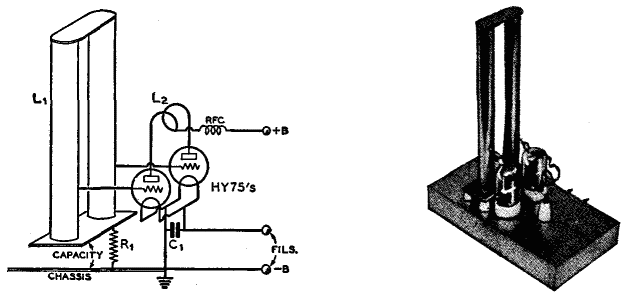
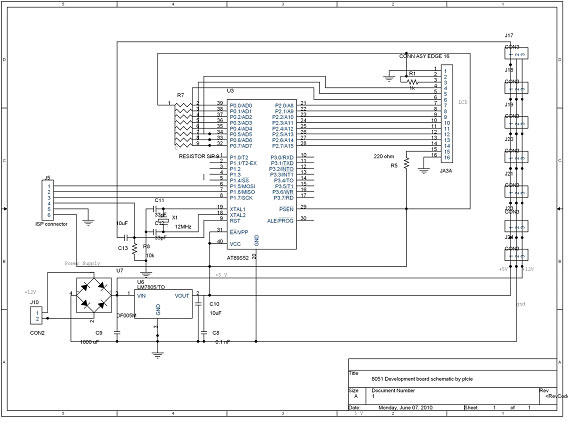
555 precision temperature sensor with temperature frequency converting circuit diagram
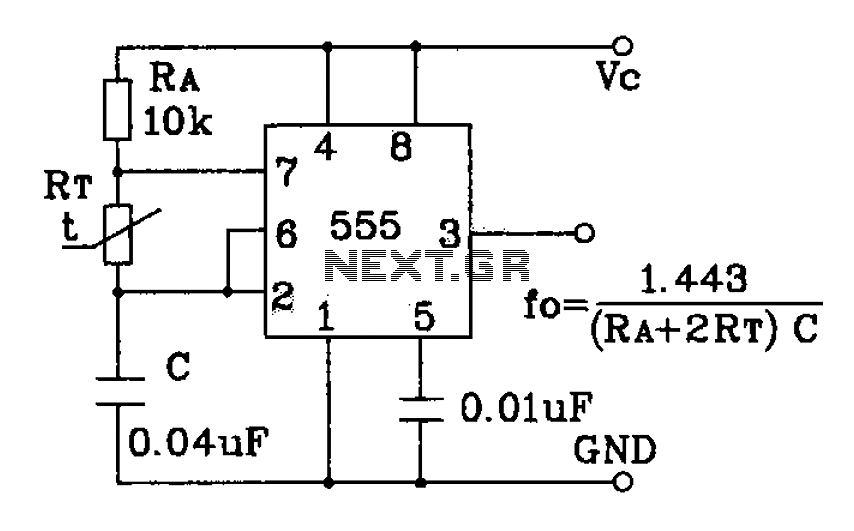
555 precision temperature sensor with temperature frequency converting circuit diagram consisting of:
The 555 precision temperature sensor operates by converting temperature variations into frequency signals. This circuit typically utilizes a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode to generate a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal whose frequency is directly proportional to the temperature being measured.
In this configuration, the temperature sensor (often a thermistor or an integrated temperature sensing component) is connected to the input of the 555 timer. As the temperature changes, the resistance of the sensor alters, which in turn modifies the charge and discharge times of the timing capacitor connected to the 555 timer. This results in a frequency output that varies with temperature.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to fine-tune the frequency response and to stabilize the operation of the 555 timer. The output frequency can be measured using a frequency counter or microcontroller, allowing for precise temperature monitoring and control applications.
This design is particularly useful in applications that require temperature measurement in real-time, such as in HVAC systems, environmental monitoring, and industrial processes where temperature regulation is critical. The simplicity and reliability of the 555 timer make it an excellent choice for integrating temperature sensing capabilities into various electronic systems.555 precision temperature sensor with temperature frequency converting circuit diagram consisting of:
The 555 precision temperature sensor operates by converting temperature variations into frequency signals. This circuit typically utilizes a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode to generate a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal whose frequency is directly proportional to the temperature being measured.
In this configuration, the temperature sensor (often a thermistor or an integrated temperature sensing component) is connected to the input of the 555 timer. As the temperature changes, the resistance of the sensor alters, which in turn modifies the charge and discharge times of the timing capacitor connected to the 555 timer. This results in a frequency output that varies with temperature.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to fine-tune the frequency response and to stabilize the operation of the 555 timer. The output frequency can be measured using a frequency counter or microcontroller, allowing for precise temperature monitoring and control applications.
This design is particularly useful in applications that require temperature measurement in real-time, such as in HVAC systems, environmental monitoring, and industrial processes where temperature regulation is critical. The simplicity and reliability of the 555 timer make it an excellent choice for integrating temperature sensing capabilities into various electronic systems.555 precision temperature sensor with temperature frequency converting circuit diagram consisting of:
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713