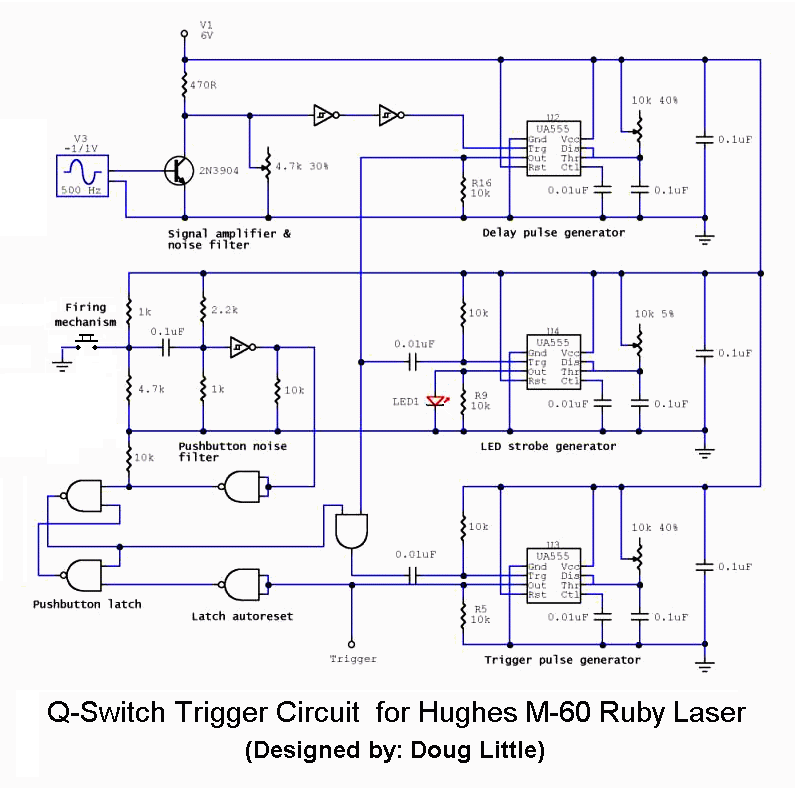
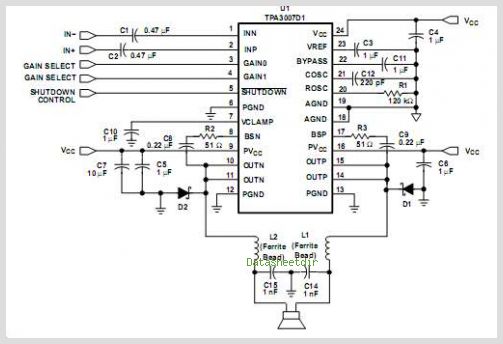
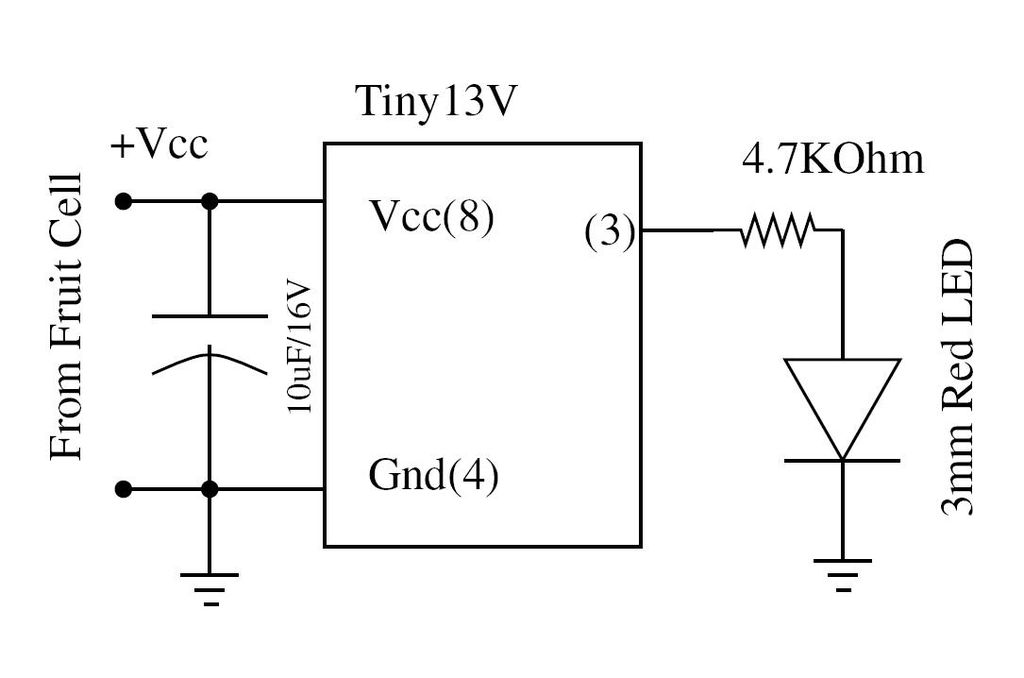
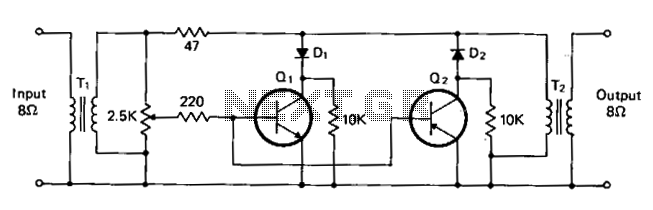
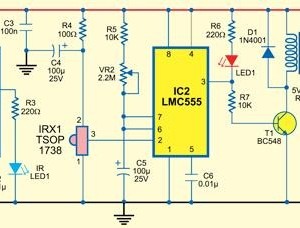
555 low power timing circuit diagram
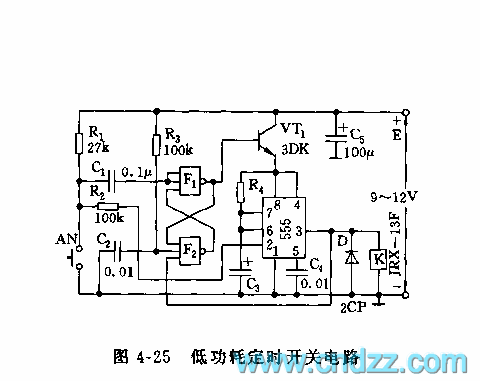
555 low power timing circuit diagram. The diagram is from the technical information of Chinaicmart. For more detailed information about the circuit diagram.
The 555 timer IC is widely utilized in various applications due to its versatility and ease of use. In a low power timing circuit configuration, the 555 timer can function in both astable and monostable modes, allowing it to generate precise timing intervals or oscillations.
In the astable mode, the circuit continuously oscillates between high and low states, producing a square wave output. This configuration requires two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C1) connected to the threshold and discharge pins of the 555 timer. The frequency of oscillation and duty cycle can be calculated using the formulas:
Frequency (f) = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C1)
Duty Cycle (%) = (R2 / (R1 + 2 * R2)) * 100
In monostable mode, the 555 timer generates a single pulse when triggered. The duration of the pulse is determined by a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C) connected to the timing pins. The pulse width can be calculated as:
Pulse Width (T) = 1.1 * R * C
To minimize power consumption, low value resistors and capacitors can be selected, and the timer can be powered using low voltage sources. Additionally, the use of bypass capacitors near the power supply pins can help reduce noise and improve circuit stability.
The application of the 555 low power timing circuit can be found in timer applications, pulse generation, LED flashing circuits, and many other timing-related tasks. Proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed to ensure optimal performance and minimize interference.555 low power timing circuit diagram The diagram is from the tech information of chinaicmart. IF for more detailed infomation of the circuit diagram.. 🔗 External reference
