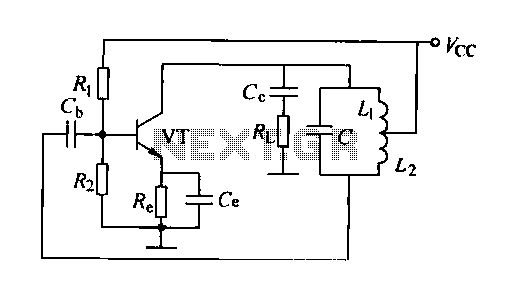
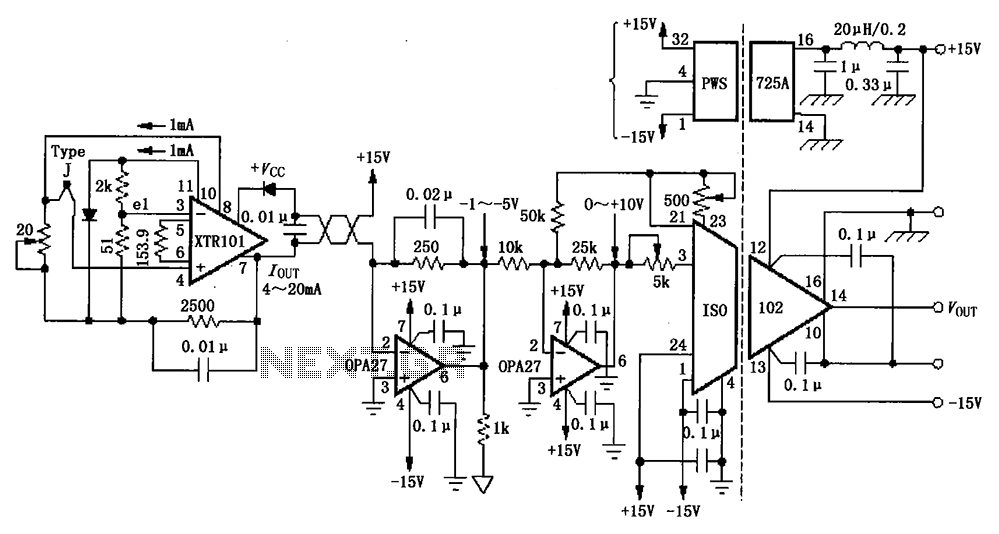
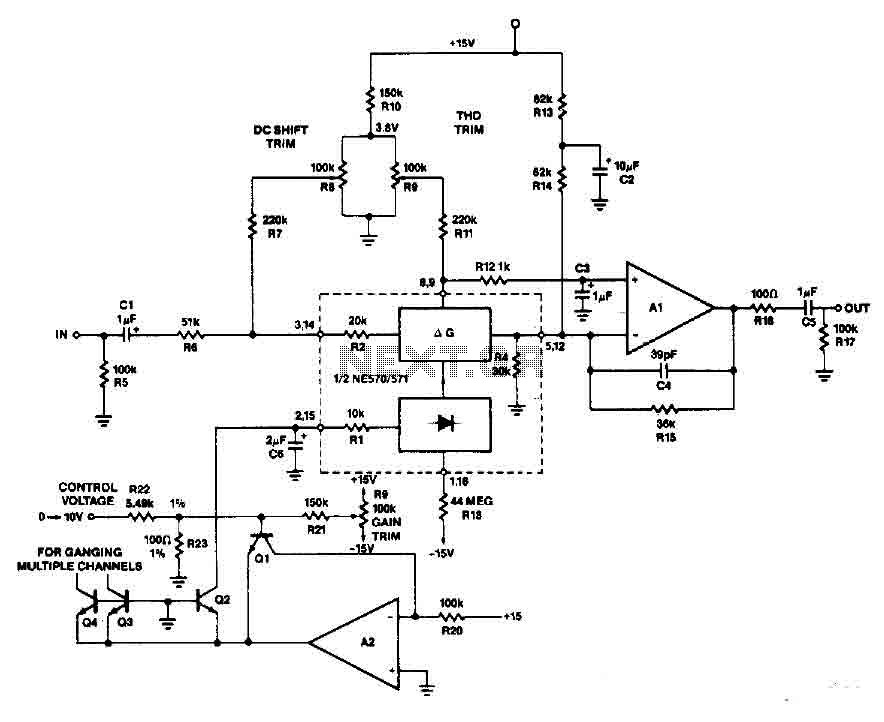
555 IC For 12V Lead Acid Battery Desulphator Circuit
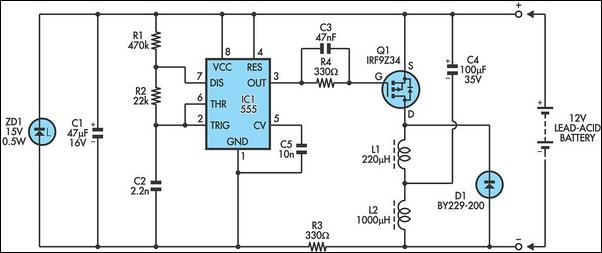
The following circuit illustrates a 6/12/24V Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuit Diagram. Features: It is essentially a high-voltage pulse generator.
