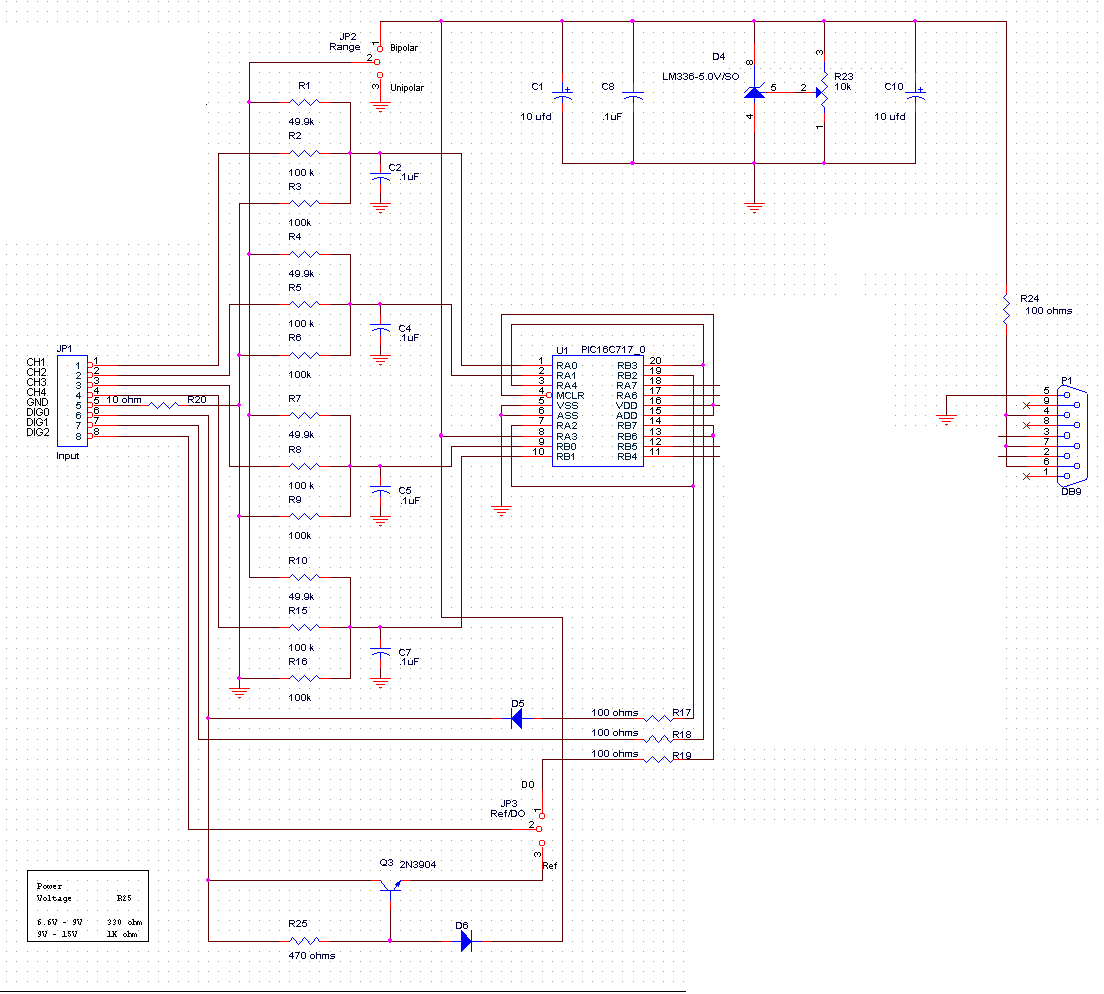
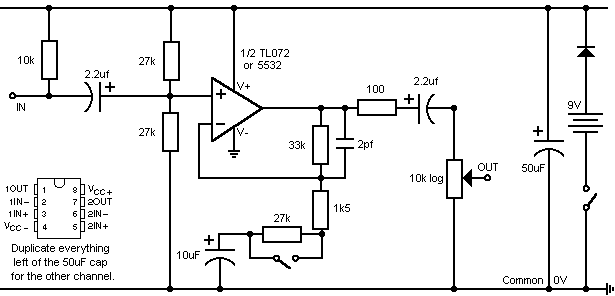
70W High Power Amplifier with MOSFET
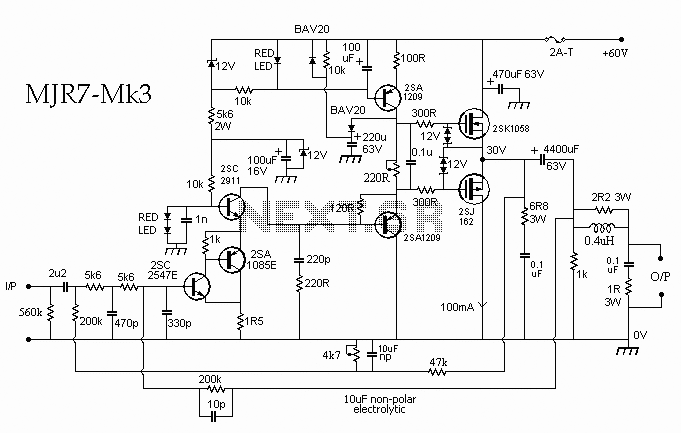
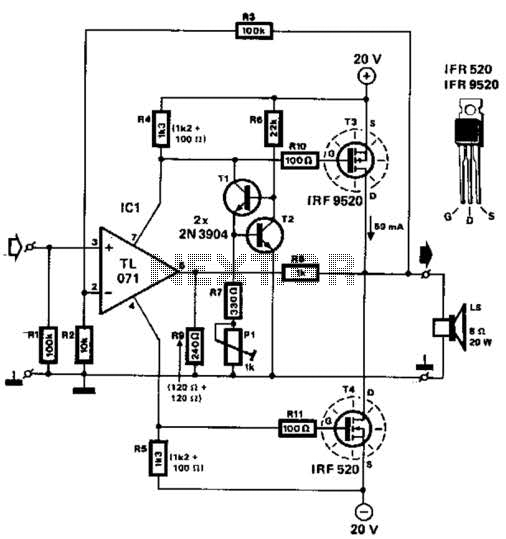
This schematic diagram illustrates a 70W power amplifier utilizing MOSFET technology for audio systems. Alternative input stage transistors include the Toshiba 2SA970BL and 2SC2240BL, which serve as suitable substitutes for the Hitachi 2SA1085E.
The 70W power amplifier is designed to deliver high-quality audio amplification with efficient performance. The use of MOSFETs in the output stage provides several advantages, including high linearity, low distortion, and the ability to handle larger currents compared to traditional bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). This makes the amplifier capable of driving demanding speaker loads while maintaining sound fidelity.
The input stage, where audio signals are initially processed, can utilize alternative transistors such as the Toshiba 2SA970BL and 2SC2240BL. These transistors are chosen for their excellent frequency response and low noise characteristics, which are critical for maintaining audio clarity. The circuit configuration may include biasing resistors and capacitors to ensure stable operation and proper signal coupling.
In the output stage, the MOSFETs are typically arranged in a complementary push-pull configuration to improve efficiency and reduce crossover distortion. The power supply section should be designed to deliver adequate voltage and current, with decoupling capacitors included to filter out noise and stabilize the power rails.
Overall, the schematic represents a robust design suitable for high-performance audio applications, with flexibility in component selection to accommodate different performance needs and availability of parts. Proper thermal management should also be considered, as MOSFETs can generate significant heat during operation, necessitating adequate heat sinking and ventilation in the final assembly.Here the schematic diagram of 70W power amplifier with MOSFET for your audio system. There are possible alternative input stage transistors, the Toshiba 2SA970BL and 2SC2240BL, which appear to be good substitutes for the Hitachi 2SA1085E an.. 🔗 External reference
