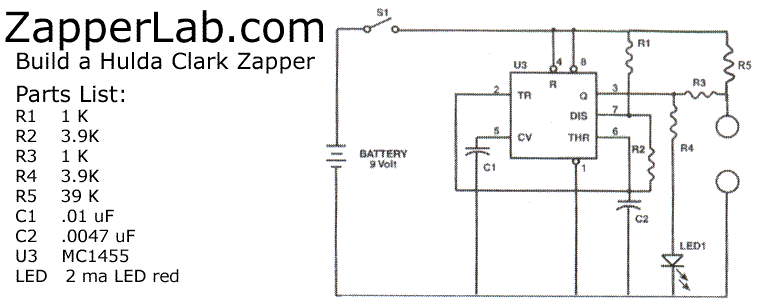
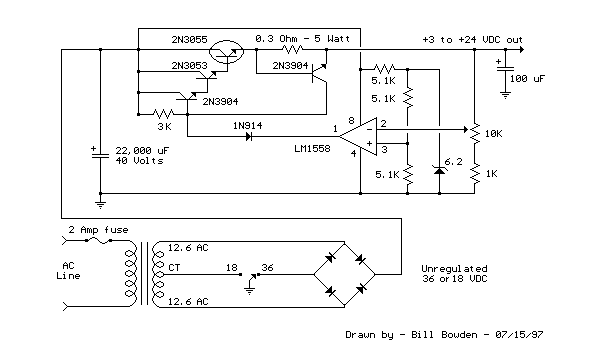
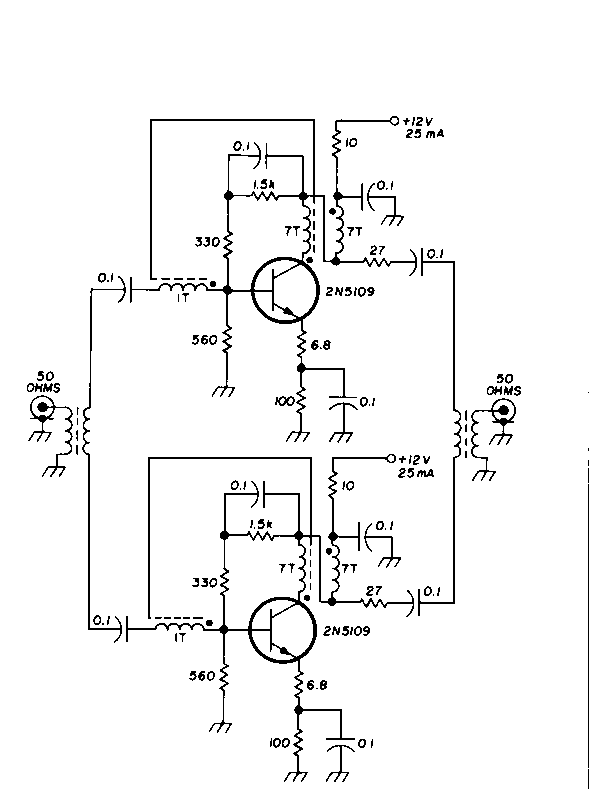
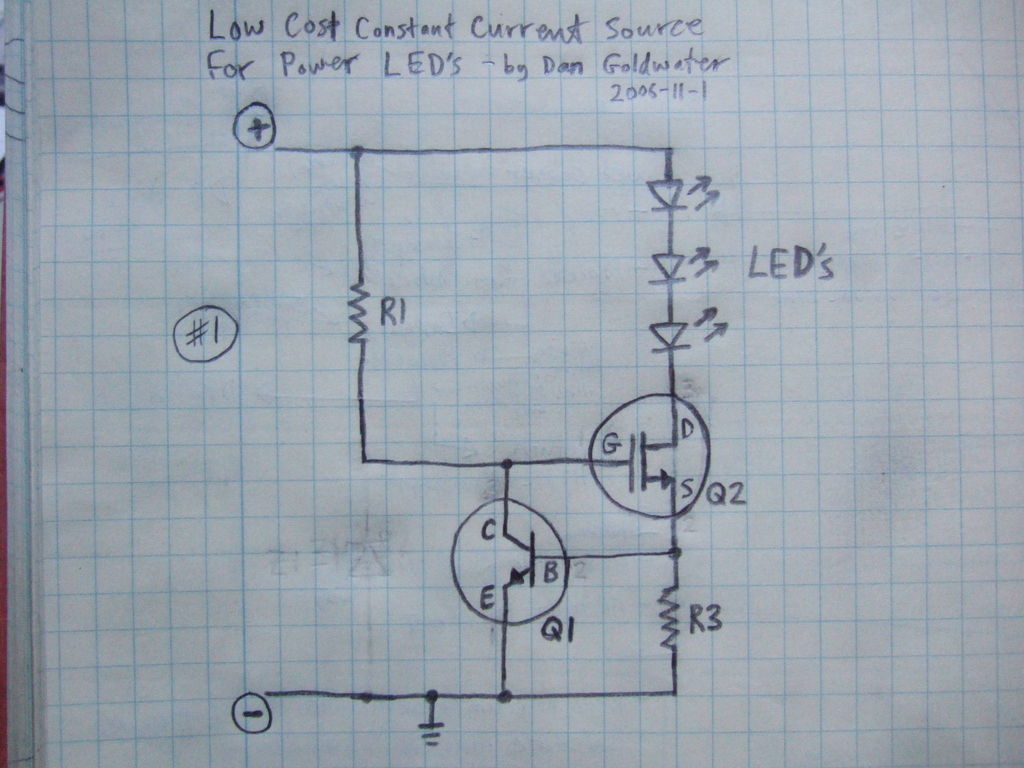
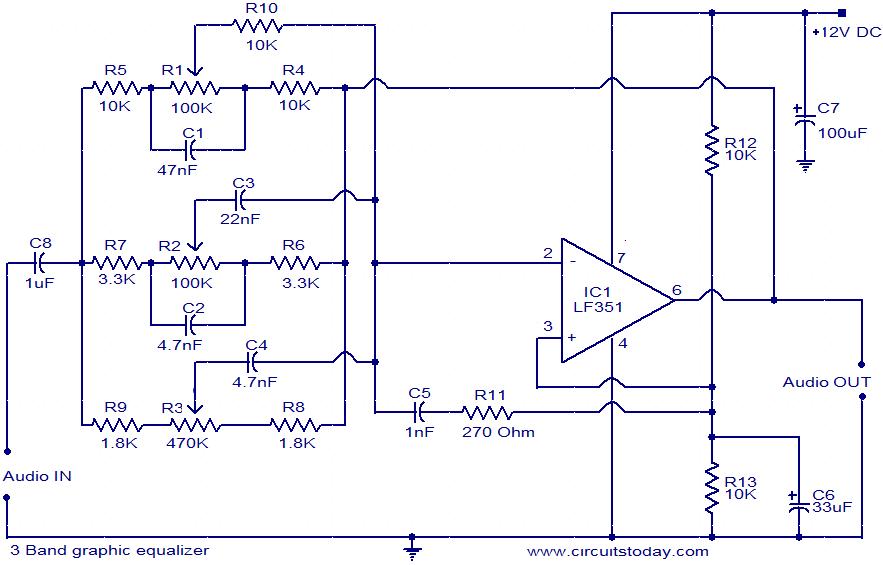
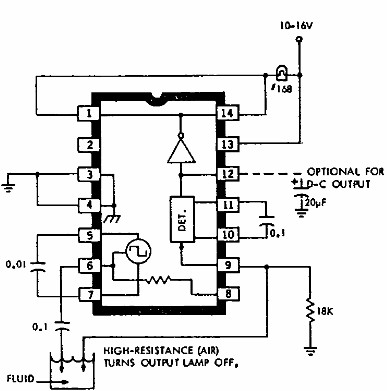
Mosfet Power Amplifier Circuit
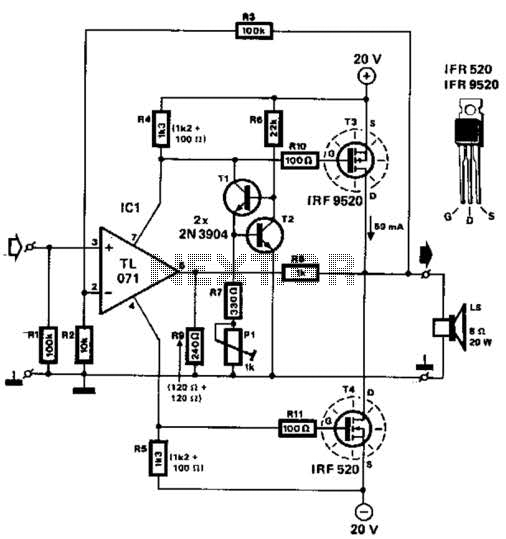
Two complementary MOSFETs are utilized to deliver 20 W into an 8-ohm load. A TL071 operational amplifier serves as the input amplifier. The MOSFETs must be equipped with a heatsink that has a thermal resistance of better than 5 °C/W. Total harmonic distortion (THD) is maintained at less than 0.15% across a frequency range from 100 Hz to 10 kHz.
