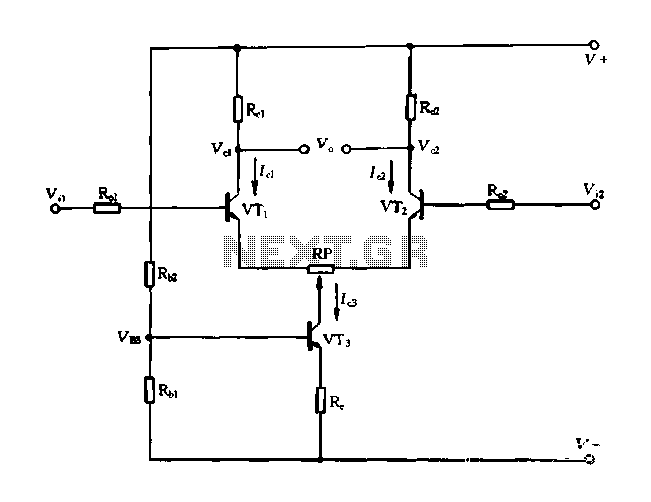
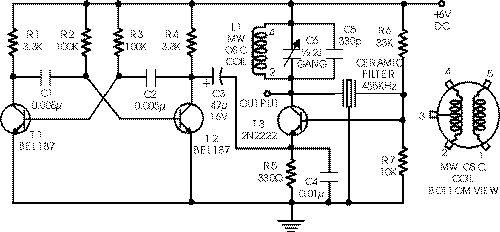
555 high voltage generator circuit
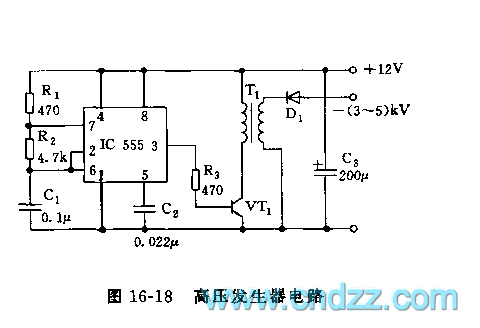
The high voltage generator depicted in figure 16-18 utilizes the 555 timer IC as its primary component. The oscillating voltage produced is enhanced through a step-up transformer. The astable multivibrator configuration comprises the 555 timer along with resistors R1 and R2, and capacitor C1. The oscillation frequency is calculated using the formula f = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2R2) * C1), resulting in a frequency of approximately 2000 Hz. The square wave output generated by the 555 timer is subsequently amplified by transistor VT1 and further boosted by transformer T1.
The high voltage generator circuit operates on the principle of pulse-width modulation (PWM) generated by the 555 timer in astable mode. In this mode, the timer continuously switches between its high and low states, creating a square wave output. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of resistors R1 and R2, and capacitor C1, which set the charge and discharge times of the capacitor, thereby influencing the duty cycle and frequency of the output waveform.
The output square wave from the 555 timer is fed into the base of the transistor VT1, which acts as a switch. When the 555 timer output goes high, VT1 is turned on, allowing current to flow through the primary winding of transformer T1. This action induces a magnetic field in the transformer, which, due to the principles of electromagnetic induction, generates a higher voltage in the secondary winding.
Transformer T1 is critical in stepping up the voltage to the desired high voltage level. The turns ratio of the transformer determines the increase in voltage, and careful selection of this ratio is essential to achieve the required output voltage without exceeding the ratings of the components involved.
Overall, this high voltage generator is suitable for applications where a compact and efficient voltage boosting solution is required. It is important to ensure that all components, especially the transformer and the transistor, are rated for the expected high voltage output to ensure safe and reliable operation. Proper heat dissipation measures should also be considered for the transistor to prevent thermal overload during prolonged operation.As the figure 16-18 shows, the high voltage generator uses the 555 as the core, the oscillation voltage is boosted by the step-up transformer. The astable multivibrator is composed of the 555 and R1?R2?C1, the oscillation frequency f=1.44/(R1+2R2)C1, it is about 2000Hz.
The 555 oscillation square-wave is amplified by VT1, and is boosted by transformer T1, an.. 🔗 External reference
The high voltage generator circuit operates on the principle of pulse-width modulation (PWM) generated by the 555 timer in astable mode. In this mode, the timer continuously switches between its high and low states, creating a square wave output. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of resistors R1 and R2, and capacitor C1, which set the charge and discharge times of the capacitor, thereby influencing the duty cycle and frequency of the output waveform.
The output square wave from the 555 timer is fed into the base of the transistor VT1, which acts as a switch. When the 555 timer output goes high, VT1 is turned on, allowing current to flow through the primary winding of transformer T1. This action induces a magnetic field in the transformer, which, due to the principles of electromagnetic induction, generates a higher voltage in the secondary winding.
Transformer T1 is critical in stepping up the voltage to the desired high voltage level. The turns ratio of the transformer determines the increase in voltage, and careful selection of this ratio is essential to achieve the required output voltage without exceeding the ratings of the components involved.
Overall, this high voltage generator is suitable for applications where a compact and efficient voltage boosting solution is required. It is important to ensure that all components, especially the transformer and the transistor, are rated for the expected high voltage output to ensure safe and reliable operation. Proper heat dissipation measures should also be considered for the transistor to prevent thermal overload during prolonged operation.As the figure 16-18 shows, the high voltage generator uses the 555 as the core, the oscillation voltage is boosted by the step-up transformer. The astable multivibrator is composed of the 555 and R1?R2?C1, the oscillation frequency f=1.44/(R1+2R2)C1, it is about 2000Hz.
The 555 oscillation square-wave is amplified by VT1, and is boosted by transformer T1, an.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713