60 Watt Guitar Amplifier

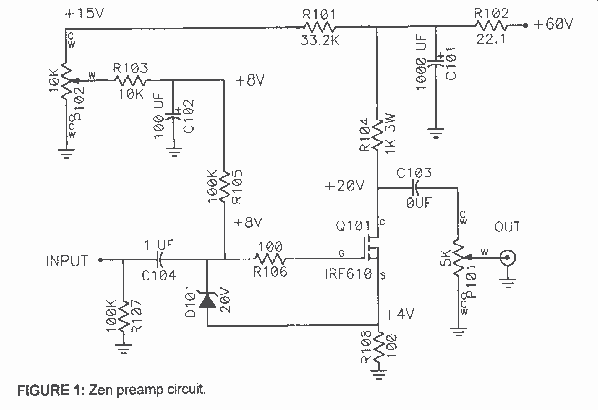
This design utilizes a well-established circuit topology for the power amplifier, employing a single-rail supply of approximately 60V and capacitor coupling for the speakers. The advantages of this configuration for a guitar amplifier include a straightforward circuit design, even at relatively high power outputs, and an inherent degree of loudspeaker protection provided by capacitor C8, which prevents the voltage supply from reaching the loudspeakers in the event of output transistor failure. The preamplifier operates on the same 60V rails as the power amplifier, enabling the implementation of a two-transistor gain block capable of delivering around 20V RMS output, thus ensuring a high input overload capability. The specified Darlington transistor types may be oversized for this application; alternatives such as MJ11014 (Q3) and MJ11013 (Q4) or TIP142 (Q3) and TIP147 (Q4) can be used instead. Diodes D1 and D2 can be any Schottky-barrier types, but using common 1N4148 silicon diodes for D1 and D2 results in a softer harmonic modifier operation. It is crucial that the sensing transistor (Q2) is thermally coupled as closely as possible to the output transistors when using Darlington transistors as output devices. A TO126-case transistor type is selected for easy mounting on the heatsink, positioned close to the output pair. Resistor R9 requires adjustment to measure approximately half the voltage supply across the positive lead of capacitor C7 and ground. Fine-tuning can be accomplished with an oscilloscope to achieve symmetrical clipping of the output waveform at maximum output power.
This power amplifier circuit design is characterized by its efficient use of a single-rail power supply, which simplifies the overall architecture while maintaining high performance levels. The capacitor coupling method employed for the speakers not only facilitates the necessary AC signal transmission but also serves as a protective barrier against DC faults that could potentially damage the loudspeakers. The integration of a two-transistor gain block in the preamplifier stage allows for substantial voltage gain, enhancing the amplifier's ability to handle high input signals without distortion.
The choice of output transistors is critical; while Darlington pairs are known for their high current gain, their size can lead to inefficiencies in this specific application. The suggested alternatives (MJ11014, MJ11013, TIP142, and TIP147) provide a balance between performance and size, ensuring that the amplifier operates within its optimal range without unnecessary excess.
The inclusion of Schottky-barrier diodes for protection against back EMF and other transients is a standard practice in amplifier design. However, opting for 1N4148 diodes softens the harmonic distortion characteristics, which may be desirable in a guitar amplifier context where musicality and tonal quality are paramount.
Thermal management is another crucial aspect of this design. The close thermal coupling of the sensing transistor (Q2) to the output transistors enables accurate temperature feedback, ensuring that the circuit can respond effectively to changes in operating conditions. This is vital for maintaining performance and reliability under varying load conditions.
Finally, the adjustment of resistor R9 to achieve a specific voltage across C7 is essential for optimizing the amplifier's performance. Using an oscilloscope for this calibration allows for precise adjustments, ensuring that the output waveform remains symmetrical and free from unwanted clipping, which is particularly important for maintaining audio fidelity at high power levels. This attention to detail in both component selection and circuit configuration contributes to a robust and effective guitar amplifier design.This design adopts a well established circuit topology for the power amplifier, using a single-rail supply of about 60V and capacitor-coupling for the speaker(s). The advantages for a guitar amplifier are the very simple circuitry, even for comparatively high power outputs, and a certain built-in degree of loudspeaker protection, due to capacitor
C8, preventing the voltage supply to be conveyed into loudspeakers in case of output transistors` failure. The preamp is powered by the same 60V rails as the power amplifier, allowing to implement a two-transistors gain-block capable of delivering about 20V RMS output.