The 70W power amplifier is designed to deliver high-quality audio amplification with efficient performance. The use of MOSFETs in the output stage provides several advantages, including high linearity, low distortion, and the ability to handle larger currents compared to traditional bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). This makes the amplifier capable of driving demanding speaker loads while maintaining sound fidelity.
The input stage, where audio signals are initially processed, can utilize alternative transistors such as the Toshiba 2SA970BL and 2SC2240BL. These transistors are chosen for their excellent frequency response and low noise characteristics, which are critical for maintaining audio clarity. The circuit configuration may include biasing resistors and capacitors to ensure stable operation and proper signal coupling.
In the output stage, the MOSFETs are typically arranged in a complementary push-pull configuration to improve efficiency and reduce crossover distortion. The power supply section should be designed to deliver adequate voltage and current, with decoupling capacitors included to filter out noise and stabilize the power rails.
Overall, the schematic represents a robust design suitable for high-performance audio applications, with flexibility in component selection to accommodate different performance needs and availability of parts. Proper thermal management should also be considered, as MOSFETs can generate significant heat during operation, necessitating adequate heat sinking and ventilation in the final assembly.Here the schematic diagram of 70W power amplifier with MOSFET for your audio system. There are possible alternative input stage transistors, the Toshiba 2SA970BL and 2SC2240BL, which appear to be good substitutes for the Hitachi 2SA1085E an.. 🔗 External reference