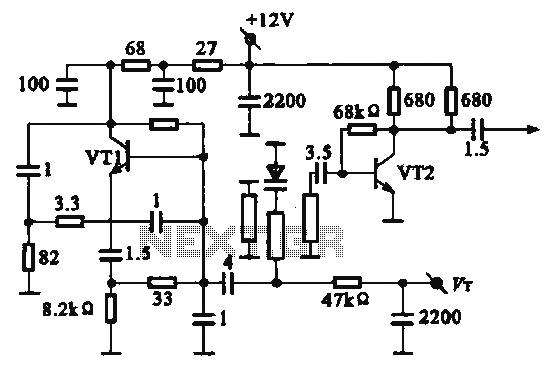
Assemble the AVR Tiny MIcrocontroller Circuit
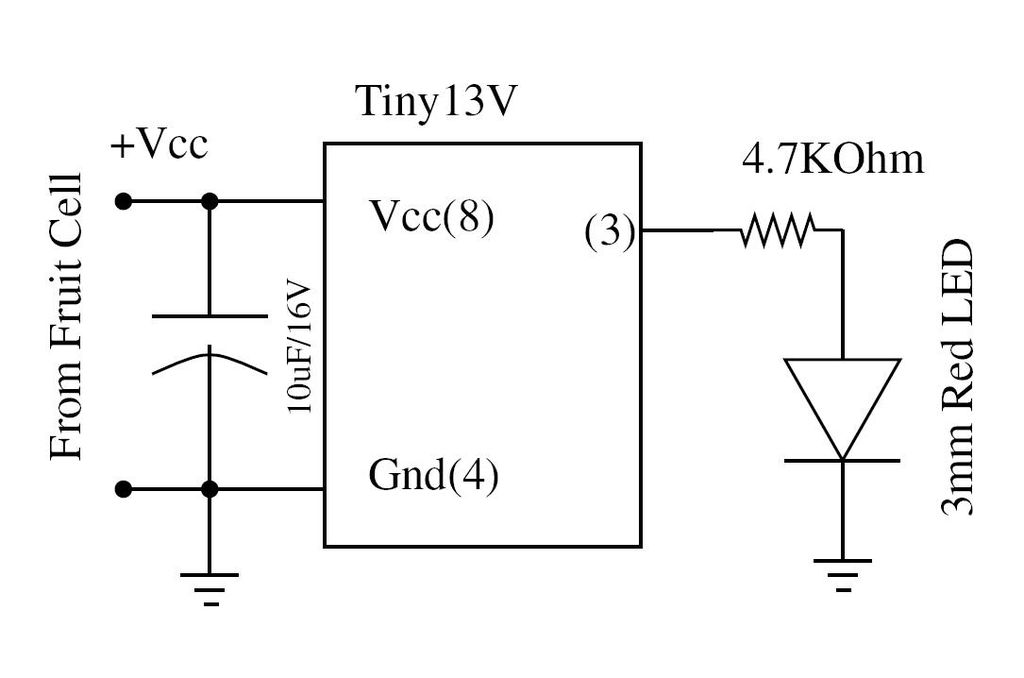
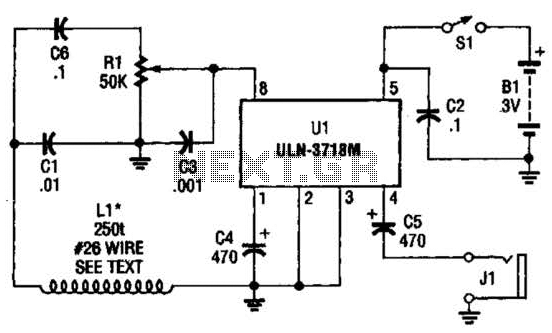
Wire the circuit diagram shown here on a breadboard. The choice of V type of AVR is important. For example, Tiny13V is very appropriate for such an application.
To successfully implement the circuit diagram on a breadboard, several considerations must be taken into account. The AVR microcontroller, specifically the ATtiny13V, is a compact, low-power option suitable for various applications, particularly in embedded systems. This microcontroller operates at a voltage range of 1.8V to 5.5V, making it versatile for battery-powered projects.
When wiring the circuit, it is essential to ensure that the power supply voltage corresponds to the requirements of the ATtiny13V. The microcontroller should be connected to a stable power source, with appropriate decoupling capacitors placed close to its power pins to minimize noise and voltage fluctuations. Typically, a 0.1µF capacitor is used for decoupling.
The input and output pins of the ATtiny13V must be configured according to the intended application. For example, if the circuit involves interfacing with sensors or actuators, the corresponding pins should be connected to the respective components. Pull-up or pull-down resistors may be necessary to ensure proper logic levels are maintained on the input pins.
Moreover, it is advisable to incorporate a reset button in the design to allow for easy reinitialization of the microcontroller. This button should be connected to the reset pin, typically with a pull-up resistor to the Vcc.
For programming the ATtiny13V, a suitable programmer must be connected to the appropriate pins on the microcontroller. The ISP (In-System Programming) interface is commonly used for this purpose, allowing for easy updates and modifications to the firmware.
In summary, careful attention to the wiring and configuration of the ATtiny13V on the breadboard will facilitate successful operation of the circuit, ensuring that all components are properly connected and that the microcontroller receives the necessary power and signals for its intended function.Wire the circuit diagram shown here on a bread board. The choice of V type of AVR is important. For example Tiny13V is very appropriate for such an ex.. 🔗 External reference
To successfully implement the circuit diagram on a breadboard, several considerations must be taken into account. The AVR microcontroller, specifically the ATtiny13V, is a compact, low-power option suitable for various applications, particularly in embedded systems. This microcontroller operates at a voltage range of 1.8V to 5.5V, making it versatile for battery-powered projects.
When wiring the circuit, it is essential to ensure that the power supply voltage corresponds to the requirements of the ATtiny13V. The microcontroller should be connected to a stable power source, with appropriate decoupling capacitors placed close to its power pins to minimize noise and voltage fluctuations. Typically, a 0.1µF capacitor is used for decoupling.
The input and output pins of the ATtiny13V must be configured according to the intended application. For example, if the circuit involves interfacing with sensors or actuators, the corresponding pins should be connected to the respective components. Pull-up or pull-down resistors may be necessary to ensure proper logic levels are maintained on the input pins.
Moreover, it is advisable to incorporate a reset button in the design to allow for easy reinitialization of the microcontroller. This button should be connected to the reset pin, typically with a pull-up resistor to the Vcc.
For programming the ATtiny13V, a suitable programmer must be connected to the appropriate pins on the microcontroller. The ISP (In-System Programming) interface is commonly used for this purpose, allowing for easy updates and modifications to the firmware.
In summary, careful attention to the wiring and configuration of the ATtiny13V on the breadboard will facilitate successful operation of the circuit, ensuring that all components are properly connected and that the microcontroller receives the necessary power and signals for its intended function.Wire the circuit diagram shown here on a bread board. The choice of V type of AVR is important. For example Tiny13V is very appropriate for such an ex.. 🔗 External reference