The circuit diagram for a 6/12/24V Lead Acid Battery Charger is designed to efficiently charge lead-acid batteries of varying voltages. The primary function of this circuit is to convert the input AC voltage into a suitable DC voltage that can be used to charge the batteries while ensuring the safety and longevity of the battery cells.
At the core of the circuit is a high-voltage pulse generator, which is responsible for producing the necessary charging pulses. This pulse generator typically consists of a transformer, rectifier diodes, and a smoothing capacitor. The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a lower level suitable for charging the battery. The rectifier diodes convert the AC voltage to pulsating DC, which is then smoothed by the capacitor to provide a more stable DC output.
The circuit also incorporates a voltage regulator to prevent overcharging, which can be detrimental to lead-acid batteries. This regulator monitors the output voltage and adjusts the charging current accordingly, ensuring that the battery receives the correct voltage level. Additionally, a current limiting feature may be included to restrict the charging current to a safe level, further protecting the battery from damage.
For versatility, the charger can be designed with selectable voltage outputs (6V, 12V, and 24V) using a switch or jumper settings. This allows the charger to be used with different battery configurations without the need for multiple chargers.
Safety features, such as fuses and thermal protection, are critical in this design to prevent overheating and potential hazards during the charging process. Overall, this circuit serves as an effective solution for charging lead-acid batteries, ensuring optimal performance and extending the life of the batteries.The following circuit shows about 6/12/24V Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuit Diagram. Features: ssentially a high-voltage pulse generator which is .. 🔗 External reference
The circuit diagram for a 6/12/24V Lead Acid Battery Charger is designed to efficiently charge lead-acid batteries of varying voltages. The primary function of this circuit is to convert the input AC voltage into a suitable DC voltage that can be used to charge the batteries while ensuring the safety and longevity of the battery cells.
At the core of the circuit is a high-voltage pulse generator, which is responsible for producing the necessary charging pulses. This pulse generator typically consists of a transformer, rectifier diodes, and a smoothing capacitor. The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a lower level suitable for charging the battery. The rectifier diodes convert the AC voltage to pulsating DC, which is then smoothed by the capacitor to provide a more stable DC output.
The circuit also incorporates a voltage regulator to prevent overcharging, which can be detrimental to lead-acid batteries. This regulator monitors the output voltage and adjusts the charging current accordingly, ensuring that the battery receives the correct voltage level. Additionally, a current limiting feature may be included to restrict the charging current to a safe level, further protecting the battery from damage.
For versatility, the charger can be designed with selectable voltage outputs (6V, 12V, and 24V) using a switch or jumper settings. This allows the charger to be used with different battery configurations without the need for multiple chargers.
Safety features, such as fuses and thermal protection, are critical in this design to prevent overheating and potential hazards during the charging process. Overall, this circuit serves as an effective solution for charging lead-acid batteries, ensuring optimal performance and extending the life of the batteries.The following circuit shows about 6/12/24V Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuit Diagram. Features: ssentially a high-voltage pulse generator which is .. 🔗 External reference