The circuit employs two complementary MOSFETs configured in a push-pull arrangement to efficiently drive an 8-ohm load, delivering a total output power of 20 W. This configuration allows for improved linearity and reduced distortion, making it suitable for audio amplification applications. The choice of MOSFETs ensures high efficiency and thermal performance, which is critical in maintaining the integrity of the audio signal.
The TL071 operational amplifier is chosen for its low noise and high gain characteristics, making it an ideal candidate for the input stage of the amplifier circuit. The op-amp is configured in a non-inverting configuration to amplify the input audio signal before it is fed into the MOSFETs. Proper biasing of the op-amp is essential to ensure optimal performance and minimize distortion.
Thermal management is a crucial aspect of this design. The selected MOSFETs must be mounted on a heatsink with a thermal resistance of less than 5 °C/W to dissipate heat effectively. This ensures that the MOSFETs operate within their safe temperature limits, preventing thermal runaway and ensuring reliable operation over extended periods.
The circuit is designed to maintain a total harmonic distortion (THD) of less than 0.15% across a frequency range of 100 Hz to 10 kHz. This specification indicates that the amplifier will produce high-fidelity audio, making it suitable for high-quality audio applications. The careful selection of components and design parameters contributes to the overall performance and reliability of the amplifier circuit. Two complementary MOSFETs are used to deliver 20 W into 8 . A TL071 op amp is used as an input amplifier. The MOSFETs should be heatsinked with a heatsink of better than 5C/W capability. THD is less than 0.15% from 100 Hz to 10 kHz.
The circuit employs two complementary MOSFETs configured in a push-pull arrangement to efficiently drive an 8-ohm load, delivering a total output power of 20 W. This configuration allows for improved linearity and reduced distortion, making it suitable for audio amplification applications. The choice of MOSFETs ensures high efficiency and thermal performance, which is critical in maintaining the integrity of the audio signal.
The TL071 operational amplifier is chosen for its low noise and high gain characteristics, making it an ideal candidate for the input stage of the amplifier circuit. The op-amp is configured in a non-inverting configuration to amplify the input audio signal before it is fed into the MOSFETs. Proper biasing of the op-amp is essential to ensure optimal performance and minimize distortion.
Thermal management is a crucial aspect of this design. The selected MOSFETs must be mounted on a heatsink with a thermal resistance of less than 5 °C/W to dissipate heat effectively. This ensures that the MOSFETs operate within their safe temperature limits, preventing thermal runaway and ensuring reliable operation over extended periods.
The circuit is designed to maintain a total harmonic distortion (THD) of less than 0.15% across a frequency range of 100 Hz to 10 kHz. This specification indicates that the amplifier will produce high-fidelity audio, making it suitable for high-quality audio applications. The careful selection of components and design parameters contributes to the overall performance and reliability of the amplifier circuit. Two complementary MOSFETs are used to deliver 20 W into 8 . A TL071 op amp is used as an input amplifier. The MOSFETs should be heatsinked with a heatsink of better than 5C/W capability. THD is less than 0.15% from 100 Hz to 10 kHz.