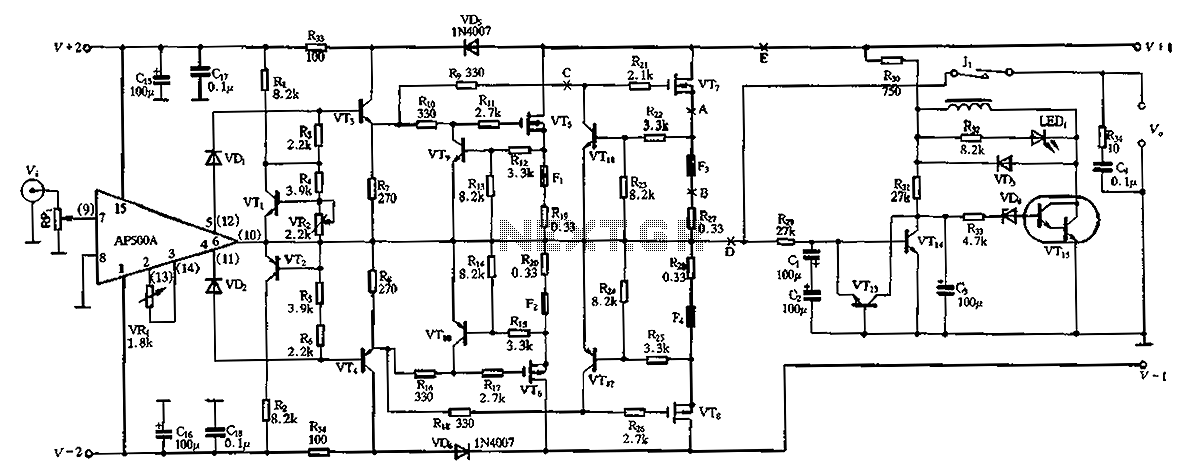
6w audio amplifier with preamplifier
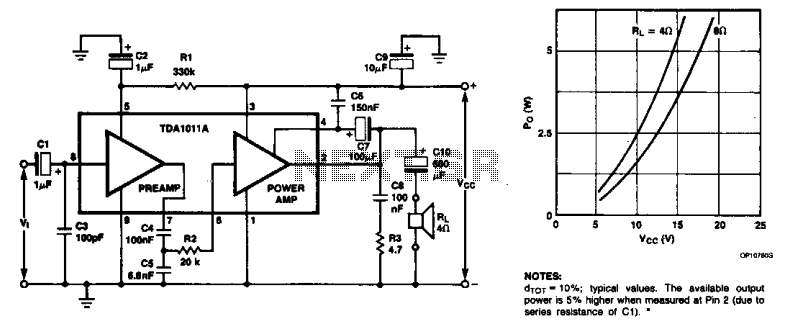
The monolithic integrated audio amplifier circuit is specifically designed for portable radio and recorder applications, delivering up to 4 W into a 4-ohm load impedance. The power output is close to 6 watts RMS.
The monolithic integrated audio amplifier circuit is engineered to provide high-quality audio amplification suitable for compact devices such as portable radios and recorders. With an output capability of up to 4 watts into a 4-ohm load, this amplifier is optimized for efficiency and performance in battery-powered applications.
The circuit typically employs a Class AB design, which allows for a balance between power efficiency and audio fidelity, minimizing distortion while maximizing output power. The amplifier's architecture may include integrated components such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors, all housed within a single chip to reduce size and improve reliability.
In addition to its nominal output of 4 watts, the amplifier can achieve a peak power output of approximately 6 watts RMS under certain conditions, making it suitable for driving small speakers or headphones effectively. The design may also incorporate features such as thermal protection, short-circuit protection, and a built-in gain control to enhance usability and safeguard the device during operation.
The circuit's input stage is typically configured for low noise and high input impedance, allowing it to interface easily with various audio sources. The output stage is designed to deliver sufficient current to drive the load while maintaining low distortion levels, ensuring clear and dynamic sound reproduction.
Overall, this monolithic integrated audio amplifier circuit is a versatile solution for audio amplification in portable devices, combining compact size with robust performance characteristics.The monolithic integrated audio amplifier circuit is especially designed for portable radio and recorder applications and delivers up to 4 W in a 4 ohm load impedance. the power out is near to 6 watts rms. 🔗 External reference
The monolithic integrated audio amplifier circuit is engineered to provide high-quality audio amplification suitable for compact devices such as portable radios and recorders. With an output capability of up to 4 watts into a 4-ohm load, this amplifier is optimized for efficiency and performance in battery-powered applications.
The circuit typically employs a Class AB design, which allows for a balance between power efficiency and audio fidelity, minimizing distortion while maximizing output power. The amplifier's architecture may include integrated components such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors, all housed within a single chip to reduce size and improve reliability.
In addition to its nominal output of 4 watts, the amplifier can achieve a peak power output of approximately 6 watts RMS under certain conditions, making it suitable for driving small speakers or headphones effectively. The design may also incorporate features such as thermal protection, short-circuit protection, and a built-in gain control to enhance usability and safeguard the device during operation.
The circuit's input stage is typically configured for low noise and high input impedance, allowing it to interface easily with various audio sources. The output stage is designed to deliver sufficient current to drive the load while maintaining low distortion levels, ensuring clear and dynamic sound reproduction.
Overall, this monolithic integrated audio amplifier circuit is a versatile solution for audio amplification in portable devices, combining compact size with robust performance characteristics.The monolithic integrated audio amplifier circuit is especially designed for portable radio and recorder applications and delivers up to 4 W in a 4 ohm load impedance. the power out is near to 6 watts rms. 🔗 External reference