This provides a very high input overload capability. The Darlington transistor types listed could be too oversized for such a design. You can substitute them with MJ11014 (Q3) and MJ11013 (Q4) or TIP142 (Q3) and TIP147 (Q4). D1 and D2 can be any Schottky-barrier diode types. With these devices, the harmonic modifier operation will be hard. Using for D1 and D2 two common 1N4148 silicon diodes, the harmonic modifier operation will be softer. In all cases where Darlington transistors are used as the output devices it is essential that the sensing transistor (Q2) should be in as close thermal contact with the output transistors as possible.
Therefore a TO126-case transistor type was chosen for easy bolting on the heatsink, very close to the output pair. R9 must be trimmed in order to measure about half the voltage supply across the positive lead of C7 and ground.
A better setting can be done using an oscilloscope, in order to obtain a symmetrical clipping of the output wave form at maximum output power. 🔗 External reference
This power amplifier circuit design is characterized by its efficient use of a single-rail power supply, which simplifies the overall architecture while maintaining high performance levels. The capacitor coupling method employed for the speakers not only facilitates the necessary AC signal transmission but also serves as a protective barrier against DC faults that could potentially damage the loudspeakers. The integration of a two-transistor gain block in the preamplifier stage allows for substantial voltage gain, enhancing the amplifier's ability to handle high input signals without distortion.
The choice of output transistors is critical; while Darlington pairs are known for their high current gain, their size can lead to inefficiencies in this specific application. The suggested alternatives (MJ11014, MJ11013, TIP142, and TIP147) provide a balance between performance and size, ensuring that the amplifier operates within its optimal range without unnecessary excess.
The inclusion of Schottky-barrier diodes for protection against back EMF and other transients is a standard practice in amplifier design. However, opting for 1N4148 diodes softens the harmonic distortion characteristics, which may be desirable in a guitar amplifier context where musicality and tonal quality are paramount.
Thermal management is another crucial aspect of this design. The close thermal coupling of the sensing transistor (Q2) to the output transistors enables accurate temperature feedback, ensuring that the circuit can respond effectively to changes in operating conditions. This is vital for maintaining performance and reliability under varying load conditions.
Finally, the adjustment of resistor R9 to achieve a specific voltage across C7 is essential for optimizing the amplifier's performance. Using an oscilloscope for this calibration allows for precise adjustments, ensuring that the output waveform remains symmetrical and free from unwanted clipping, which is particularly important for maintaining audio fidelity at high power levels. This attention to detail in both component selection and circuit configuration contributes to a robust and effective guitar amplifier design.This design adopts a well established circuit topology for the power amplifier, using a single-rail supply of about 60V and capacitor-coupling for the speaker(s). The advantages for a guitar amplifier are the very simple circuitry, even for comparatively high power outputs, and a certain built-in degree of loudspeaker protection, due to capacitor
C8, preventing the voltage supply to be conveyed into loudspeakers in case of output transistors` failure. The preamp is powered by the same 60V rails as the power amplifier, allowing to implement a two-transistors gain-block capable of delivering about 20V RMS output.
This provides a very high input overload capability. The Darlington transistor types listed could be too oversized for such a design. You can substitute them with MJ11014 (Q3) and MJ11013 (Q4) or TIP142 (Q3) and TIP147 (Q4). D1 and D2 can be any Schottky-barrier diode types. With these devices, the harmonic modifier operation will be hard. Using for D1 and D2 two common 1N4148 silicon diodes, the harmonic modifier operation will be softer. In all cases where Darlington transistors are used as the output devices it is essential that the sensing transistor (Q2) should be in as close thermal contact with the output transistors as possible.
Therefore a TO126-case transistor type was chosen for easy bolting on the heatsink, very close to the output pair. R9 must be trimmed in order to measure about half the voltage supply across the positive lead of C7 and ground.
A better setting can be done using an oscilloscope, in order to obtain a symmetrical clipping of the output wave form at maximum output power. 🔗 External reference