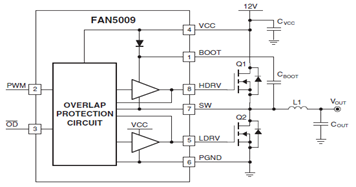
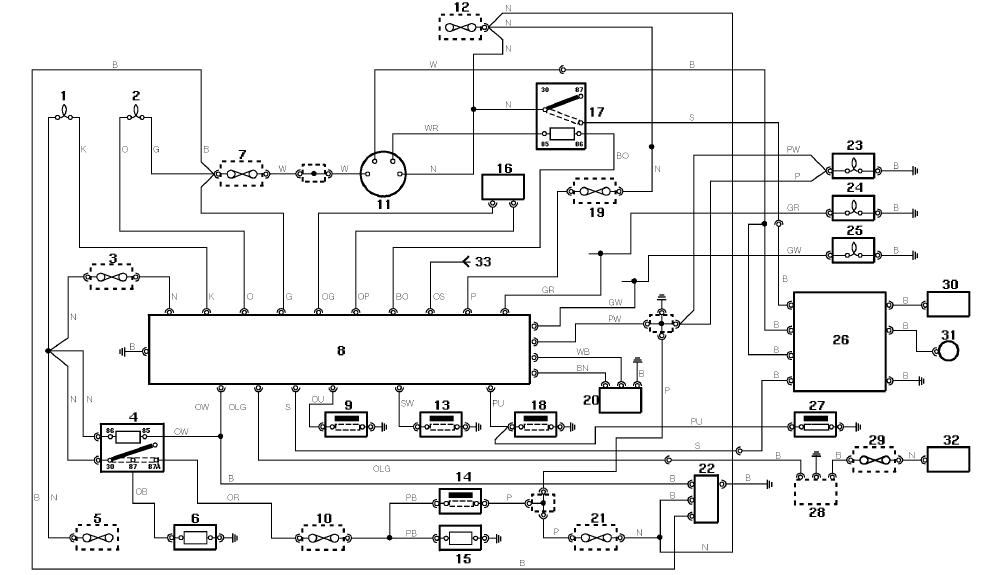
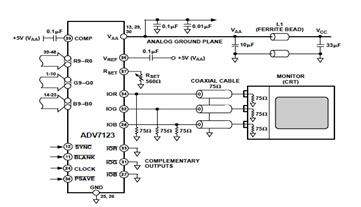
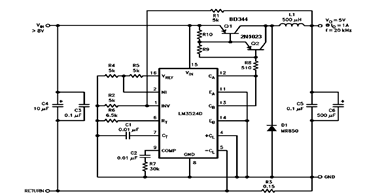
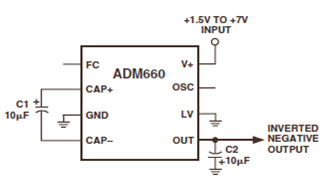
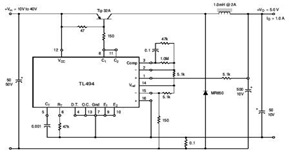
9400 Selling Leads 9400 Datasheet PDF
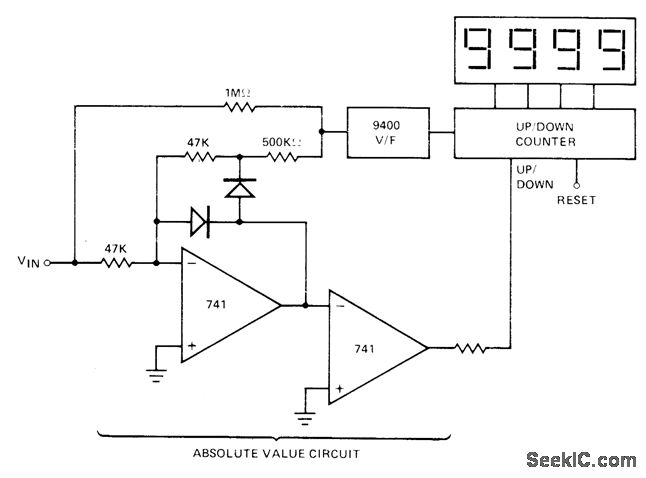
The absolute-value integrator circuit generates the effect of producing negative frequencies when the input signal is negative. It accomplishes this by allowing the counter to count up for positive voltage and count down for negative voltage. The specific types of diodes used are not critical.
