v but input winding must be capable to bear 20A. 🔗 External reference