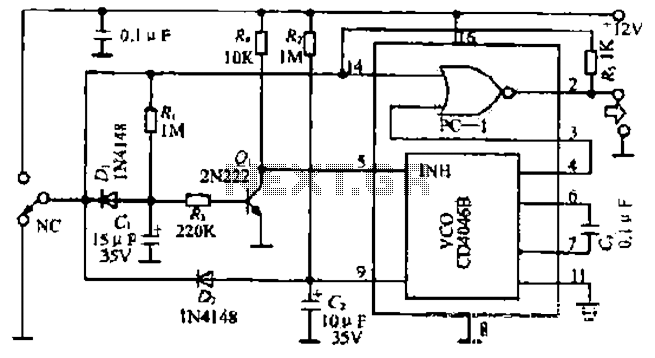
555 make use of digital amplifier circuit diagram
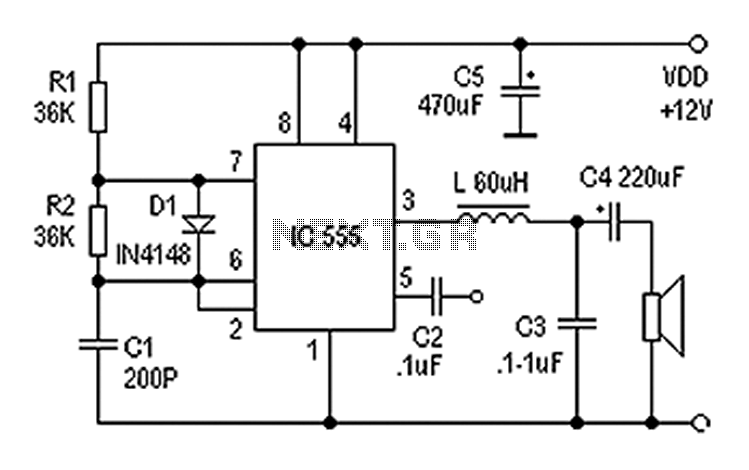
Also known as a digital amplifier, the Class-D amplifier is characterized by its compact size and high efficiency. This circuit utilizes a 555 timer IC to create a Class D amplifier. The 555 timer operates as a controllable multivibrator, where an audio signal is fed into the control terminal to generate a pulse width modulated (PWM) signal. This setup meets the basic requirements for general audio listening. The 555 timer, along with resistors R1 and R2, and capacitor C1, is configured to create a 100 kHz multivibrator with a 50% duty cycle. The audio signal is applied to pin 5 of the IC, and the output at pin 3 produces a PWM signal with an amplitude that is proportional to the input audio signal. This PWM signal is then processed through an inductor L and capacitor C3 to filter the output before driving the speaker.
The Class-D amplifier circuit described is based on the operation of the 555 timer IC, which functions as a versatile multivibrator capable of generating PWM signals. The circuit is designed for audio amplification, taking advantage of the high efficiency and compact nature of Class-D amplification technology.
In this configuration, the input audio signal is connected to pin 5 of the 555 timer. The resistors R1 and R2, along with capacitor C1, are selected to set the frequency of the PWM output to 100 kHz with a 50% duty cycle. This frequency is optimal for audio applications, allowing for effective modulation of the audio signal without significant distortion.
The output from pin 3 of the 555 timer provides a PWM signal that varies in width according to the amplitude of the input audio signal. This relationship is crucial for maintaining audio fidelity, as the width of the pulses directly correlates to the amplitude of the original audio waveform.
To drive a speaker, the PWM signal is passed through an inductor L and capacitor C3, which serve as a low-pass filter. This filtering process smooths the PWM signal, converting it back into an analog audio signal suitable for driving a speaker. The inductor helps to block high-frequency components, while the capacitor assists in smoothing the output, ensuring that the final signal is clean and free of unwanted artifacts.
Overall, this Class-D amplifier circuit using the 555 timer is an efficient and effective solution for audio amplification, providing a compact design with high performance for various listening applications.Also known as digital amplifier Class-D amplifier with small size, high efficiency characteristics. Here are a circuit made easy with 555 Class D amplifier. It is the use of ci rcuit 555 constitute a controllable multivibrator, an audio signal input to the control terminal to obtain a pulse width modulated signal (as shown), to meet the basic requirements for general listening. By the IC 555 and R1, R2, C1 and other components 100KHz controlled multivibrator 50% duty cycle, control the input audio signal terminal 5 feet, 3 feet will get the pulse width of the input signal amplitude is proportional to the pulse signal by L, C3 to answer the call, push the speaker after filtering.
The Class-D amplifier circuit described is based on the operation of the 555 timer IC, which functions as a versatile multivibrator capable of generating PWM signals. The circuit is designed for audio amplification, taking advantage of the high efficiency and compact nature of Class-D amplification technology.
In this configuration, the input audio signal is connected to pin 5 of the 555 timer. The resistors R1 and R2, along with capacitor C1, are selected to set the frequency of the PWM output to 100 kHz with a 50% duty cycle. This frequency is optimal for audio applications, allowing for effective modulation of the audio signal without significant distortion.
The output from pin 3 of the 555 timer provides a PWM signal that varies in width according to the amplitude of the input audio signal. This relationship is crucial for maintaining audio fidelity, as the width of the pulses directly correlates to the amplitude of the original audio waveform.
To drive a speaker, the PWM signal is passed through an inductor L and capacitor C3, which serve as a low-pass filter. This filtering process smooths the PWM signal, converting it back into an analog audio signal suitable for driving a speaker. The inductor helps to block high-frequency components, while the capacitor assists in smoothing the output, ensuring that the final signal is clean and free of unwanted artifacts.
Overall, this Class-D amplifier circuit using the 555 timer is an efficient and effective solution for audio amplification, providing a compact design with high performance for various listening applications.Also known as digital amplifier Class-D amplifier with small size, high efficiency characteristics. Here are a circuit made easy with 555 Class D amplifier. It is the use of ci rcuit 555 constitute a controllable multivibrator, an audio signal input to the control terminal to obtain a pulse width modulated signal (as shown), to meet the basic requirements for general listening. By the IC 555 and R1, R2, C1 and other components 100KHz controlled multivibrator 50% duty cycle, control the input audio signal terminal 5 feet, 3 feet will get the pulse width of the input signal amplitude is proportional to the pulse signal by L, C3 to answer the call, push the speaker after filtering.