The absolute-value integrator circuit is designed to process analog signals by integrating the input voltage over time while maintaining a non-negative output. This is particularly useful in applications where it is necessary to analyze both positive and negative portions of a waveform without losing information due to the signal's polarity.
In this circuit, the input signal is fed into an integrator, which can be implemented using operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured for integration. The output of the integrator reflects the integral of the input voltage, effectively translating the input signal's area under the curve into a corresponding voltage level. To ensure that negative input voltages do not adversely affect the operation of the circuit, an absolute-value mechanism is employed. This can be accomplished using a combination of diodes and op-amps.
When the input signal is positive, the integrator counts up, reflecting the accumulation of positive voltage over time. Conversely, when the input signal turns negative, the absolute-value integrator allows the circuit to reverse the polarity of the negative voltage, effectively enabling the counter to count down. This dual counting mechanism results in the generation of negative frequencies, which can be particularly beneficial in various signal processing applications, such as in frequency modulation or in systems requiring phase detection.
The choice of diodes in this circuit is flexible, as long as they can handle the required forward current and reverse voltage. Standard silicon diodes are often sufficient, but Schottky diodes may be used for faster switching times if required by the application. The integration time constant can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values in the feedback loop of the op-amp, allowing for customization based on the desired response characteristics.
Overall, the absolute-value integrator circuit is a versatile tool in electronic signal processing, capable of transforming waveforms while preserving essential information about both positive and negative signal components.Absolute-value integrator circuit gives effect of generating negative frequencies when input signal is negative by making counter count up for positive voltage and count down for negative voltage. Diode types are not criticaL-M. O. Paiva, "Applications of the 9400 Voltage to Frequency Frequency to Voltage Converter, " Teledyne Semiconductor, Mounta
in View, CA, 1978, AN. 10, p 3. 🔗 External reference
The absolute-value integrator circuit is designed to process analog signals by integrating the input voltage over time while maintaining a non-negative output. This is particularly useful in applications where it is necessary to analyze both positive and negative portions of a waveform without losing information due to the signal's polarity.
In this circuit, the input signal is fed into an integrator, which can be implemented using operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured for integration. The output of the integrator reflects the integral of the input voltage, effectively translating the input signal's area under the curve into a corresponding voltage level. To ensure that negative input voltages do not adversely affect the operation of the circuit, an absolute-value mechanism is employed. This can be accomplished using a combination of diodes and op-amps.
When the input signal is positive, the integrator counts up, reflecting the accumulation of positive voltage over time. Conversely, when the input signal turns negative, the absolute-value integrator allows the circuit to reverse the polarity of the negative voltage, effectively enabling the counter to count down. This dual counting mechanism results in the generation of negative frequencies, which can be particularly beneficial in various signal processing applications, such as in frequency modulation or in systems requiring phase detection.
The choice of diodes in this circuit is flexible, as long as they can handle the required forward current and reverse voltage. Standard silicon diodes are often sufficient, but Schottky diodes may be used for faster switching times if required by the application. The integration time constant can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values in the feedback loop of the op-amp, allowing for customization based on the desired response characteristics.
Overall, the absolute-value integrator circuit is a versatile tool in electronic signal processing, capable of transforming waveforms while preserving essential information about both positive and negative signal components.Absolute-value integrator circuit gives effect of generating negative frequencies when input signal is negative by making counter count up for positive voltage and count down for negative voltage. Diode types are not criticaL-M. O. Paiva, "Applications of the 9400 Voltage to Frequency Frequency to Voltage Converter, " Teledyne Semiconductor, Mounta
in View, CA, 1978, AN. 10, p 3. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713