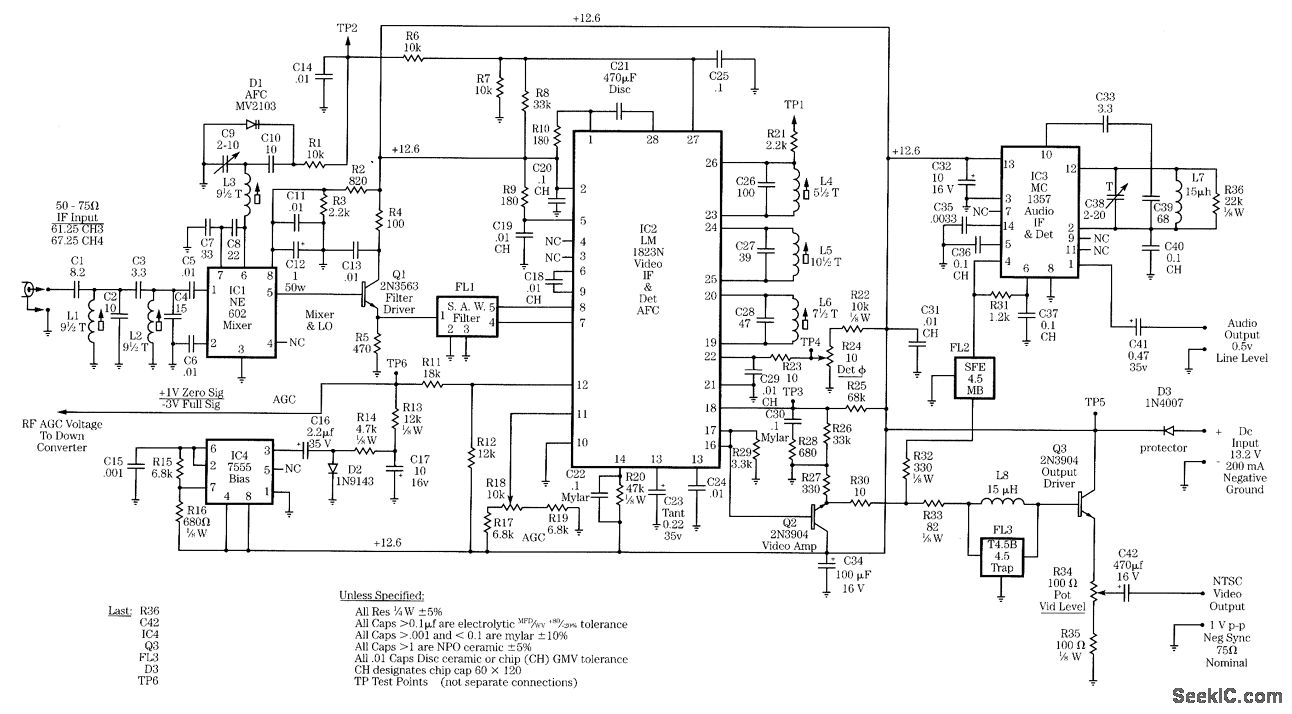
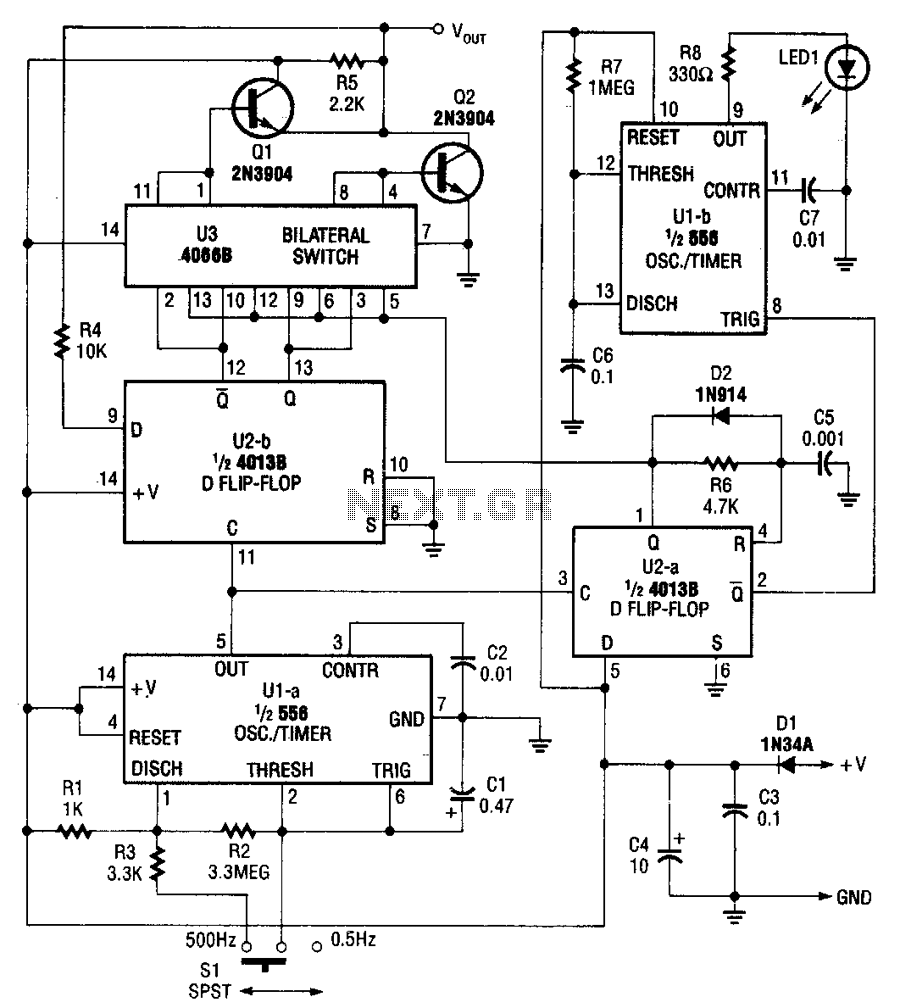
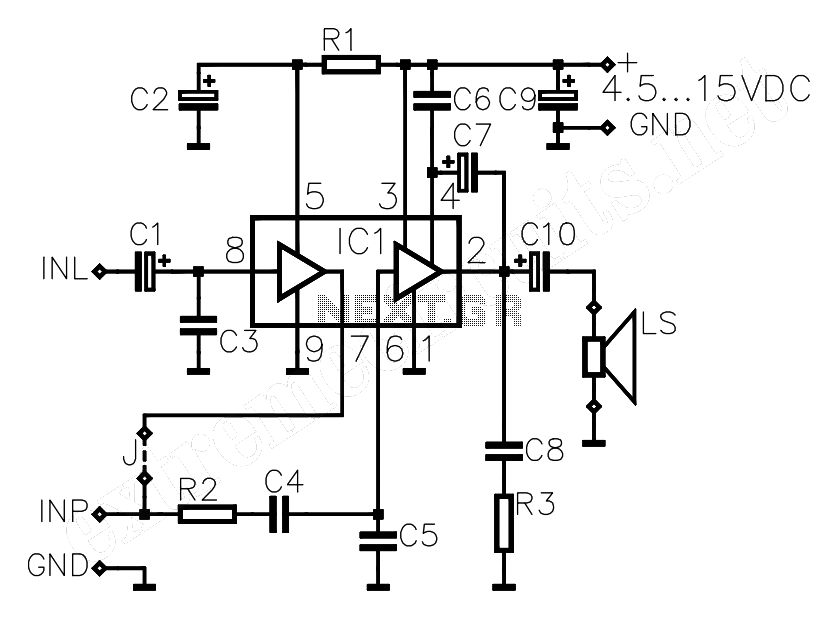
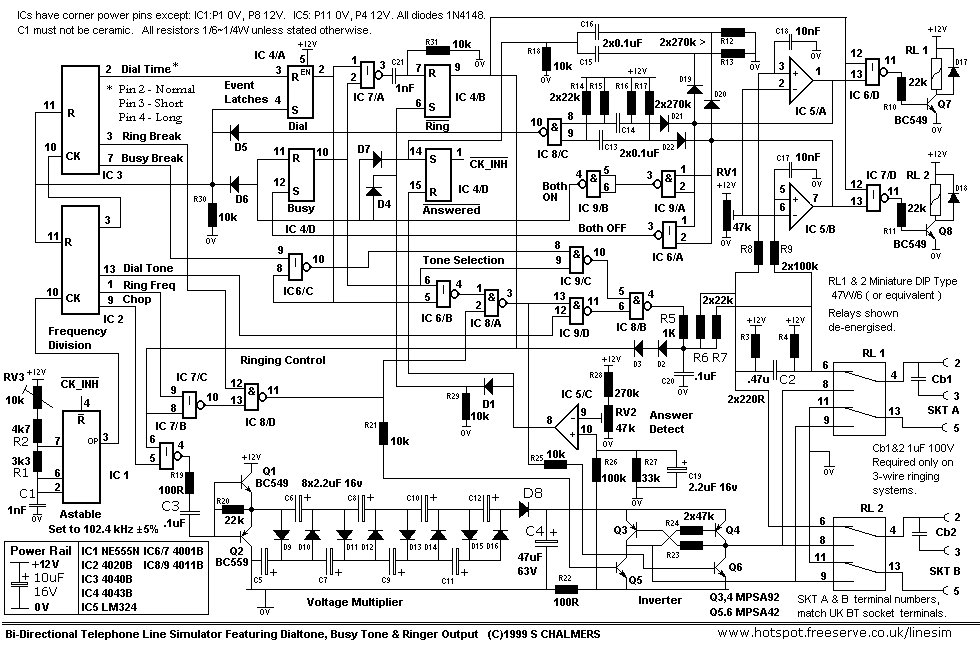
simple line follower robot logic circuits
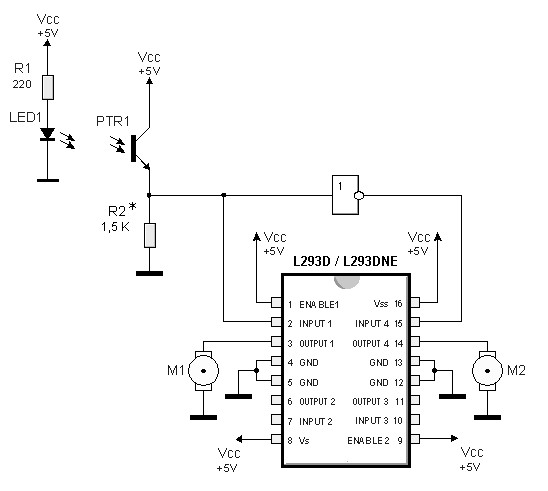
By utilizing logic chips, the behavior of a robot can be enhanced, allowing for the implementation of more complex algorithms.
Logic chips, also known as logic gates or digital logic integrated circuits, are fundamental components in digital electronics that perform logical operations on one or more binary inputs to produce a single binary output. These chips can be combined in various configurations to create more sophisticated decision-making processes within robotic systems.
For instance, a combination of AND, OR, and NOT gates can be used to develop a simple control system that allows a robot to respond to environmental stimuli. By integrating multiple logic chips, a robot can be programmed to execute complex tasks such as obstacle avoidance, pathfinding, and adaptive learning based on its interactions with the surroundings.
To design a circuit using logic chips for a robot, one might start with a truth table that defines the desired behavior. This table will outline the inputs (such as sensors detecting obstacles) and the corresponding outputs (such as motor controls for movement). The logic functions derived from the truth table can then be implemented using various logic gates, which can be arranged on a breadboard or printed circuit board (PCB).
