TDA8920BTH 200 watts d class amplifier circuit diagram
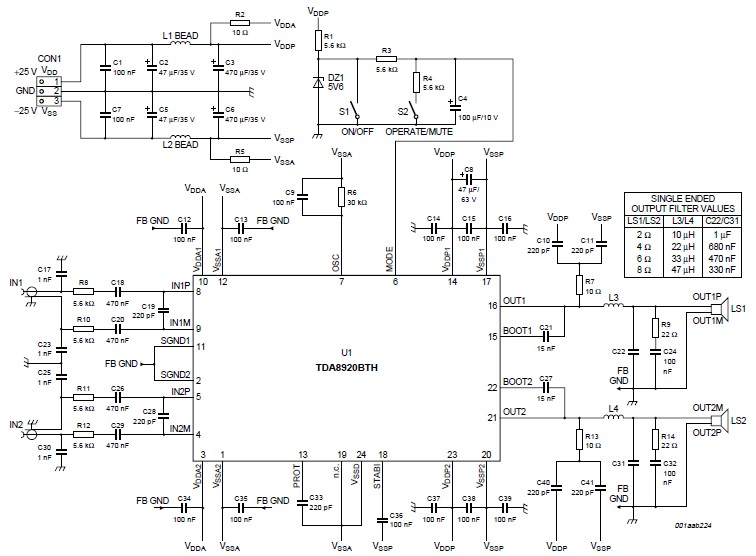
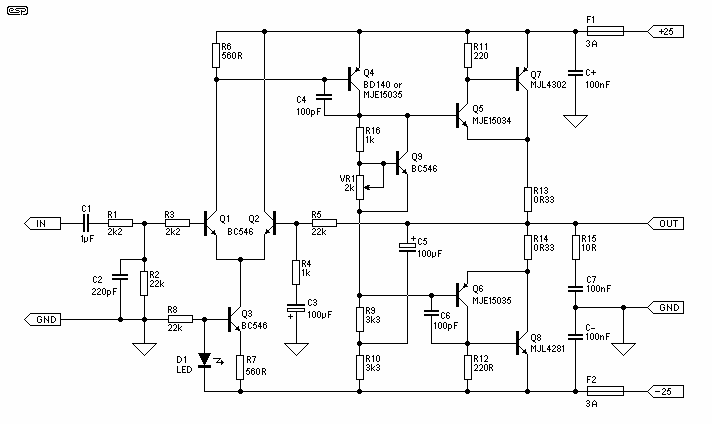
This high-power Class D audio amplifier electronic project is designed using the TDA8920BTH audio power amplifier IC. This power amplifier IC offers very high efficiency with minimal dissipation, yielding significant output power. The typical output power is 200 watts (2 x 100 W). The TDA8920BTH Class D amplifier operates over a wide supply voltage range from ±12.5 V to ±30 V (±32 V when not operating) and consumes a very low quiescent current. The audio input signal for this 200-watt Class D amplifier is transformed into a digital pulse-width modulated signal through an analog input stage and Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) modulator. To drive the output power transistors, this digital PWM signal is sent to a control and handshake block, along with driver circuits for both the high side and low side.
The TDA8920BTH is a highly efficient Class D audio amplifier IC, capable of delivering substantial power while maintaining low thermal dissipation. The design allows for a dual output configuration, providing 100 watts per channel in a stereo setup, making it suitable for various audio applications including home theater systems and professional audio equipment.
The amplifier operates within a voltage range of ±12.5 V to ±30 V, which allows for flexibility in power supply selection. The quiescent current, which is the current consumed when the amplifier is idle, is notably low, enhancing overall energy efficiency and reducing heat generation during operation.
The input stage of the amplifier is crucial as it converts the analog audio signal into a digital format. This conversion is achieved using a PWM modulator, which encodes the audio signal into a series of pulses that represent the amplitude of the audio waveform. The PWM technique allows for high fidelity reproduction of audio signals while minimizing distortion.
Following the PWM modulation, the digital signal is processed by a control and handshake block, which ensures that the output stage operates correctly and safely. This block coordinates the timing and operation of the driver circuits, which are responsible for controlling the high-side and low-side output transistors. The synchronization of these transistors is essential for efficient power delivery and to prevent crossover distortion, a common issue in amplifier designs.
Overall, the TDA8920BTH Class D audio amplifier represents a sophisticated solution for high-power audio amplification, combining efficiency, low heat generation, and high output capabilities, making it an ideal choice for robust audio applications.This high power class D audio amplifier electronic project is designed using the TDA8920BTH audio power amplifier IC. This power amplifier audio IC has a very high efficiency with very low dissipation, providing a very high output power.
The typical output power is 200 watts ( 2 x 100 W). The TDA8920BTH 200 watts d class amplifier operates over a wide supply voltage range from ±12. 5 V to ±30 V ( ±32 V non operating) and consumes a very low quiescent current. The audio input signal of this 200 watts d class amplifier is converted into a digital pulse width modulated signal via an analog input stage and Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) modulator. To enable the output power transistors to be driven, this digital PWM signal is applied to a control and handshake block and driver circuits for both the high side and low side.
🔗 External reference
The TDA8920BTH is a highly efficient Class D audio amplifier IC, capable of delivering substantial power while maintaining low thermal dissipation. The design allows for a dual output configuration, providing 100 watts per channel in a stereo setup, making it suitable for various audio applications including home theater systems and professional audio equipment.
The amplifier operates within a voltage range of ±12.5 V to ±30 V, which allows for flexibility in power supply selection. The quiescent current, which is the current consumed when the amplifier is idle, is notably low, enhancing overall energy efficiency and reducing heat generation during operation.
The input stage of the amplifier is crucial as it converts the analog audio signal into a digital format. This conversion is achieved using a PWM modulator, which encodes the audio signal into a series of pulses that represent the amplitude of the audio waveform. The PWM technique allows for high fidelity reproduction of audio signals while minimizing distortion.
Following the PWM modulation, the digital signal is processed by a control and handshake block, which ensures that the output stage operates correctly and safely. This block coordinates the timing and operation of the driver circuits, which are responsible for controlling the high-side and low-side output transistors. The synchronization of these transistors is essential for efficient power delivery and to prevent crossover distortion, a common issue in amplifier designs.
Overall, the TDA8920BTH Class D audio amplifier represents a sophisticated solution for high-power audio amplification, combining efficiency, low heat generation, and high output capabilities, making it an ideal choice for robust audio applications.This high power class D audio amplifier electronic project is designed using the TDA8920BTH audio power amplifier IC. This power amplifier audio IC has a very high efficiency with very low dissipation, providing a very high output power.
The typical output power is 200 watts ( 2 x 100 W). The TDA8920BTH 200 watts d class amplifier operates over a wide supply voltage range from ±12. 5 V to ±30 V ( ±32 V non operating) and consumes a very low quiescent current. The audio input signal of this 200 watts d class amplifier is converted into a digital pulse width modulated signal via an analog input stage and Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) modulator. To enable the output power transistors to be driven, this digital PWM signal is applied to a control and handshake block and driver circuits for both the high side and low side.
🔗 External reference