The 555 timer IC is widely utilized in various applications due to its versatility and ease of use. In a low power timing circuit configuration, the 555 timer can function in both astable and monostable modes, allowing it to generate precise timing intervals or oscillations.
In the astable mode, the circuit continuously oscillates between high and low states, producing a square wave output. This configuration requires two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C1) connected to the threshold and discharge pins of the 555 timer. The frequency of oscillation and duty cycle can be calculated using the formulas:
Frequency (f) = 1.44 / ((R1 + 2 * R2) * C1)
Duty Cycle (%) = (R2 / (R1 + 2 * R2)) * 100
In monostable mode, the 555 timer generates a single pulse when triggered. The duration of the pulse is determined by a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C) connected to the timing pins. The pulse width can be calculated as:
Pulse Width (T) = 1.1 * R * C
To minimize power consumption, low value resistors and capacitors can be selected, and the timer can be powered using low voltage sources. Additionally, the use of bypass capacitors near the power supply pins can help reduce noise and improve circuit stability.
The application of the 555 low power timing circuit can be found in timer applications, pulse generation, LED flashing circuits, and many other timing-related tasks. Proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed to ensure optimal performance and minimize interference.555 low power timing circuit diagram The diagram is from the tech information of chinaicmart. IF for more detailed infomation of the circuit diagram.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713