In addition to basic logic operations, flip-flops can be incorporated to create memory elements that allow the robot to retain state information between actions. This enables the implementation of more advanced algorithms, such as state machines or finite automata, which can significantly enhance the robot's operational capabilities.
Overall, the use of logic chips in robotic design not only simplifies the implementation of complex behaviors but also allows for scalability and adaptability in the robot's functionality.Using logic chips we can make the robot`s behavior more interesting and can implement more complex algorithms.. 🔗 External reference
Logic chips, also known as logic gates or digital logic integrated circuits, are fundamental components in digital electronics that perform logical operations on one or more binary inputs to produce a single binary output. These chips can be combined in various configurations to create more sophisticated decision-making processes within robotic systems.
For instance, a combination of AND, OR, and NOT gates can be used to develop a simple control system that allows a robot to respond to environmental stimuli. By integrating multiple logic chips, a robot can be programmed to execute complex tasks such as obstacle avoidance, pathfinding, and adaptive learning based on its interactions with the surroundings.
To design a circuit using logic chips for a robot, one might start with a truth table that defines the desired behavior. This table will outline the inputs (such as sensors detecting obstacles) and the corresponding outputs (such as motor controls for movement). The logic functions derived from the truth table can then be implemented using various logic gates, which can be arranged on a breadboard or printed circuit board (PCB).
In addition to basic logic operations, flip-flops can be incorporated to create memory elements that allow the robot to retain state information between actions. This enables the implementation of more advanced algorithms, such as state machines or finite automata, which can significantly enhance the robot's operational capabilities.
Overall, the use of logic chips in robotic design not only simplifies the implementation of complex behaviors but also allows for scalability and adaptability in the robot's functionality.Using logic chips we can make the robot`s behavior more interesting and can implement more complex algorithms.. 🔗 External reference